編輯:Android技術基礎
本節介紹的UI基礎控件是:ImageView(圖像視圖),見名知意,就是用來顯示圖像的一個View或者說控件! 官方API:ImageView;本節講解的內容如下:
在API文檔中我們發現ImageView有兩個可以設置圖片的屬性,分別是:src和background
常識:
①background通常指的都是背景,而src指的是內容!!
②當使用src填入圖片時,是按照圖片大小直接填充,並不會進行拉伸
而使用background填入圖片,則是會根據ImageView給定的寬度來進行拉伸
寫個簡單的布局測試下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.jay.example.imageviewdemo.MainActivity" >
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/pen" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/pen" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/pen" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/pen" />
</LinearLayout>
效果圖如下:

結果分析:
寬高都是wrap_content那就一樣,是原圖大小,但是,當我們固定了寬或者高的話, 差別就顯而易見了,blackground完全填充了整個ImageView,而src依舊是那麼大, 而且他居中了哦,這就涉及到了ImageView的另一個屬性scaleType了! 另外還有一點,這裡我們說了只設置width或者height哦!加入我們同時設置了 width和height的話,blackground依舊填充,但是,src的大小可能發生改變哦! 比如,我們測試下下面這段代碼:
<ImageView
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:src="@drawable/pen" />
運行效果圖:
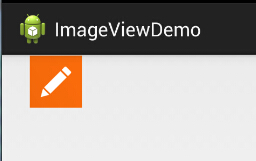
PS:scaleType下面會講~
在前面的效果圖中的第二個Imageview中我們可以看到圖片已經被拉伸變形了, 正方形變成了長方形,對於和我一樣有輕微強迫症的人來說,顯然是不可接受的, 有沒有辦法去設置呢?答案肯定是有的,筆者暫時知道的有以下兩種方式:
這個適用於動態加載ImageView的,代碼也漸漸,只要在添加View的時候,把大小寫死就可以了
LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParam = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(48, 48);
layout.addView(ibtnPen, layoutParam);
除了動態加載view,更多的時候,我們還是會通過xml布局的方式引入ImageView的 解決方法也不難,就是通過drawable的Bitmap資源文件來完成,然後blackground屬性設置為該文件即可! 這個xml文件在drawable文件夾下創建,這個文件夾是要自己創建的哦!!
pen_bg.xml:
<bitmap
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@id/pen_bg"
android:gravity="top"
android:src="@drawable/pen"
android:tileMode="disabled" >
</bitmap>
上述代碼並不難理解,估計大家最迷惑的是titleMode屬性吧,這個屬性是平鋪,就是我們windows設置 背景時候的平鋪,多個小圖標鋪滿整個屏幕捏!記得了吧!不記得自己可以試試!disabled就是把他給禁止了!
就是上面這串簡單的代碼,至於調用方法如下:
動態: ibtnPen.setBacklgroundResource(R.drawable.penbg);
靜態: android:background = "@drawable/penbg"
說完前面兩個區別,接著再說下setAlpha屬性咯!這個很簡單,這個屬性,只有src時才是有效果的!!
網上的一張圖:
一看去是一個簡單的GridView,每個item都是一個ImageView,但是細心的你可能發現了, 上面的ICON都不是規則的,而是圓形,圓角矩形等等,於是乎這裡用到了src + background了! 要實現上述的效果,你只需要兩個操作: 找一張透明的png圖片 + 設置一個黑色的背景 (當然你也可以設置png的透明度來實現,不過結果可能和預想的有出入哦!) 我們寫個簡單例子:

如圖,呆萌呆萌的小豬就這樣顯示到ImageView上了,哈哈,blackground設置了藍色背景!
實現代碼:
<ImageView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/pig"
android:background="#6699FF" />
PS: 當然你也可以用selctor實現點擊效果,設置不同的情況設置不同的圖片,以實現點擊或者觸摸效果!
前景(對應src屬性):setImageDrawable( );
背景(對應background屬性):setBackgroundDrawable( );
ImageView為我們提供了adjustViewBounds屬性,用於設置縮放時是否保持原圖長寬比! 單獨設置不起作用,需要配合maxWidth和maxHeight屬性一起使用!而後面這兩個屬性 也是需要adjustViewBounds為true才會生效的~
- android:maxHeight:設置ImageView的最大高度
- android:maxWidth:設置ImageView的最大寬度
代碼示例:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!-- 正常的圖片 -->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
<!-- 限制了最大寬度與高度,並且設置了調整邊界來保持所顯示圖像的長寬比-->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:adjustViewBounds="true"
android:maxHeight="200px"
android:maxWidth="200px"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
</LinearLayout>
運行效果圖:

結果分析: 大的那個圖片是沒有任何處理的圖片,尺寸是:541374;而下面的那個的話我們通過maxWidth和maxHeight 限制ImageView最大寬度與高度為200px,就是最多只能顯示200200的圖片,我們又設置了一個 adjustViewBounds = "true"調整我們的邊界來保持圖片的長寬比,此時的ImageView寬高為是128*200~
android:scaleType用於設置顯示的圖片如何縮放或者移動以適應ImageView的大小 Java代碼中可以通過imageView.setScaleType(ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER);來設置~ 可選值如下:
- fitXY:對圖像的橫向與縱向進行獨立縮放,使得該圖片完全適應ImageView,但是圖片的橫縱比可能會發生改變
- fitStart:保持縱橫比縮放圖片,知道較長的邊與Image的編程相等,縮放完成後將圖片放在ImageView的左上角
- fitCenter:同上,縮放後放於中間;
- fitEnd:同上,縮放後放於右下角;
- center:保持原圖的大小,顯示在ImageView的中心。當原圖的size大於ImageView的size,超過部分裁剪處理。
- centerCrop:保持橫縱比縮放圖片,知道完全覆蓋ImageView,可能會出現圖片的顯示不完全
- centerInside:保持橫縱比縮放圖片,直到ImageView能夠完全地顯示圖片
- matrix:默認值,不改變原圖的大小,從ImageView的左上角開始繪制原圖, 原圖超過ImageView的部分作裁剪處理
接下來我們一組組的來對比:
這裡以fitEnd為例,其他兩個類似:
示例代碼:
<!-- 保持圖片的橫縱比縮放,知道該圖片能夠顯示在ImageView組件上,並將縮放好的圖片顯示在imageView的右下角 -->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView3"
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:scaleType="fitEnd"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
運行效果圖:
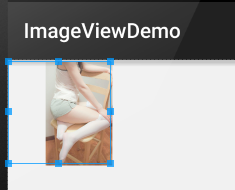
示例代碼:
<ImageView
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:scaleType="centerInside"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
運行效果圖:
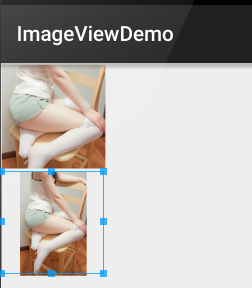
不按比例縮放圖片,目標是把圖片塞滿整個View
示例代碼:
<ImageView
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:scaleType="fixXY"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
運行效果圖:
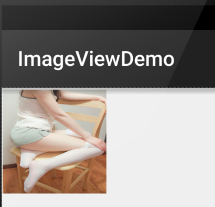
好吧,明顯扁了=-=~
從ImageView的左上角開始繪制原圖,原圖超過ImageView的部分作裁剪處理
示例代碼:
<ImageView
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:scaleType="matrix"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
運行效果圖:
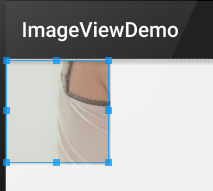
保持原圖的大小,顯示在ImageView的中心。當原圖的size大於ImageView的size,超過部分裁剪處理。
示例代碼:
<ImageView
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:scaleType="center"
android:src="@mipmap/meinv" />
運行效果圖:
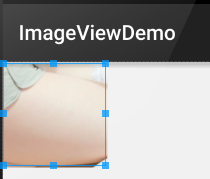
相信大家對圓形或者圓角的ImageView不陌生吧,現在很多的APP都很喜歡圓形的頭像是吧~
這裡就簡單的寫個圓形的ImageView吧,當然這只是一個示例,再不考慮性能與抗鋸齒的情況下!!!
可以說是寫來玩玩,實際項目的話可以考慮用Github上牛人寫的控件,比如下面這兩個:
git怎麼玩前面已經教過大家了~把項目clone下來把相關文件復制到自己的項目即可~
RoundedImageView
CircleImageView
代碼示例:
運行效果圖:

實現代碼:
自定義ImageView:**RoundImageView.java
package com.jay.demo.imageviewdemo;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.PaintFlagsDrawFilter;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.graphics.Region;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.ImageView;
/**
* Created by coder-pig on 2015/7/18 0018.
*/
public class RoundImageView extends ImageView {
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private Rect mRect = new Rect();
private PaintFlagsDrawFilter pdf = new PaintFlagsDrawFilter(0, Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
private Paint mPaint = new Paint();
private Path mPath=new Path();
public RoundImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
//傳入一個Bitmap對象
public void setBitmap(Bitmap bitmap) {
this.mBitmap = bitmap;
}
private void init() {
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setFlags(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);// 抗鋸尺
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if(mBitmap == null)
{
return;
}
mRect.set(0,0,getWidth(),getHeight());
canvas.save();
canvas.setDrawFilter(pdf);
mPath.addCircle(getWidth() / 2, getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2, Path.Direction.CCW);
canvas.clipPath(mPath, Region.Op.REPLACE);
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, null, mRect, mPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
}
布局代碼:activity_main.xml:
<com.jay.demo.imageviewdemo.RoundImageView
android:id="@+id/img_round"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_margin="5px"/>
MainActivity.java:
package com.jay.demo.imageviewdemo;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private RoundImageView img_round;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
img_round = (RoundImageView) findViewById(R.id.img_round);
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.mipmap.meinv);
img_round.setBitmap(bitmap);
}
}
本節講解了ImageView(圖像視圖),內容看上很多,不過都是一些詳述性的東西,知道即可~ 最後的自定義圓形ImageView也是,只是寫來玩玩的,實際項目中還是建議使用那兩個第三方的自定義控件吧~
 第83章、Service之一(從零開始學Android)
第83章、Service之一(從零開始學Android)
android中的Service(服務)是一個什麼樣的東東呢?如果你對Windows系統中的服務理解,可以認為他們同理。如果你不了解也沒有關系,你只管把Service當成
 第85章、系統服務之ClipBoard_Service(從零開始學Android)
第85章、系統服務之ClipBoard_Service(從零開始學Android)
在開發一些系統應用的時候,我們可以需要用到Android的剪貼板功能,比如將文本復制到剪貼板或者從剪貼板復制數據等操作。使用起來很簡單,系統給我們提供了很方便的接口。核心
 2.2.4 FrameLayout(幀布局)
2.2.4 FrameLayout(幀布局)
本節引言FrameLayout(幀布局)可以說是六大布局中最為簡單的一個布局,這個布局直接在屏幕上開辟出一塊空白的區域,當我們往裡面添加控件的時候,
 8.3.7 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(四)
8.3.7 Paint API之—— Xfermode與PorterDuff詳解(四)
本節引言:上節我們寫了關於Xfermode與PorterDuff使用的第一個例子:圓角&圓形圖片ImageView的實現,我們體會到了Por