編輯:關於android開發
啦啦啦~(博主每次開篇都要賣個萌,大家是不是都厭倦了呢~)
本篇博文希望幫助大家掌握 Broadcast 編程基礎,實現動態注冊 Broadcast 和靜態注冊 Broadcast 的方式以及學會使用Notification。
BraodcastReceiver(廣播接收器)是為了實現系統廣播(Notification)而提供的一種組件, 它和事件處理機制類似,但是事件處理機制是程序組件級別的,而廣播事件處理 機制是系統級別的。比如,我們可以發出一種廣播來測試手機電量的變化,這時候就可以定義一個 BraodcastReceiver 來接受廣播,當手機電量較低時提示用戶。它是一個系統全局的監聽器,用於監聽系統全局的Broadcast消息,所以它可以很方便的進行系統組件之間的通信。
BroadcastReceiver雖然是一個監聽器,但是它和之前用到的OnXxxListener不同,那些只是程序級別的監聽器,運行在指定程序的所在進程中,當程序退出的時候,OnXxxListener監聽器也就隨之關閉了,但是BroadcastReceiver屬於系統級的監聽器,它擁有自己的進程,只要存在與之匹配的Broadcast被以Intent的形式發送出來,BroadcastReceiver就會被激活。
雖然同屬Android的四大組件,BroadcastReceiver也有自己獨立的聲明周期,但是和Activity、Service又不同。當在系統注冊一個BroadcastReceiver之後,每次系統以一個Intent的形式發布Broadcast的時候,系統都會創建與之對應的BroadcastReceiver廣播接收者實例,並自動觸發它的onReceive()方法,當onReceive()方法被執行完成之後,BroadcastReceiver的實例就會被銷毀。雖然它獨自享用一個單獨的進程,但也不是沒有限制的,如果BroadcastReceiver.onReceive()方法不能在10秒內執行完成,Android系統就會認為該BroadcastReceiver對象無響應,然後彈出ANR(Application No Response)對話框,所以不要在BroadcastReceiver.onReceive()方法內執行一些耗時的操作。
如果需要根據廣播內容完成一些耗時的操作,一般考慮通過Intent啟動一個Service來完成該操作,而不應該在BroadcastReceiver中開啟一個新線程完成耗時的操作,因為BroadcastReceiver本身的生命周期很短,可能出現的情況是子線程還沒有結束,BroadcastReceiver就已經退出的情況,而如果BroadcastReceiver所在的進程結束了,該線程就會被標記為一個空線程,根據Android的內存管理策略,在系統內存緊張的時候,會按照優先級,結束優先級低的線程,而空線程無異是優先級最低的,這樣就可能導致BroadcastReceiver啟動的子線程不能執行完成。
BroadcastReceiver本質上還是一個監聽器,所以使用BroadcastReceiver的方法也是非常簡單,只需要繼承BroadcastReceiver,在其中重寫onReceive(Context context,Intent intent)即可。一旦實現了BroadcastReceiver,並部署到系統中後,就可以在系統的任何位置,通過sendBroadcast、sendOrderedBroadcast方法發送Broadcast給這個BroadcastReceiver。
我們既可以用 Intent 來啟動一個組件,也可以用 sendBroadcast()方法發起一個系統級別的事件廣播來傳遞消息。我們同樣可以在自己的應用程序中實現 BroadcastReceiver 來監聽和響應廣播的Intent。在程序中使用 BraodcastReceiver 是比較簡單的。首先要定義一個類繼承 BraodcastReceiver,並且覆蓋 onReceiver()方法來響應事件。然後注冊在程序中 BraodcastReceiver。最後構建 Intent 對象調用 sendBroadcast()方法將廣播發出。
包含靜態注冊方式和動態注冊方式:
靜態廣播部分首先需要後設置 setOnItemClickListener,利用 bundle 和 intent 將圖片與文字內容發送出去。
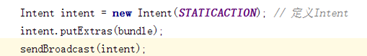
參考代碼中的 STATICATION 為自己設定的廣播名稱。由於是靜態注冊所以需要在 AndroidMainfest.xml 中進行注冊(右擊New->other->Broadcast Receiver創建一個Receiver類後,AS將自動在AndroidMainfest.xml 中進行注冊,我們只需要添加自己設定的廣播名稱):

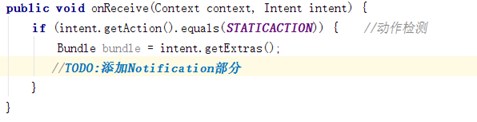
在靜態廣播類 StaticReceiver 中重寫 onReceive 方法,當接收到對應廣播時進行數據 處理,產生通知。
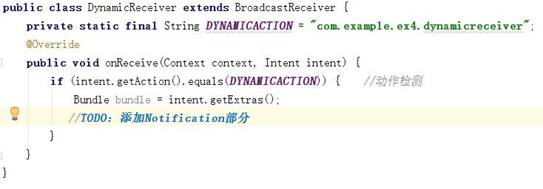
(1) 實現 BroadcastReceiver 子類(這裡命名為 DynamicReceiver),並且重寫 onReceive 方法,修改方法與靜態廣播類中類似。
(2)創建主頁面,設置注冊和注銷按鈕(set OnClickListener),使其能夠注冊或者注銷廣 播器。
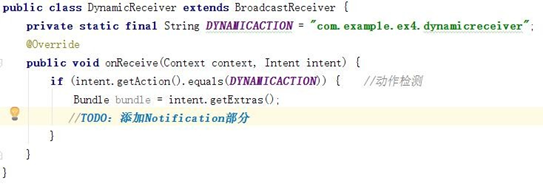
注冊關鍵代碼:

注銷關鍵代碼:
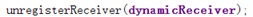
其中 dynamicReceiver 為我們之前創建的 DynamicReceiver 類。用 registerReceiver 與 unregisterReceiver 分別對其進行注冊與注銷。
(3)設置 Send 按鈕點擊事件,如果廣播注冊,則能夠點擊後發送廣播。發送方法與靜態注 冊時一直,僅需修改廣播名稱即可。(使用 sendBroadcast(intent))
(4)注意在 Android 主界面中將 launchMode 設置為 singleInstance,使得點擊 Notification 後不會另外新建一個 MainActivity:

Notification 可以提供持久的通知,位於手機最上層的狀態通知欄中。用手指按下狀 態欄,並從手機上方向下滑動,就可以打開狀態欄查看提示消息。
通知一般通過NotificationManager服務發送一個Notification對象來完成通知,NotificationManager是一個重要的系統級服務,該對象位於應用程序的框架層中,應用程序可以通過它向系統發送全局的通知。使用通知的時候,需要創建一個Notification對象用來承載通知的內容,但是一般不會直接通過Notification的構造方法來得到對象,而是使用它的內部類Notification.Builder來實例化一個Builder對象,並設置通知的各項屬性,最後通過Notification.Builder.builder()方法得到一個Notification對象,當獲得這個Notification對象之後,就可以使用NotificationManager.notify()方法發送通知。
開發 Notification 主要 涉及以下 3 個類:
(1)Notification.Builder:用於動態的設置 Notification 的一些屬性。

這裡LargeIcon獲取的參數通過以下方式來設定(獲取圖片資源的方式):
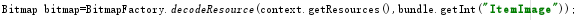
雖然通知中提供了各種屬性的設置,但是一個通知對象,有幾個屬性是必須要設置的,其他的屬性均是可選的,必須設置的屬性如下:
(2)NotificationManager:負責將 Notification 在狀態顯示出來和取消;

NotificationManager類是一個通知管理器類,這個對象是由系統維護的服務,是以單例模式的方式獲得,所以一般並不直接實例化這個對象。在Activity中,可以使用Activity.getSystemService(String)方法獲取NotificationManager對象,Activity.getSystemService(String)方法可以通過Android系統級服務的句柄,返回對應的對象。在這裡需要返回NotificationManager,所以直接傳遞Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE即可。
(3)Notification:設置 Notification 的相關屬性。

(4)點擊 notification,就可以跳轉到我們 intent 中指定的 activity。主要使用到setContentIntent 與 PendingIntent。
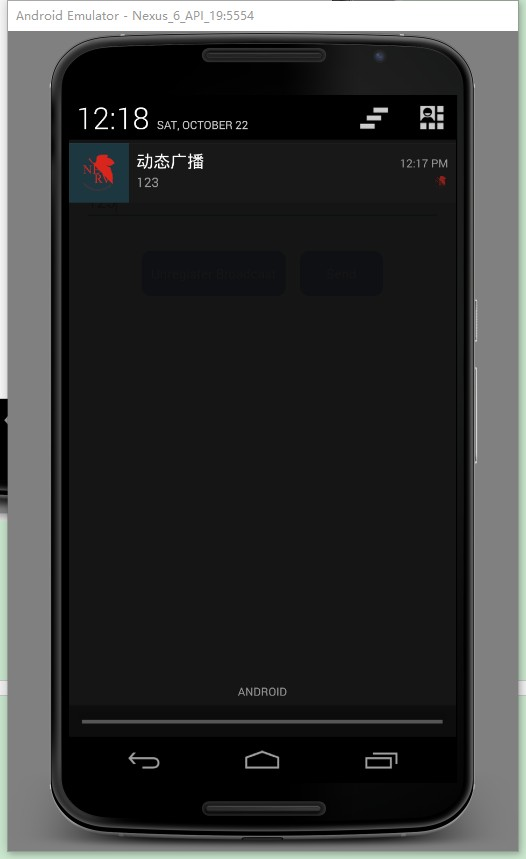
關於 Notification,不同版本的 API 顯示可能會有所不同。本次實驗中必須實現的部 分是標題、大圖標、內容、小圖標。其中標題為靜態廣播或動態廣播;大圖標與廣播發送的內容相關,為對應水果或者動態圖 dynamic;內容為水果名稱或動態廣播發送的內容; 小圖標與大圖標內容一樣。
圖片的使用方面請盡量使用 mipmap 目錄下的 image asset。否則在某些 API 中可能會 出現 Icon 過大的情況。
實現一個 Android 應用,實現靜態廣播、動態廣播兩種改變 Notification 內容的方法。 具體要求:
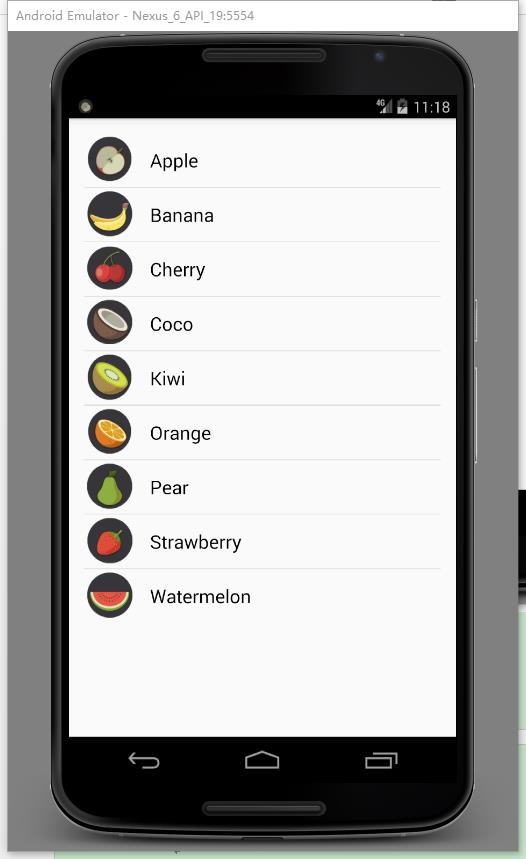
(1)該界面為應用啟動後看到的界面。

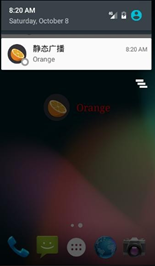
(2)點擊靜態注冊按鈕,跳轉至如下界面。

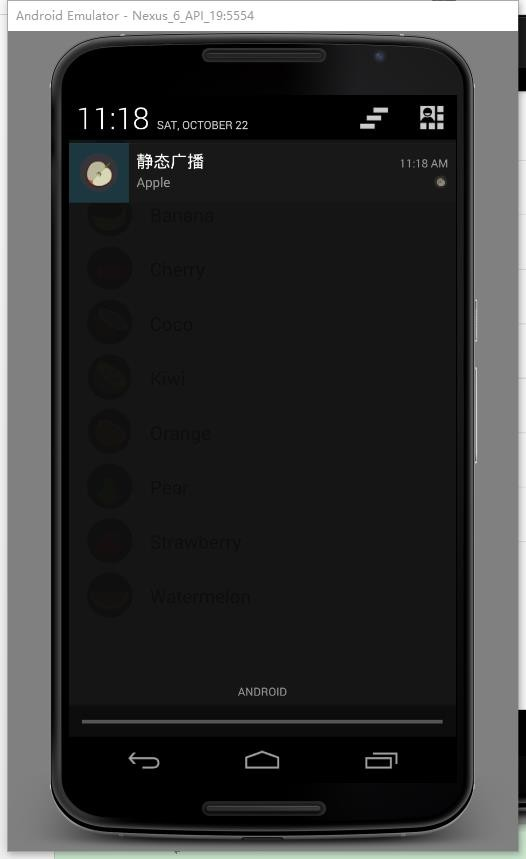
點擊表單項目。如 orange。會有對應通知產生,點擊通知返回主界面:
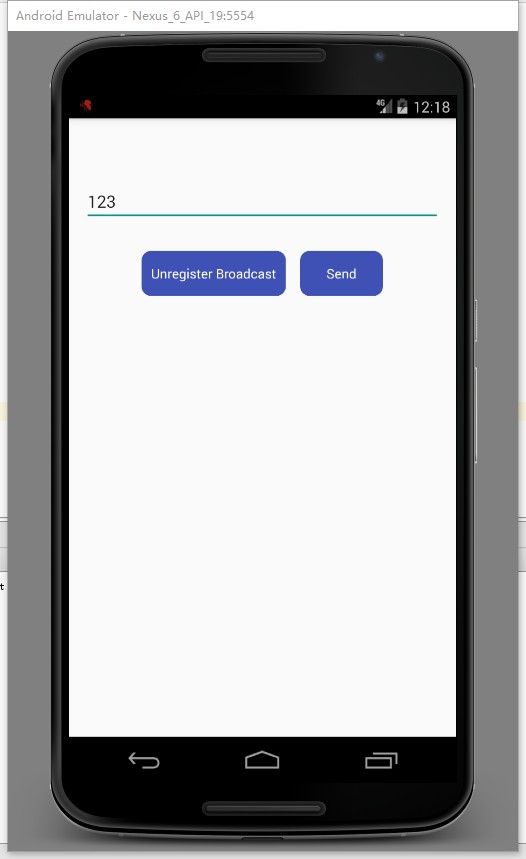
(3)點擊動態注冊按鈕,跳轉至如下界面。
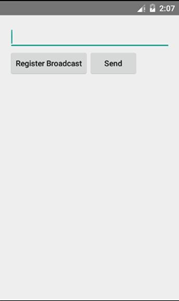
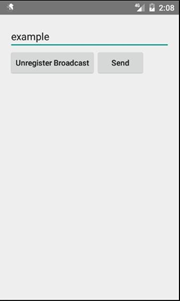
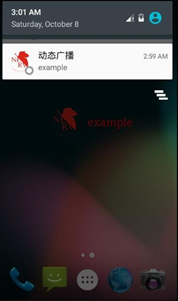
(未注冊廣播) (已注冊廣播) (已注冊後點擊發送)
實現以下功能:
a)可以編輯廣播的信息,點擊 Send 按鈕發送廣播。 b)設置一個按鈕進行廣播接收器的注冊與注銷。 c)廣播接收器若已被注冊,發送出的廣播信息會產生一個對應通知。 d)點擊 Notification 可以跳轉回主界面。
注:在設置按鈕內容的時候注意大小寫問題(使用android:textAllCaps="false"屬性)。
本實驗初始界面的 XML 布局是比較簡單的,包括初始界面的兩個按鈕、靜態 注冊布局中的 ListView 及其每一欄中的 ImageView TextView、動態布局中的 EditText Button。
在一個 xml 布局文件中寫好一個 ListView(這樣就創建了一個空的列表, 然後在.java 文件中再填充數據),在每一欄中的 ImageView TextView 使用線 性結構,分別用來存放圖片背景及聯系人的姓名。這裡和第三次實驗類似。 在 MainActivity.java 文件中,我們獲取到初始界面的兩個按鈕並使用 Intent 設置相應的點擊跳轉事件。
在 StaticActivity.java 文件中, 我們需要獲取到靜態注冊布局中的 ListView 並使用 Adapter 為這個 ListView 填充數據。我們需要獲取圖片和名稱 兩個參數,與實驗三不同的是每一欄中的圖片背景都不同。首先,我們創建一個Fruit 類,來存儲名稱數據,初始化一些變量,並使用 get 和 Set 方法來獲得或 者更改相應的數據。
接下來在 StaticActivity.java 文件中為每一項名稱數據創建一個對象,並 添加在 List 中,方便之後傳遞數據的操作。這裡我們通過獲取圖片命名將圖片 素材綁定在一個 int 類型的數組中:

首先構建好數據,把數據以 Map 鍵值對的形式添加到 list 中。然後創建Listview 的 Adapter。

在 ListView 單擊事件中,利用 bundle 和 intent 將圖片與文字內容發送出去:
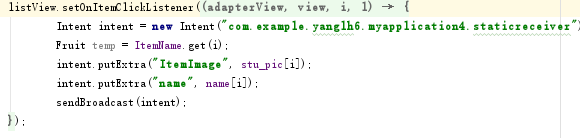
創建一個 Broadcast Receiver 類,並在 AndroidMainfest.xml 中進行注冊。 然後在靜態廣播類 StaticReceiver 中重寫 onReceive 方法,當接收到對應廣 播時進行數據 處理,產生通知。
這裡我們獲取到點擊產生的圖片和文字信息,並使用 Notification(可以 提供持久的通知,位於手機最上層的狀態通知欄中。用手指按下狀態欄,並從手 機上方向下滑動,就可以打開狀態欄查看提示消息)。設置好 Notification 涉 及的 3 個類: Notification.Builder(用於動態的設置)、 NotificationManager (負責將 Notification 在狀態顯示出來和取消)、Notification(設置 Notification 的相關屬性),然後使用 setContentIntent 與 PendingIntent 使得點擊 notification,就可以跳轉到我們 intent 中指定的 activity:
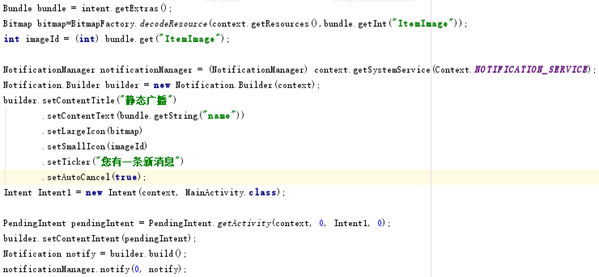
在這一部分中有兩個按鈕,Register Broadcast 按鈕再按下後將會變換按 鈕文本並實現一些按鈕事件,並且再次按下時的事件也會有所改變。受實驗三中 星星切換的啟發,這裡我們可以使用 tag,每個 View 都可以設置 tag,通過 tag 可以用來判斷該 View 現在的狀態。在初始化的時候,將 tag 設置為 0。然後在 相應位置完成注冊和注銷按鈕功能的設置:
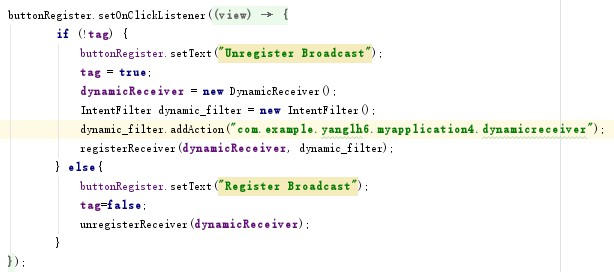
在 send 按鈕事件中,也要注意此時 Register Broadcast 按鈕的狀態問題, 所以也需要使用 tag 來進行判斷(設置 Send 按鈕點擊事件,如果廣播注冊,則 能夠點擊後發送廣播。發送方法與靜態注冊時一致,僅需修改廣播名稱即可。在 這裡我們也需獲取到 EditText 中獲取到的文本,作為傳遞的參數之一):

相應的,創建一個 Broadcast Receiver 類,並在 AndroidMainfest.xml 中進行 注冊。然後在動態廣播類中重寫 onReceive 方法,當接收到對應廣播時進行數 據處理,產生通知。
完成實驗~
此外:
在 Android 主界面中將 launchMode 設置為 singleInstance,使得點擊 Notification 後不會另外新建一個 MainActivity;
為了防止縮圖在 mipmap 裡新建 image assert,將所有使用的圖片都進行創 建。
StaticActivity.java
package com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Created by lenovo on 2016/10/21.
*/
public class StaticActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.static_layout);
final int[] stu_pic = {
R.mipmap.apple,
R.mipmap.banana,
R.mipmap.cherry,
R.mipmap.coco,
R.mipmap.kiwi,
R.mipmap.orange,
R.mipmap.pear,
R.mipmap.strawberry,
R.mipmap.watermelon};
final List<Map<String, Object>> data = new ArrayList<>();
/*生成動態數組,加入數據*/
final List<Fruit> ItemName = new ArrayList<Fruit>();
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Apple"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Banana"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Cherry"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Coco"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Kiwi"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Orange"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Pear"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Strawberry"));
ItemName.add(new Fruit("Watermelon"));
final String[] name = new String[ItemName.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < ItemName.size(); i++) {
String x = ItemName.get(i).getItemName();
name[i] = x;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ItemName.size(); i++) {
Map<String, Object> temp = new LinkedHashMap<>();
temp.put("ItemImage", stu_pic[i]);
temp.put("name", name[i]);
data.add(temp);
}
ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.staticStart);
final SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, data, R.layout.item,
new String[]{"ItemImage", "name"}, new int[]{R.id.ItemImage, R.id.ItemName});
listView.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
/* ListView單擊事件 */
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> adapterView, View view, int i, long l) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4.staticreceiver");
Fruit temp = ItemName.get(i);
intent.putExtra("ItemImage", stu_pic[i]);
intent.putExtra("name", name[i]);
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
});
}
}
StaticReciver.java
package com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class StaticReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (intent.getAction().equals("com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4.staticreceiver")) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
Bitmap bitmap=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(),bundle.getInt("ItemImage"));
int imageId = (int) bundle.get("ItemImage");
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(context);
builder.setContentTitle("靜態廣播")
.setContentText(bundle.getString("name"))
.setLargeIcon(bitmap)
.setSmallIcon(imageId)
.setTicker("您有一條新消息")
.setAutoCancel(true);
Intent Intent1 = new Intent(context, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0, Intent1, 0);
builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
Notification notify = builder.build();
notificationManager.notify(0, notify);
}
}
}
DynamicActivity.java
package com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
/**
* Created by lenovo on 2016/10/21.
*/
public class DynamicActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private boolean tag = false;
private DynamicReceiver dynamicReceiver = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.dynamic_layout);
final Button buttonRegister = (Button) findViewById(R.id.register);
Button buttonSend = (Button) findViewById(R.id.send);
buttonRegister.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if (!tag) {
buttonRegister.setText("Unregister Broadcast");
tag = true;
dynamicReceiver = new DynamicReceiver();
IntentFilter dynamic_filter = new IntentFilter();
dynamic_filter.addAction("com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4.dynamicreceiver");
registerReceiver(dynamicReceiver, dynamic_filter);
} else {
buttonRegister.setText("Register Broadcast");
tag = false;
unregisterReceiver(dynamicReceiver);
}
}
});
buttonSend.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if (!tag) {
} else {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4.dynamicreceiver");
String str1 = "";
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText);
str1 = editText.getText().toString();
intent.putExtra("ItemImage", R.mipmap.dynamic);
intent.putExtra("name", str1);
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}
});
}
}
DynamicReceiver.java
package com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class DynamicReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
public DynamicReceiver() {
}
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (intent.getAction().equals("com.example.yanglh6.myapplication4.dynamicreceiver")) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(), bundle.getInt("ItemImage"));
int imageId = (int) bundle.get("ItemImage");
NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(context);
builder.setContentTitle("動態廣播")
.setContentText(bundle.getString("name"))
.setLargeIcon(bitmap)
.setSmallIcon(imageId)
.setTicker("您有一條新消息")
.setAutoCancel(true);
Intent mIntent = new Intent(context, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0, mIntent, 0);
builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
Notification notify = builder.build();
notificationManager.notify(0, notify);
}
}
}

BraodcastReceiver(廣播接收器)是為了實現系統廣播而提供的一種組件, 它和事件處理機制類似,但是事件處理機制是程序組件級別的,而廣播事件處理 機制是系統級別的。比如,我們可以發出一種廣播來測試手機電量的變化,這時 候就可以定義一個 BraodcastReceiver 來接受廣播,當手機電量較低時提示用 戶。我們既可以用 Intent 來啟動一個組件,也可以用 sendBroadcast()方法發 起一個系統級別的事件廣播來傳遞消息。我們同樣可以在自己的應用程序中實現 BroadcastReceiver 來監聽和響應廣播的 Intent。
在程序中使用 BraodcastReceiver 是比較簡單的。首先要定義一個類繼承 BraodcastReceiver,並且覆蓋 onReceiver()方法來響應事件。然後注冊在程序 中 BraodcastReceiver。最後構建 Intent 對象調用 sendBroadcast()方法將廣播 發出。
包含靜態注冊方式和動態注冊方式:
(1)靜態注冊方式
靜態注冊方式是在 AndroidManifest.xml 的 application 裡面定義 receiver 並設置要接收的 action。靜態注冊方式的特點:不管改應用程序是否 處於活動狀態,都會進行監聽,比如某個程序時監聽內存的使用情況的,當 在手機上安裝好後,不管改應用程序是處於什麼狀態,都會執行改監聽方法中的內容。
(2)動態注冊方式
在 activity 裡面調用函數來注冊,和靜態的內容差不多。一個形參是 receiver, 另一個是 IntentFilter,其中裡面是要接收的 action。動態注冊方式特點:在 代碼中進行注冊後,當應用程序關閉後,就不再進行監聽。當然,也可手工調用unregisterReceiver()進行銷毀。
(3)BroadcastReceiver 的生命周期
一個BroadcastReceiver 對象只有在被調用onReceive(Context, Intent)的才有效的,當從該函數返回後,該對象就無效的了,結束生命周期。
(4)Notification
Notification 可以提供持久的通知,位於手機最上層的狀態通知欄中。用手指按下狀 態欄,並從手機上方向下滑動,就可以打開狀態欄查看提示消息。
通知一般通過NotificationManager服務發送一個Notification對象來完成通知,NotificationManager是一個重要的系統級服務,該對象位於應用程序的框架層中,應用程序可以通過它向系統發送全局的通知。使用通知的時候,需要創建一個Notification對象用來承載通知的內容,但是一般不會直接通過Notification的構造方法來得到對象,而是使用它的內部類Notification.Builder來實例化一個Builder對象,並設置通知的各項屬性,最後通過Notification.Builder.builder()方法得到一個Notification對象,當獲得這個Notification對象之後,就可以使用NotificationManager.notify()方法發送通知。
1、本實驗實驗環境:
操作系統 Windows 10
實驗軟件 Android Studio 2.2.1
虛擬設備:Nexus_6
API:19(其他高版本的API可能會將提示圖表顯示成一個白圓點,API19測試可正常顯示)
2、貼代碼的時候由於插入代碼框的大小問題,代碼格式不太嚴整,望見諒~
 OpenCV學習筆記(七)—— OpenCV for Android實時圖像處理
OpenCV學習筆記(七)—— OpenCV for Android實時圖像處理
OpenCV學習筆記(七)—— OpenCV for Android實時圖像處理 在上篇中我們已經實現了相機打開和實時圖像信息的獲取,那麼接下來我們可以嘗
 Android學習指南之三十四:Android定時器Timer的使用
Android學習指南之三十四:Android定時器Timer的使用
我們將JDK中自帶的Timer和TimerTask兩個類結合使用,可以實現執行
 Android中使用Notification實現寬視圖通知欄(Notification示例二),notification大視圖
Android中使用Notification實現寬視圖通知欄(Notification示例二),notification大視圖
Android中使用Notification實現寬視圖通知欄(Notification示例二),notification大視圖Notification是在你的應用常規界面
 Android學習指南之十七:Android對話框(Dialog)
Android學習指南之十七:Android對話框(Dialog)
上一節所講內容為Android菜單的知識,本節來講另一種界面元素,對