編輯:初級開發
import android.content.Context;
import android.Net.Uri;
import android.os.PowerManager;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.util.Log;
import Java.io.IOException;
import Java.lang.IllegalStateException;
import Java.util.LinkedList;
public class AsyncPlayer {
private static final int PLAY = 1;
private static final int STOP = 2;
private static final boolean mDebug = false;
private static final class Command {
int code;
Context context;
Uri uri;
boolean looping;
int stream;
long requestTime;
public String toString() {
return "{ code=" + code + " looping=" + looping + " stream=" + stream
+ " uri=" + uri + " }";
}
}
private LinkedList<Command> mCmdQueue = new LinkedList(); //用一個鏈表保存播放參數隊列
private void startSound(Command cmd) {
try {
MediaPlayer player = new MediaPlayer();
player.setAudiOStreamType(cmd.stream);
player.setDataSource(cmd.context, cmd.uri); //設置媒體源,這裡android123提示大家本類的public void play (Context context, Uri uri, boolean looping, int stream) 類第二個參數Uri為媒體位置。
player.setLooping(cmd.looping);
player.prepare();
player.start();
if (mPlayer != null) {
mPlayer.release();
}
mPlayer = player;
}
catch (IOException e) {
Log.w(mTag, "error loading sound for " + cmd.uri, e);
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
Log.w(mTag, "IllegalStateException (content provider dIEd?) " + cmd.uri, e);
}
}
private final class Thread extends Java.lang.Thread { //通過多線程方式不阻塞調用者
Thread() {
super("AsyncPlayer-" + mTag);
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
Command cmd = null;
synchronized (mCmdQueue) { //同步方式執行
cmd = mCmdQueue.removeFirst();
}
switch (cmd.code) {
case PLAY:
startSound(cmd);
break;
case STOP:
if (mPlayer != null) {
mPlayer.stop();
mPlayer.release();
mPlayer = null;
} else {
Log.w(mTag, "STOP command without a player");
}
break;
}
synchronized (mCmdQueue) {
if (mCmdQueue.size() == 0) {
mThread = null;
releaseWakeLock();
return;
}
}
}
}
}
private String mTag;
private Thread mThread;
private MediaPlayer mPlayer;
private PowerManager.WakeLock mWakeLock;
private int mState = STOP;
public AsyncPlayer(String tag) {
if (tag != null) {
mTag = tag;
} else {
mTag = "AsyncPlayer";
}
}
public void play(Context context, Uri uri, boolean looping, int stream) {
Command cmd = new Command();
cmd.requestTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); //這裡為了測試性能,傳遞了開始執行前的系統tickcount計時器值
cmd.code = PLAY;
cmd.context = context;
cmd.uri = uri;
cmd.looping = looping;
cmd.stream = stream;
synchronized (mCmdQueue) {
enqueueLocked(cmd);
mState = PLAY;
}
}
public void stop() {
synchronized (mCmdQueue) {
if (mState != STOP) {
Command cmd = new Command();
cmd.requestTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
cmd.code = STOP;
enqueueLocked(cmd);
mState = STOP;
}
}
}
private void enqueueLocked(Command cmd) {
mCmdQueue.add(cmd);
if (mThread == null) {
acquireWakeLock();
mThread = new Thread();
mThread.start();
}
}
一般對於android游戲而言下面的代碼不用考慮,一般用戶都在交互操作,不會出現屏幕鎖問題
public void setUsesWakeLock(Context context) { //電源管理wakelock處理
if (mWakeLock != null || mThread != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("assertion failed mWakeLock=" + mWakeLock
+ " mThread=" + mThread);
}
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager)context.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
mWakeLock = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, mTag);
}
private void acquireWakeLock() { //加鎖
if (mWakeLock != null) {
mWakeLock.acquire();
}
}
private void releaseWakeLock() { //解鎖
if (mWakeLock != null) {
mWakeLock.release();
}
}
}
 Android AIDL全攻略一
Android AIDL全攻略一
Android的服務開發中我們可能都是Activity和Service同進程處理,但想象過系統提供的各種ServiceManager嗎? 比如 SensorManage
 android讀取手機通訊錄
android讀取手機通訊錄
下面展示一段在android1.5上讀取手機通訊錄的代碼1 //鏈接通訊錄數據庫 2 ContentResolver content = getContentResol
 Android 開發TextView 部分字符高亮
Android 開發TextView 部分字符高亮
TextVIEw 部分字體高[功能]TextVIEw是不支持部分字段高亮的 但是我們可以進行擴展[思路]1. 利用LinearLayout 作為 TextVIEw 的
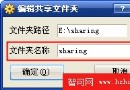 終於在XP host的VirtualBox Ubuntu系統下掛載成功Host下的文件夾
終於在XP host的VirtualBox Ubuntu系統下掛載成功Host下的文件夾
准備在虛擬機下的Ubuntu系統編譯Android源代碼,但是發現在線下載源代碼老是出現問題,幸好在Windows下已經下載成功了android源代碼,於是就想在Ubu