Android系統是一款基於Linux的移動操作系統,那麼Android是如何啟動起來的呢?本文就詳細闡述Android系統的啟動過程。
從內核之上,我們首先應該從文件系統的init開始,因為 init 是內核進入文件系統後第一個運行的程序,通常我們可以在linux的命令行中指定內核第一個調用誰,如果沒指定那麼內核將會到/sbin/、/bin/ 等目錄下查找默認的init,如果沒有找到那麼就報告出錯。
init.c位置:system/core/init/init.c。
在init.c的main函數裡面完成以下步驟:
1、創建設備節點。
2、初始化log系統。
3、解析init.rc文件,解析函數在同一目錄的parser.c裡面實現。
4、初始化屬性服務器,在同一目錄下的property_service.c裡面實現。
。。。。
最後、進入loop等待事件到來。
init.rc的解析過程
init.rc是一個初始化腳本,路徑(不確定):device/renesas/emev/init.rc
在init.c的main函數裡面,調用parser.c的parse_config_file("/init.rc");執行解析過程。
先讀取文件內容到data裡面,再調用parse_config(fn, data);進行解析。
init.rc包含Android初始化語言的四大類聲明:行為類(Actions)、命令類(Commands)、服務類(Services)、選項類(Options),解析完會形成兩個列表service_list 和action_list。
其中有一個很重要的服務就是zygote,在init.rc裡面的片段:
Java代碼
- service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
- socket zygote stream 666
- onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
- onrestart write /sys/power/state on
- onrestart restart media
這是腳本中service的格式:
Java代碼
- service <name> <pathname> [ <argument> ]*
- <option>
- <option>
- ...
zygote對應的可執行文件為app_process,android2.2中它的源代碼位置:framework/base/cmds/app_process。
app_main.cpp的main函數,它先調用AndroidRuntime::addVmArguments將它的參數“-Xzygote /system/bin”傳給AndroidRuntime作為啟動JavaVM用。接著如果定位余下的參數,如果有"--zygote",執行下面代碼,從參數可以知道,這時候要求啟動start system server,並且將com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit裝載至虛擬機。
C++代碼
- ZygoteInit.java的main方法)。
- if (0 == strcmp("--zygote", arg)) {
- bool startSystemServer = (i < argc) ?
- strcmp(argv[i], "--start-system-server") == 0 : false;
- setArgv0(argv0, "zygote");
- set_process_name("zygote");
- runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
- startSystemServer);
- }
否則不啟動system server:
C++代碼
- set_process_name(argv0);
-
- runtime.mClassName = arg;
-
- // Remainder of args get passed to startup class main()
- runtime.mArgC = argc-i;
- runtime.mArgV = argv+i;
-
-
- LOGV("App process is starting with pid=%d, class=%s.\n",
- getpid(), runtime.getClassName());
- runtime.start();
runtime是AppRuntime對象,繼承自AndroidRuntime,在AndroitRuntime.app裡的start()函數如下,默認裝載的是RuntimeInit進程,不啟動system server。
C++代碼
- void AndroidRuntime::start()
- {
- start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit",
- false /* Don't start the system server */);
- }
在AndroidRuntime.cpp的start方法內,先啟動JAVA虛擬機,在定位執行className類的main方法(如果才存在的話)。
C++代碼
- void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const bool startSystemServer)
- {
- LOGD("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>> AndroidRuntime START <<<<<<<<<<<<<<\n");
-
-
- /* start the virtual machine */
- if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0)
- goto bail;
-
-
- startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
- if (startClass == NULL) {
- LOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
- /* keep going */
- } else {
- startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
- "([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
- if (startMeth == NULL) {
- LOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
- /* keep going */
- } else {
- env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
- }
- }
- }
先看怎麼啟動虛擬機的,在startVm方法內,先將一些系統參數選項,包括虛擬機相關的屬性,保存到一個JavaVMOption的實例內,比如虛擬機的堆大小,是否check jni,JNI版本信息,最後將這些參數傳給JNI_CreateJavaVM,創建JAVA虛擬機實例。
C++代碼
- //JNI_CreateJavaVM在jni.h中有聲明,代碼位置:dalvik/libnativehelper/include/nativehelper/,在Jni.c中有定義
- jint JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs(void*);
- jint JNI_CreateJavaVM(JavaVM**, JNIEnv**, void*);
- jint JNI_GetCreatedJavaVMs(JavaVM**, jsize, jsize*);
在JNI_CreateJavaVM中,先檢查JNI的版本,為JavaVM,JNIEnv開辟空間,保存通用接口,最後解析傳進來的參數,最後調用dvmStartup啟動虛擬機(有些傳給JNI_CreateJavaVM的參數,也直接傳給了dvmStartup)。
這裡的JNIEnv實際是JNIEnvExt強制轉換過來的,JNIEnvExt是JNIEnv結構體的擴展,JNIEnExt前端與JNIEnv完全對齊,都是JNI函數指針。相當於JNIEnExt對JNIEnv進行了賦值。
C++代碼
- pEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) dvmCreateJNIEnv(NULL);
在dvmStartup在Init.c定義,先調用setCommandLineDefaults進行一些默認的設置,比如虛擬機的默認heap大小。
C++代碼
- static void setCommandLineDefaults()
- {
- gDvm.heapSizeStart = 2 * 1024 * 1024; // Spec says 16MB; too big for us.
- gDvm.heapSizeMax = 16 * 1024 * 1024; // Spec says 75% physical mem
- gDvm.stackSize = kDefaultStackSize;
- }
然後調用dvmProcessOptions處理傳進來的參數,比如是否執行zygote,最後,根據gDvm.zygote的值,是否申請一個新的堆,這個值在有參數-Xzygote置1。
C++代碼
- if (gDvm.zygote) {
- if (!dvmInitZygote())
- goto fail;
- } else {
- if (!dvmInitAfterZygote())
- goto fail;
- }
到這裡,虛擬機算是啟動成功了。
回到AndroidRuntime.cpp的start方法,現在我們要啟動ZygoteInit進程,找到ZygoteInit的main方法,調用env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);去啟動它。
CallStaticVoidMethod在Jni.c裡面有定義,但不是直接定義的,因此用CallStaticVoidMethod作為函數名直接查定義是查不到的,是這樣定義的:
CALL_STATIC(void, Void, , , false);
再看CALL_STATIC的宏定義:
C++代碼
- #define CALL_STATIC(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) \
- static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
- jmethodID methodID, ...) \
- { \
- UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
- JNI_ENTER(); \
- JValue result; \
- va_list args; \
- va_start(args, methodID); \
- dvmCallMethodV(_self, (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);\
- va_end(args); \
- if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(_self)) \
- result.l = addLocalReference(env, result.l); \
- JNI_EXIT(); \
- return _retok; \
- } \
- static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
- jmethodID methodID, va_list args) \
- { \
- UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
- JNI_ENTER(); \
- JValue result; \
- dvmCallMethodV(_self, (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);\
- if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(_self)) \
- result.l = addLocalReference(env, result.l); \
- JNI_EXIT(); \
- return _retok; \
- } \
- static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
- jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) \
- { \
- UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
- JNI_ENTER(); \
- JValue result; \
- dvmCallMethodA(_self, (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);\
- if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(_self)) \
- result.l = addLocalReference(env, result.l); \
- JNI_EXIT(); \
- return _retok; \
- }
因此CallStaticVoidMethod調用的是dvmCallMethodV方法,至於怎麼樣再調用到ZygoteInit的main方法,有待研究,現在直接看ZygoteInit的main方法,它的參數是這樣定義的:
C++代碼
- stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
- assert(stringClass != NULL);
- strArray = env->NewObjectArray(2, stringClass, NULL);
- assert(strArray != NULL);
- classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
- assert(classNameStr != NULL);
- env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
- startSystemServerStr = env->NewStringUTF(startSystemServer ?
- "true" : "false");
- env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 1, startSystemServerStr);
申請一個String變量,給把類名作為第0個參數,第二個參數是"ture"或"false",用來決定是否啟動system service,在ZygoteInit的main方法會讀取這個參數。
C++代碼
- if (argv[1].equals("true")) {
- startSystemServer();
- } else if (!argv[1].equals("false")) {
- throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
- }
它讀取到第一個參數是"true",所以調用startSystemServer啟動system server,在startSystemServer中,調用Zygote的forkSystemServer,fork出來的子進程,就是system server了,調用事的參數如下:
C++代碼
- String args[] = {
- "--setuid=1000",
- "--setgid=1000",
- "--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,3001,3002,3003",
- "--capabilities=130104352,130104352",
- "--runtime-init",
- "--nice-name=system_server",
- "com.android.server.SystemServer",
- };
這些參數解析到一個ZygoteConnection.Arguments對象中。forkSystemServer方法實際上是JNI方法,在vm/native/dalvik_system_Zygote.c中有定義。
C++代碼
- static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_Zygote_forkSystemServer(
- const u4* args, JValue* pResult)
- {
- pid_t pid;
- pid = forkAndSpecializeCommon(args);
- if (pid > 0) {
- int status;
-
-
- LOGI("System server process %d has been created", pid);
- gDvm.systemServerPid = pid;
-
-
- if (waitpid(pid, &status, WNOHANG) == pid) {
- LOGE("System server process %d has died. Restarting Zygote!", pid);
- kill(getpid(), SIGKILL);
- }
- }
- RETURN_INT(pid);
- }
具體的fork操作在forkAndSpecializeCommon裡面進行,父進程檢查子進程是否died。
在forkAndSpecializeCommon,先判斷是否zygote模式,是否剩余有足夠的heap空間,最後才執行fork()系統調用。
fork之後,父進程不做操作,子進程調用dvmInitAfterZygote去為自己申請堆空間。
子進程返回到startSystemServer方法。
C++代碼
- /* For child process */
- if (pid == 0) {
- handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
- }
調用handleSystemServerProcess方法,在裡面先設置uid的權限,再調用RuntimeInit.zygoteInit。
C++代碼
- /*
- * Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
- * "--nice-name=system_server com.android.server.SystemServer"
- */
- RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
- /* should never reach here */
在zygoteInit裡面調用invokeStaticMain,invokeStaticMain先將com.android.server.Systemserver類的main方法取出,作為Method對象,然後和參數一起傳給ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller,MethodAndArgsCaller繼承自Runner,最終MethodAndArgsCaller調用Method.invode函數啟動System Server。
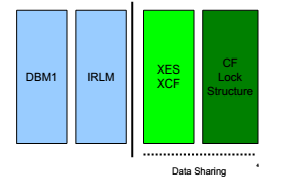 A DB2 Performance Tuning Roadmap --DIVE INTO LOCK
A DB2 Performance Tuning Roadmap --DIVE INTO LOCK
 Android中Action Bar的使用
Android中Action Bar的使用
 Activity啟動模式之SingleInstance,singleinstance模式
Activity啟動模式之SingleInstance,singleinstance模式
 自定義左下角弧形旋轉菜單欄
自定義左下角弧形旋轉菜單欄