編輯:高級開發
開發過程中參考JDK的文檔和android的sdk文檔可以清楚遇到的很多問題,遇到問題是現在這兩個文檔中一般都能找到原因(安裝sdk的文檔參考http://www.cnblogs.com/2018/archive/2011/02/17/1957356.Html)
分層結構android Layers
Ø Prominent code librarIEs, including:
? Browser technology from WebKit, the same open source engine powering Mac’s Safari and the iPhone’s Mobile Safari browser. WebKit has become the de facto standard for most mobile platforms.
? Database support via SQLite, an easy-to-use SQL database.
? Advanced graphics support, including 2D, 3D, animation from Scalable Games Language (SGL), and OpenGL ES.
? Audio and video media support from PacketVideo’sOpenCORE, and Google’s own Stagefright media framework.
? Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) capabilitIEs from the apache project.
Ø An array of managers that provide service
? Activities and vIEws ? Telephony
? Windows ? Resources
? Location-based services
Ø The android runtime, which provides:
? Core Java packages for a nearly full-featured Java programming environment. Note that this isn’t a Java ME environment.
? The Dalvik VM employs services of the Linux-based kernel to provide an environment to host android applications.
Ø A Linux kernel
provides a foundational hardware abstraction layer, as well as core services such as process, memory, and filesystem management. The kernel is where hardware-specific drivers are implemented—capabilitIEs such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are here. The android stack is designed to be flexible, with many optional components that largely rely on the availability of specific hardware on a given device. These components include features such as touch screens,
接上頁
cameras, GPS receivers, and accelerometers.API Level
API Level is an integer value that uniquely identifIEs the framework API revision offered by a version of the android platform.
Platform Version
API Level
android 2.3
9
android 2.2
8
android 2.1
7
android 2.0.1
6
android 2.0
5
android 1.6
4
android 1.5
3
android 1.1
2
android 1.0
1
Intent IntentFilters
Intents and IntentFilters, android’s innovative navigation and triggering mechanisms.
An Intent is a declaration of need. It’s made up of a number of pieces of information that describe the desired action or service. We’re going to examine the requested action and, generically, the data that accompanIEs the requested action.
An IntentFilter is a declaration of capability and interest in offering assistance to those in need. It can be generic or specific with respect to which Intents it offers to service.
The action attribute of an Intent is typically a verb,The data component of an Intent is expressed in the form of a URI
The IntentFilter defines the relationship between the Intent and the application. IntentFilters can be specific to the data portion of the Intent, the action portion, or both. IntentFilters also contain a fIEld known as a category. The category helps classify the action.
IntentFilters are often defined in an application’s androidManifest.XML file with the < intent-filter> tag.
Activity
An application might have a UI, but it doesn’t have to have one. If it has a UI, it’ll have at least one Activity.
Service
If an application is to have a long lifecycle, it’s often best to put it
接上頁
into a Service.BroadcastReceiver
If an application wants to receive and respond to a global event, such as a ringing phone or an incoming text message, it must register as a BroadcastReceiver.
ContentProvider
If an application manages data and needs to expose that data to other applications running in the android environment, you should consider a ContentProvider.
androidManifest.XML
A fundamental fact of Android development is that an Android application contains at least one Activity, Service, BroadcastReceiver, or ContentProvider. Some of these elements advertise the Intents they’re interested in processing via the IntentFilter mechanism. All these pieces of information need to be tIEd together for an Android application to execute. The glue mechanism for this task of defining relationships is the androidManifest.XML file.
< service>Servicemight also include the < intent-filter>
< receiver>BroadcastReceivermight have an explicit < intent-filter> tag
< uses-permission>
< application
Core android packages
java.lang—Core Java language classes
Java.io—Input/output capabilitIEs
Java.Net—Network connections
Java.text—Text-handling utilitIEs
Java.math—Math and number-manipulation classes
Javax.Net—Network classes
Javax.security—Security-related classes
Javax.xml—DOM-based XML classes
org.apache.*—HTTP-related classes
org.xml—SAX-based XML classes
android.app—android application model Access
android.bluetooth—android’s Bluetooth functionality
android.content—Accessing and publishing data in android
android.Net—Contains the Uri class, used for Accessing content
接上頁
android.gesture—Create, recognize, load, and save gestures
android.graphics—Graphics primitives
android.location—Location-based services (such as GPS)
android.opengl—OpenGL classes
android.os—System-level Access to the android environment
android.provider—ContentProvider-related classes
android.telephony—Telephony capability access, including support for both Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) and Global System for Mobile communication (GSM) devices
android.text—Text layout
android.util—Collection of utilitIEs for logging and text manipulation, including XML
android.vIEw—UI elements
android.webkit—Browser functionality
android.widget—More UI elements
Application Fundamentals
SDK的文檔目錄file:///。。。/android-sdk-Windows/docs/guide/topics/fundamentals.Html 有詳細的說明
Activity lifecycle
As an activity transitions from state to state, it is notifIEd of the change by calls to the following protected methods:
voidonCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
void onStart()
void onRestart()
void onResume()
void onPause()
void onStop()
void onDestroy()
由android SDK/NDK默認管理的目錄和文件:
androidManifest.XML
軟件的android關鍵配置文件
涉及安全、啟動的Activty等
default.propertIEs
API Level的設置等
proguard.cfg
代碼混淆使用
界面資源和訪問代碼
res gen 兩個字目錄下的文件
res下有如下類別
res/anim:用XML表示的基於幀的動畫
res/drawable:不同規格的圖標、圖片等,drawable-hdpidrawable-ldpidrawable-mdpi三個子目錄
res/layout:視圖對象的XML表示
res/values:strings, colors, styles, dimensions, arrays的XML表示
接上頁
res/xml:User-defined XML files that are compiled into a binary representation
res/raw:Arbitrary and uncompiled files that can be added
gen res中加入的資源在gen中生成訪問代碼R.Java
assets
數據等文件
android.content.res.AssetManager asset = Application.getAssets()這個類輔助訪問
src
Java代碼
NDK
Jniobj libs目錄
Jni: 放C/C++代碼
Obj/libs:是c/c++的編譯obj文件和so庫
在這些默認文件和目錄的基礎上可以加入自己的需要管理的目錄或文件
 2010年最值得擁有的五大Android應用
2010年最值得擁有的五大Android應用
斗轉星移,2011年這麼快就來到了。我們給大家介紹過《2010年Google十大android應用》,好的應用並不一定需要擁有,今天再給大家介紹值得你擁有的五個應用。2
 有關Android系統手機插架兼容性述說
有關Android系統手機插架兼容性述說
android系統手機推出這也許對大家而言是一種好事,但要提醒大家的是在方便的同時也確實給我們埋下了不少的隱患,無論什麼樣的系統,一定會有他的強大之處,也會有不少瑕疵,
 深度剖析Android JDK 日志框架
深度剖析Android JDK 日志框架
全球為數眾多的移動電話用戶從未使用過任何基於android JDK 日志框架,谷歌的目標是讓不依賴於設備甚至平台,希望大家看完本文能給大家帶來相關幫助。日志記錄對於軟件
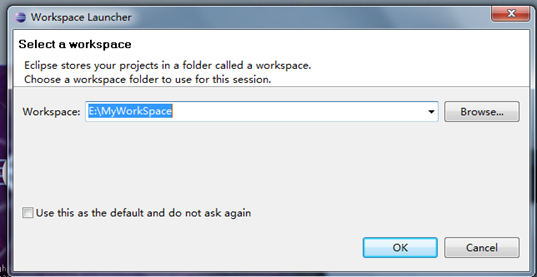 Win7 配置Android開發環境(4)
Win7 配置Android開發環境(4)
即: eclipse-Java-heliOS-SR2-win32-x86_64.zip 這個文件。 下載後解壓縮後就可以用了。 使用時選擇一個Workspace 即