編輯:關於android開發
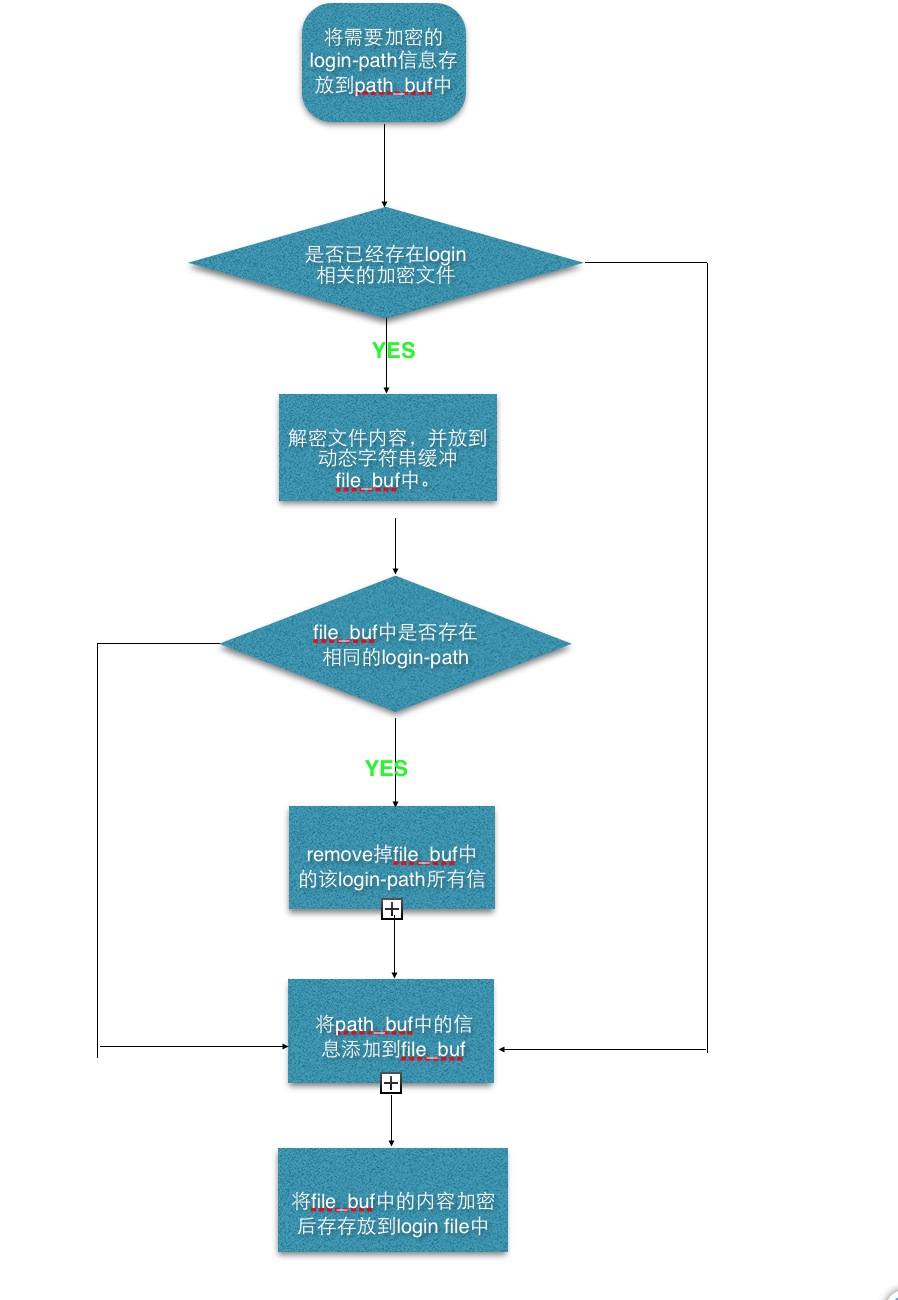
- static int set_command(void)
- {
- DBUG_ENTER("set_command");
- DYNAMIC_STRING file_buf, path_buf;
- init_dynamic_string(&path_buf, "", MY_LINE_MAX, MY_LINE_MAX);
- init_dynamic_string(&file_buf, "", file_size, 3 * MY_LINE_MAX);
- if (tty_password)
- opt_password= get_tty_password(NullS);
- if (file_size)
- {
- if (read_and_decrypt_file(&file_buf) == -1) //如果文件存在,就讀取文件,並將文件的密文解密後存放到file_buf中.
- goto error;
- }
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "["); /* --login=path */
- if (opt_login_path)
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, opt_login_path);
- else
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "client");
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "]");
- if (opt_user) /* --user */
- {
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "\nuser = ");
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, opt_user);
- }
- if (opt_password) /* --password */
- {
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "\npassword = ");
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, opt_password);
- }
- if (opt_host) /* --host */
- {
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "\nhost = ");
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, opt_host);
- }
- if (opt_socket)
- {
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "\nsocket = ");
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, opt_socket);
- }
- if (opt_port)
- {
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "\nport = ");
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, opt_port);
- }
- dynstr_append(&path_buf, "\n");
- /* Warn if login path already exists */
- if (opt_warn && ((locate_login_path (&file_buf, opt_login_path)) //判斷該login-path是否已經存在
- != NULL))
- {
- int choice;
- printf ("WARNING : \'%s\' path already exists and will be "
- "overwritten. \n Continue? (Press y|Y for Yes, any "
- "other key for No) : ",
- opt_login_path);
- choice= getchar();
- if (choice != (int) 'y' && choice != (int) 'Y’) //如果login-path存在是否選擇覆蓋
- goto done; /* skip */
- }
- /* Remove the login path. */
- remove_login_path(&file_buf, opt_login_path); //從原來文件中讀取的內容中,刪掉該login-path信息
- /* Append the new login path to the file buffer. */
- dynstr_append(&file_buf, path_buf.str); //將該login-path的信息加到file_buf的末尾
- if (encrypt_and_write_file(&file_buf) == -1) //將包含新的log-path的所有信息和原來的信息加密寫入文件
- goto error;
- done:
- dynstr_free(&file_buf);
- dynstr_free(&path_buf);
- DBUG_RETURN(0);
- error:
- dynstr_free(&file_buf);
- dynstr_free(&path_buf);
- DBUG_RETURN(-1);
- }
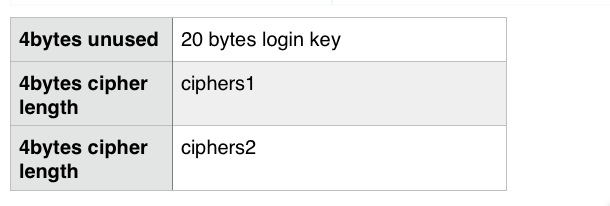
- /*
- Header length for the login file.
- 4-byte (unused) + LOGIN_KEY_LEN
- */
- #define MY_LOGIN_HEADER_LEN (4 + LOGIN_KEY_LEN)
- static int read_and_decrypt_file(DYNAMIC_STRING *file_buf)
- {
- DBUG_ENTER("read_and_decrypt_file");
- char cipher[MY_LINE_MAX], plain[MY_LINE_MAX];
- uchar len_buf[MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN];
- int cipher_len= 0, dec_len= 0;
- /* Move past key first. */
- if (my_seek(g_fd, MY_LOGIN_HEADER_LEN, SEEK_SET, MYF(MY_WME)) //跳過之前的unused bytes和login key部分
- != (MY_LOGIN_HEADER_LEN))
- goto error; /* Error while seeking. */
- /* First read the length of the cipher. */
- while (my_read(g_fd, len_buf, MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN, //獲取密文的長度
- MYF(MY_WME)) == MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN)
- {
- cipher_len= sint4korr(len_buf); //將密文的長度轉換成整形
- if (cipher_len > MY_LINE_MAX)
- goto error;
- /* Now read 'cipher_len' bytes from the file. */
- if ((int) my_read(g_fd, (uchar *) cipher, cipher_len, MYF(MY_WME)) == cipher_len) //讀取相應密文長度的密文
- {
- if ((dec_len= decrypt_buffer(cipher, cipher_len, plain)) < 0) //解密該密文
- goto error;
- plain[dec_len]= 0;
- dynstr_append(file_buf, plain); //將解密後的密文追加到file_buf中
- }
- }
- verbose_msg("Successfully decrypted the login file.\n");
- DBUG_RETURN(0);
- error:
- my_perror("couldn't decrypt the file");
- DBUG_RETURN(-1);
- }
- #define int4store(T,A) do { *((char *)(T))=(char) ((A));\
- *(((char *)(T))+1)=(char) (((A) >> 8));\
- *(((char *)(T))+2)=(char) (((A) >> 16));\
- *(((char *)(T))+3)=(char) (((A) >> 24));\
- } while(0)
- #define sint4korr(A) (int32) (((int32) ((uchar) (A)[0])) +\
- (((int32) ((uchar) (A)[1]) << 8)) +\
- (((int32) ((uchar) (A)[2]) << 16)) +\
- (((int32) ((int16) (A)[3]) << 24)))
該函數主要功能如下:
- static int encrypt_and_write_file(DYNAMIC_STRING *file_buf)
- {
- DBUG_ENTER("encrypt_and_write_file");
- my_bool done= FALSE;
- char cipher[MY_LINE_MAX], *tmp= NULL;
- uint bytes_read=0, len= 0;
- int enc_len= 0; // Can be negative.
- if (reset_login_file(0) == -1) //清空文件,並重新生成隨機加密秘鑰,並將對稱加密秘鑰寫入文件頭部
- goto error;
- /* Move past key first. */
- if (my_seek(g_fd, MY_LOGIN_HEADER_LEN, SEEK_SET, MYF(MY_WME))
- != (MY_LOGIN_HEADER_LEN))
- goto error; /* Error while seeking. */
- tmp= &file_buf->str[bytes_read];
- while(! done)
- {
- len= 0;
- while(*tmp++ != '\n’) //讀取file_buf中的每一行內容
- if (len < (file_buf->length - bytes_read))
- len ++;
- else
- {
- done= TRUE;
- break;
- }
- if (done)
- break;
- if ((enc_len= encrypt_buffer(&file_buf->str[bytes_read],++len,cipher+MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN))<0) //對讀到的這一行內容進行加密,並將密文存放到cipher + MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN的地址處
- goto error;
- bytes_read += len;
- if (enc_len > MY_LINE_MAX)
- goto error;
- /* Store cipher length first. */
- int4store(cipher, enc_len); //將密文的長度存放到cipher的頭部
- if ((my_write(g_fd, (const uchar *)cipher, enc_len + MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN,
- MYF(MY_WME))) != (enc_len + MAX_CIPHER_STORE_LEN)) //將該行加密過的密文寫到文件
- goto error;
- }
- verbose_msg("Successfully written encrypted data to the login file.\n");
- /* Update file_size */
- file_size= bytes_read; //更新文件大小
- DBUG_RETURN(0);
- error:
- my_perror("couldn't encrypt the file");
- DBUG_RETURN(-1);
- }
 狀態欄一體化及其帶來的軟鍵盤自適應問題
狀態欄一體化及其帶來的軟鍵盤自適應問題
狀態欄一體化及其帶來的軟鍵盤自適應問題 狀態欄一體化及其帶來的軟鍵盤自適應問題 應項目需求才開始了解狀態欄一體化的問題,作為一個android新手,之前從未接觸過。第
 git 上的pull request 是什麼意思?,gitpull
git 上的pull request 是什麼意思?,gitpull
git 上的pull request 是什麼意思?,gitpull 1、git 上有常見的pull request 功能
 Android 底部彈出Dialog(橫向滿屏),androiddialog
Android 底部彈出Dialog(橫向滿屏),androiddialog
Android 底部彈出Dialog(橫向滿屏),androiddialog項目中經常需要底部彈出框,這裡我整理一下其中我用的比較順手的一個方式(底部彈出一個橫向滿屏的d
 OrmLite數據庫的使用方法,ormlite數據庫
OrmLite數據庫的使用方法,ormlite數據庫
OrmLite數據庫的使用方法,ormlite數據庫第一步:導入架包 1、將orm的兩個支持包放入project視圖下的你的工程的l