Android構建系統編譯你的app資源和源碼並且打包到APK中,你可以用來測試,部署,簽名和發布。Android Studio使用Gradle,一個高級的構建套件,來自動化和管理構建進程,同時可以允許你靈活的自定義構建配置。每個構建配置可以定義它自己的代碼和資源集合。
Gradle和Android插件獨立於Android Studio運行。這就意味著你可以在你的機器上在命令行、Android Studio、或者沒有安裝Android Studio的機器中構建你的Android APP。
Android構建系統的靈活性允許你在不修改你的APP核心代碼的情況下運行自定義的構建配置。
構建進程
構建進程包含很多工具和進程來幫助將你的項目轉化為APK(Android Application Package)。構建進程非常靈活。
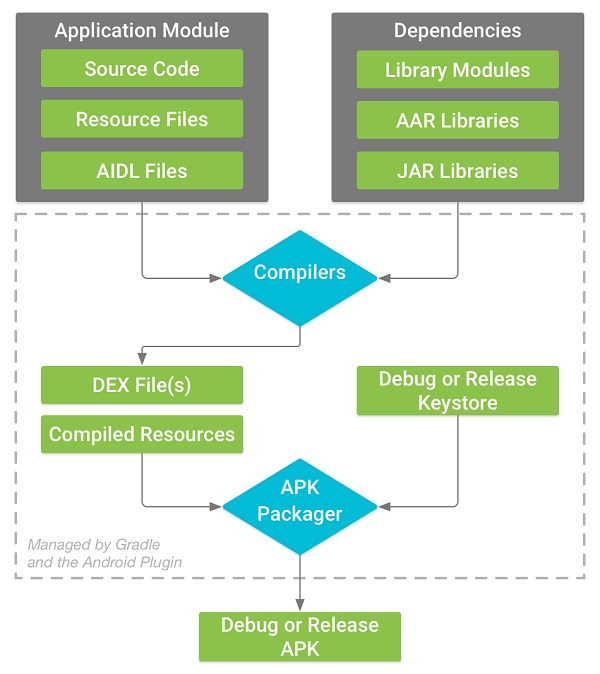
遵循如下幾步:
1、 編譯器將你的源碼轉化為DEX(Dalvik Executable)文件,包含Android設備中可以運行的字節碼和其他編譯的資源文件。
2、 APK打包工具將DEX文件和編譯後的資源打包到一個單獨的APK中,但是在你安裝和部署之前,APK必須進行簽名。
3、 APK打包工具會用debug key或者release key對你的APK進行簽名。
4、 在你生成最終的APK之前,打包工具只用aipalign工具來優化你的代碼。這可以在app運行時降低內存。
自定義構建配置
Build Types
構建類型定義在構建和打包app是Gradle使用的一些屬性配置。在不同的開發周期是不同的。比如,debug 構建類型開啟調試選項並且使用debug key對APK進行簽名。而release 構建類型可能需要壓縮、模糊並且使用release key對APK進行簽名。為了構建你的app,你必須至少聲明一種類型。
Product Flavors
Product flavors代表發布給用戶的不同版本的APP。比如,免費和付費的APP版本。你可以通過定制Product flavors來使用不同的代碼和資源,同時共用所有版本APP可復用的部分。Product Flavors是可選的,你必須手動創建它們。
Build Variants
Build variant是build type和product flavor混合的產物。這是Gradle用來構建你的app的相關配置。通過使用build variant,你可以在開發中構建你的product flavor的debug版本,或者product flavor的簽名的發布版本。雖然你沒有直接配置build variant,你可以通過配置build type和product flavor來實現對build variant的配置。創建額外的build type或者product flavor同樣可以創建額外的build variant。
Mainfest Entries
你可以在build variant配置裡聲明manifest文件裡的一些屬性值。這些值會腹瀉manifest文件中已經存在的值。
Dependencies
構建系統管理項目的依賴,從本地的依賴到遠程的依賴。這個可以讓你方便的對依賴進行管理。
Signing
構建系統允許你在構建配置中聲明簽名設置,這可以在你構建的時候自動的對你的APK進行簽名。構建系統不會對release版本進行簽名,除非你定義一個簽名配置。
ProGuard
構建系統允許你為每一個build variant聲明一個不同的ProGuard規則文件。
構建配置文件
創建自定義的配置需要你對一個或多個構建配置文件進行更改,或者build.gradle文件。這些文本使用DSL來描述和控制構建邏輯。
當你創建一個新的項目時,Android Studio自動為你創建一些文件,如圖:
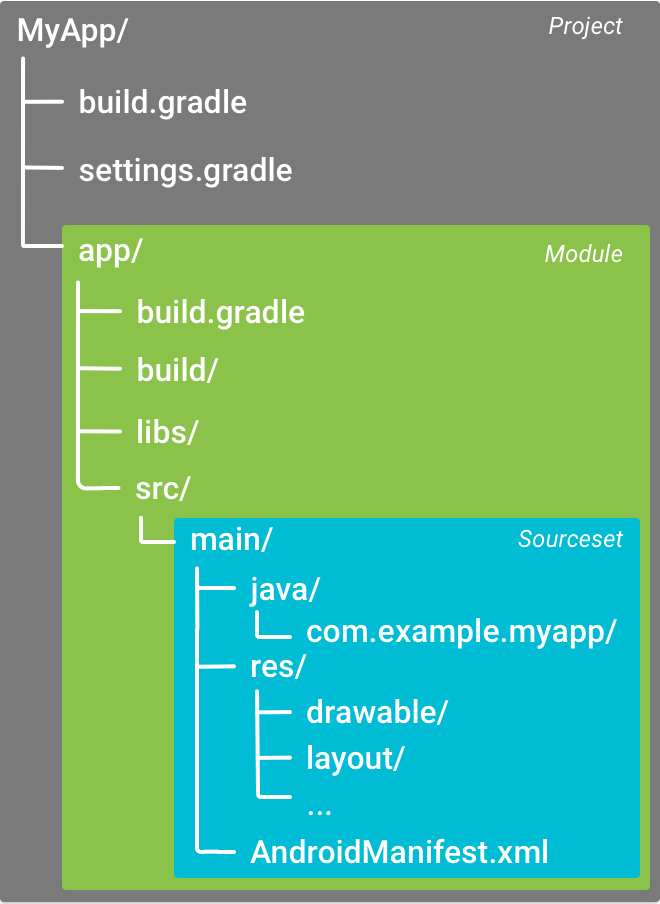
這是一些Gradle構建配置文件,作為Android應用標准項目結構的一部分。
Gradle設置文件
gradle.settings文件位於項目的根目錄下,來通知Gradle在構建你的應用的時候需要包括哪些模塊,大部分項目如下:
include ‘:app’
頂層的構建文件
位於項目根目錄的build.gradle文件,定義了可以應用於你的項目的所有模塊的構建配置。默認情況下,頂層的構建文件在buildscript{}中定義Gradle repositories和依賴,這可以應用到項目的所有的模塊中。如下:
Java代碼
- /**
- * The buildscript {} block is where you configure the repositories and
- * dependencies for Gradle itself--meaning, you should not include dependencies
- * for your modules here. For example, this block includes the Android plugin for
- * Gradle as a dependency because it provides the additional instructions Gradle
- * needs to build Android app modules.
- */
-
- buildscript {
-
- /**
- * The repositories {} block configures the repositories Gradle uses to
- * search or download the dependencies. Gradle pre-configures support for remote
- * repositories such as JCenter, Maven Central, and Ivy. You can also use local
- * repositories or define your own remote repositories. The code below defines
- * JCenter as the repository Gradle should use to look for its dependencies.
- */
-
- repositories {
- jcenter()
- }
-
- /**
- * The dependencies {} block configures the dependencies Gradle needs to use
- * to build your project. The following line adds Android Plugin for Gradle
- * version 2.0.0 as a classpath dependency.
- */
-
- dependencies {
- classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:2.0.0'
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * The allprojects {} block is where you configure the repositories and
- * dependencies used by all modules in your project, such as third-party plugins
- * or libraries. Dependencies that are not required by all the modules in the
- * project should be configured in module-level build.gradle files. For new
- * projects, Android Studio configures JCenter as the default repository, but it
- * does not configure any dependencies.
- */
-
- allprojects {
- repositories {
- jcenter()
- }
- }
模塊構建文件
模塊的build.gradle文件,位於//目錄下,允許你對特定的模塊進行構建配置。配置這些構建設置允許你提供自定義的打包選項,比如額外的build type和product flavor,復寫mainfies中的設置或者頂層build.gradle文件的配置。代碼如下:
Java代碼
- /**
- * The first line in the build configuration applies the Android plugin for
- * Gradle to this build and makes the android {} block available to specify
- * Android-specific build options.
- */
-
- apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
-
- /**
- * The android {} block is where you configure all your Android-specific
- * build options.
- */
-
- android {
-
- /**
- * compileSdkVersion specifies the Android API level Gradle should use to
- * compile your app. This means your app can use the API features included in
- * this API level and lower.
- *
- * buildToolsVersion specifies the version of the SDK build tools, command-line
- * utilities, and compiler that Gradle should use to build your app. You need to
- * download the build tools using the SDK Manager.
- */
-
- compileSdkVersion 23
- buildToolsVersion "23.0.3"
-
- /**
- * The defaultConfig {} block encapsulates default settings and entries for all
- * build variants, and can override some attributes in main/AndroidManifest.xml
- * dynamically from the build system. You can configure product flavors to override
- * these values for different versions of your app.
- */
-
- defaultConfig {
-
- /**
- * applicationId uniquely identifies the package for publishing.
- * However, your source code should still reference the package name
- * defined by the package attribute in the main/AndroidManifest.xml file.
- */
-
- applicationId 'com.example.myapp'
-
- // Defines the minimum API level required to run the app.
- minSdkVersion 14
-
- // Specifies the API level used to test the app.
- targetSdkVersion 23
-
- // Defines the version number of your app.
- versionCode 1
-
- // Defines a user-friendly version name for your app.
- versionName "1.0"
- }
-
- /**
- * The buildTypes {} block is where you can configure multiple build types.
- * By default, the build system defines two build types: debug and release. The
- * debug build type is not explicitly shown in the default build configuration,
- * but it includes debugging tools and is signed with the debug key. The release
- * build type applies Proguard settings and is not signed by default.
- */
-
- buildTypes {
-
- /**
- * By default, Android Studio configures the release build type to enable code
- * shrinking, using minifyEnabled, and specifies the Proguard settings file.
- */
-
- release {
- minifyEnabled true // Enables code shrinking for the release build type.
- proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * The productFlavors {} block is where you can configure multiple product
- * flavors. This allows you to create different versions of your app that can
- * override defaultConfig {} with their own settings. Product flavors are
- * optional, and the build system does not create them by default. This example
- * creates a free and paid product flavor. Each product flavor then specifies
- * its own application ID, so that they can exist on the Google Play Store, or
- * an Android device, simultaneously.
- */
-
- productFlavors {
- free {
- applicationId 'com.example.myapp.free'
- }
-
- paid {
- applicationId 'com.example.myapp.paid'
- }
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * The dependencies {} block in the module-level build configuration file
- * only specifies dependencies required to build the module itself.
- */
-
- dependencies {
- compile project(":lib")
- compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:22.0.1'
- compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
- }
Gradle屬性文件
Gradle也包括兩個屬性文件,在項目的根目錄。你可以用來聲明Gradle構建套件的設置:
Gradle.properties
這裡你可以設置全局Gradle設置。
Local.properties
為你的構建系統配置本地環境屬性,比如SDK安裝位置。因為這個文件的內容是Android Studio自動生成的,針對本地的開發環境,所以你不需要手動更改這個文件或者將其添加到你的版本控制系統中。
使用Gradle同步項目
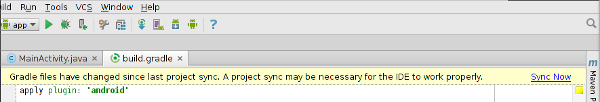
當你更改了你的項目中的構建配置文件之後,Android Studio需要你同步你的項目,這樣你就可以導入你的項目配置並且運行一些檢測來確保你的配置不會導致創建構建錯誤。
同步你的項目文件,在你更改之後,會有個提示框,點擊Sync Now。如果發現問題,Android Studio會報錯:
Source Sets
Android Studio為每個模塊合理的組織代碼和資源。一個模塊的main目錄包含了代碼和資源。



 Android Studio(二):創建一個項目
Android Studio(二):創建一個項目
 Android Studio(八):使用Layout Editor設計UI
Android Studio(八):使用Layout Editor設計UI
 Windows XP系統如何配置Android開發環境
Windows XP系統如何配置Android開發環境
 Windows系統下配置Android NDK開發環境
Windows系統下配置Android NDK開發環境