編輯:關於android開發
service—Android的四大組件之一。人稱“後台服務”指其本身的運行並不依賴於用戶可視的UI界面
實際開發中我們經常需要service和activity之間可以相互傳遞數據維持程序的運行。
先了解Service的生命周期吧。
新建一個類繼Service:
package com.example.myservicedemo.service;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
/**
* 服務類(需要在項目清單文件中注冊服務)
*
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
/**
* 服務創建的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("=========onCreate======");
}
/**
* 服務啟動的時候調用
*/
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=========onStartCommand======");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
/**
* 服務銷毀的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=========onDestroy======");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
新建以上類並繼承Service後只會重寫onBind()方法,其他方法是我手動手寫,為了弄清楚Service的生命周期
MainActivity中(設置兩個按鈕用來開始和停止服務):
package com.example.myservicedemo.ui;
import com.example.myservicedemo.R;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService.DownLoadBinder;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn_start = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_start);
Button btn_stop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_stop);
btn_start.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_stop.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int id = v.getId();
switch (id) {
/*
* 開啟服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_start:
Intent startIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
break;
/*
* 停止服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_stop:
Intent stopIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
切記android中的服務是需要在項目清單文件中注冊的(AndroidStudio可以自動,eclipse需要手動添加):
<service android:name="服務類坐所在的包名.MyService"></service>
此時運行程序,點擊開啟服務時候輸出是下圖:(我輸出多次onStartCommand()是因為我連續點擊了多次開啟服務按鈕)
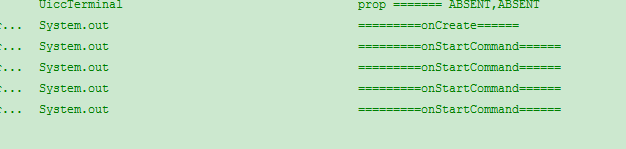
上圖可以看出服務第一次開啟時先是調用了onCreate()方法和onStartCommand()方法,多次點擊開始服務時只調用了onStartCommand()方法
so:
onCreate()方法是服務創建的時候調用的~
onStartCommand()方法在每次啟動服務的時候都會調用~
onDestory()方法在停止服務時候會調用~
點擊停止服務後,輸出如圖:

啟動服務還有一種方式是bindService();
此時的MyService類要做改變:
package com.example.myservicedemo.service;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
/**
* 服務類(需要在項目清單文件中注冊服務)
*
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
private DownLoadBinder downLoadBinder=new DownLoadBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=====onBind=====");
return downLoadBinder;
}
/**
* 內部類繼承Binder
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class DownLoadBinder extends Binder{
public void startDownLoad(){
System.out.println("=====startDownLoad()=====");
}
public void getProgress(){
System.out.println("=====getProgress()=====");
}
}
/**
* 服務創建的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("=========onCreate======");
}
/**
* 服務啟動的時候調用
*/
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=========onStartCommand======");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
/**
* 服務銷毀的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=========onDestroy======");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
以上的代碼和第一次相比,一是多了一個內部類DownLoadBinder繼承IBinder並且聲明了兩個方法,二是將onBind方法的返回值改為了DownLoadBinder類型的變量
activity bindService方法啟動服務時候一般是需要傳遞數據的,核心就在onBind()方法中,往下看
MainActivity中加兩個按鈕:綁定服務和取消綁定服務
package com.example.myservicedemo.ui;
import com.example.myservicedemo.R;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService.DownLoadBinder;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private MyService.DownLoadBinder downLoadBinder;
private MyService myService; //我們自己的service
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn_start = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_start);
Button btn_stop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_stop);
Button btn_bind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_bind);
Button btn_unbind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_unbind);
btn_start.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_stop.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_bind.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_unbind.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int id = v.getId();
switch (id) {
/*
* 開啟服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_start:
Intent startIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
break;
/*
* 停止服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_stop:
Intent stopIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
break;
/*
* 綁定服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_bind:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
bindService(bindIntent, connection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
/*
* 解除綁定服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_unbind:
unbindService(connection);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private ServiceConnection connection=new ServiceConnection() {
/**
* 服務解除綁定時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/**
* 綁定服務的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//myService=((DownLoadBinder) service).
downLoadBinder=(DownLoadBinder) service;
/*
* 調用DownLoadBinder的方法實現參數的傳遞
*/
downLoadBinder.startDownLoad();
downLoadBinder.getProgress();
}
};
}
運行後點擊綁定服務後輸出如下:

說明成功綁定了服務且傳遞了數據,點擊解除綁定服務時候ondestory()方法輸出
不過這種方法好像只能傳遞一次數據,,,,不爽,,,,比如後台在實時更新東西,activity需要實時獲取呢???
查找資料大多是以下幾種方式:
1.使用接口回調方式,activity實現相應的接口,service通過接口進行回調,比較靈活
2.使用廣播
這篇博客主要介紹第一種方法,為什麼不介紹第二種???——不願意介紹,不喜歡。
使用接口回調方式的MyService和MainActivity代碼我是備注詳細之後才粘貼的,大家可以看注釋
MyService代碼:
package com.example.myservicedemo.service;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
/**
* 服務類(需要在項目清單文件中注冊服務)
*
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
private DownLoadBinder downLoadBinder=new DownLoadBinder();
/**
* 回調
*/
private Callback callback;
/**
* Timer實時更新數據的
*/
private Timer mTimer=new Timer();
/**
*
*/
private int num;
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=====onBind=====");
return downLoadBinder;
}
/**
* 內部類繼承Binder
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class DownLoadBinder extends Binder{
/**
* 聲明方法返回值是MyService本身
* @return
*/
public MyService getService() {
return MyService.this;
}
}
/**
* 服務創建的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
/*
* 執行Timer 2000毫秒後執行,5000毫秒執行一次
*/
mTimer.schedule(task, 0, 1000);
}
/**
* 提供接口回調方法
* @param callback
*/
public void setCallback(Callback callback) {
this.callback = callback;
}
/**
*
*/
TimerTask task = new TimerTask(){
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
num++;
if(callback!=null){
/*
* 得到最新數據
*/
callback.getNum(num);
}
}
};
/**
* 回調接口
*
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public static interface Callback {
/**
* 得到實時更新的數據
*
* @return
*/
void getNum(int num);
}
/**
* 服務銷毀的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("=========onDestroy======");
/**
* 停止Timer
*/
mTimer.cancel();
super.onDestroy();
}
}
MainActivity代碼:
package com.example.myservicedemo.ui;
import com.example.myservicedemo.R;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService.Callback;
import com.example.myservicedemo.service.MyService.DownLoadBinder;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private MyService.DownLoadBinder downLoadBinder;
// private MyService myService; //我們自己的service
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btn_start = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_start);
Button btn_stop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_stop);
Button btn_bind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_bind);
Button btn_unbind = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_unbind);
btn_start.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_stop.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_bind.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_unbind.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int id = v.getId();
switch (id) {
/*
* 開啟服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_start:
Intent startIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
break;
/*
* 停止服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_stop:
Intent stopIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
break;
/*
* 綁定服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_bind:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
bindService(bindIntent, connection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
break;
/*
* 解除綁定服務點擊事件
*/
case R.id.btn_unbind:
unbindService(connection);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private ServiceConnection connection=new ServiceConnection() {
/**
* 服務解除綁定時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/**
* 綁定服務的時候調用
*/
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
downLoadBinder = (DownLoadBinder) service;
MyService service2 = downLoadBinder.getService();
/**
* 實現回調,得到實時刷新的數據
*/
service2.setCallback(new Callback() {
@Override
public void getNum(int num) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("====num===="+num);
}
});
}
};
}
運行後的結果應該輸出如圖就對了(輸出隨service中num的數量而更新):

期間遇到的問題:
bindService後無效,MyService類中的onBind()方法沒有被調用
解決:這種情況下你的Activity應該是繼承了TabBarActivity,綁定服務的時候調用寫這種形式:
this.getApplicationContext().bindService(intent, mConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
最近幾天用到,總結一下,希望可以為大家帶來幫助,有錯誤還請大神指正。
 Android 在內部存儲讀寫文件,android讀寫
Android 在內部存儲讀寫文件,android讀寫
Android 在內部存儲讀寫文件,android讀寫文件讀寫操作* Ram內存:運行內存,相當於電腦的內存* Rom內存:內部存儲空間,相當於電腦的硬盤* sd卡:外部
 提高效率的 Android Studio 技巧匯總,androidstudio
提高效率的 Android Studio 技巧匯總,androidstudio
提高效率的 Android Studio 技巧匯總,androidstudio這是從Philippe Breault的系列文章《Android Studio Tips O
 讓TextView出現跑馬燈效果,textview跑馬燈效果
讓TextView出現跑馬燈效果,textview跑馬燈效果
讓TextView出現跑馬燈效果,textview跑馬燈效果 只需要在TextView中添加一些屬性即可: <?xml version=1.0 encoding=
 Android Activity生命周期與啟動模式,androidactivity
Android Activity生命周期與啟動模式,androidactivity
Android Activity生命周期與啟動模式,androidactivityActivity的完整生命周期如下圖: Activity的加載模式有四種: stand