編輯:關於android開發
前言:
最近接觸藍牙開發,主要是通過藍牙連接獲取傳感器硬件設備的數據,並進行處理。
網上學習一番,現整理出一套比較標准的 操作流程代碼。
如果大家看得懂,將來只需要改下 硬件設備的MAC碼 和 改下對接收數據的處理 即可。 一切都是套路~~~
現在以一個小型項目需求來學習Android藍牙編程
需求: 通過藍牙獲取硬件數據,並顯示在一個隨數據即時變化的動態折線圖中。
實現思路:
(1) 配對藍牙設備
(2) 連接藍牙設備 ,根據MAC地址,代碼中修改
(3) 接收數據
(4) 處理數據 ,根據硬件廠商提供給你的數據轉換公式,在BluetoothService類中 修改
(5) 傳數據給折線圖,展現實時變化
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
藍牙知識了解:
(1)、MAC地址:每個設備都有全球唯一的,根據此MAC地址判斷藍牙設備
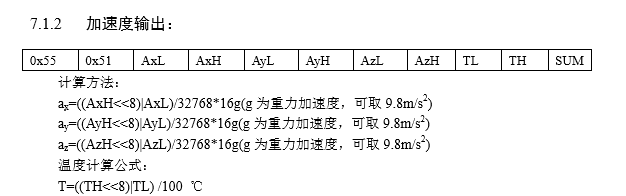
(2)、藍牙傳輸數據,通常一秒鐘會傳輸很多個包,每個包的數據情況如下:
此時,這個包有11個字節,0x55 是首碼,通常通過他來判斷一個包的開始
SUM是驗證碼,會有一套公式來計算,判斷當前包是不是一個有效的完整的包
中間的即是數據,然後硬件方面會給我們一套計算公式,可以以此獲取我們要的數據。
當然每個硬件的包的數據大小都是不同的,有的可能有21個字節,每個硬件的數據的計算方式也不想同
代碼實現:
一共就三部分,因為代碼篇幅可能較大,不適合一段段代碼講解,直接貼出整個代碼。所有的解釋都在注釋當中。
其中:
(1)、紅色部分是需要大家根據個人硬件情況進行修改的
(2)、紫色部分是根據個人數據情況添加刪除修改的。
一:MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private BluetoothService mBluetoothService; //自定義藍牙服務類
private BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter;
private String mConnectedDeviceName = null; //連接設備的名稱
//默認是1,因為程序啟動時首先會連接一個藍牙
private int current_pos = 1;
//hanlder消息標識 message.what
public static final int MESSAGE_STATE_CHANGE = 1; // 狀態改變
public static final int MESSAGE_READ = 2; // 讀取數據
public static final int MESSAGE_WRITE = 3; // 給硬件傳數據,暫不需要,看具體需求
public static final int MESSAGE_DEVICE_NAME = 4; // 設備名字
public static final int MESSAGE_TOAST = 5; // Toast
//傳感器 ,這裡默認同時需要和三個硬件連接,分別設置id 1,2,3進行區分,demo中實際只用到 MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN = 1
//可以根據情況自行添加刪除
public static final int MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP = 2;
public static final int MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN = 1;
public static final int MAGIKARE_SENSOR_CENTER = 3;
public static float[] m_receive_data_up; //傳感器的數據
public static float[] m_receive_data_down; //傳感器的數據 ,demo中我們只需要這一個,因為只有一個硬件設備,
public static float[] m_receive_data_center; //傳感器的數據
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//獲取藍牙適配器
mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
// 1、判斷設備是否支持藍牙功能
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null) {
//設備不支持藍牙功能
Toast.makeText(this, "當前設備不支持藍牙功能!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
// 2、打開設備的藍牙功能
if (!mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
boolean enable = mBluetoothAdapter.enable(); //返回值表示 是否成功打開了藍牙設備
if (enable) {
Toast.makeText(this, "打開藍牙功能成功!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(this, "打開藍牙功能失敗,請到'系統設置'中手動開啟藍牙功能!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
}
// 3、創建自定義藍牙服務對象
if (mBluetoothService == null) {
mBluetoothService = new BluetoothService(MainActivity.this, mHandler);
}
if (mBluetoothService != null) {
//根據MAC地址遠程獲取一個藍牙設備,這裡固定了,實際開發中,需要動態設置參數(MAC地址)
BluetoothDevice sensor_down = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice("20:16:06:15:78:76");
if (sensor_down != null) {
//成功獲取到遠程藍牙設備(傳感器),這裡默認只連接MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN = 1這個設備
mBluetoothService.connect(sensor_down, MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN);
}
}
}
private Handler mHandler = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what){
case MESSAGE_READ:
try {
String str=msg.getData().getString("index");
int index=Integer.valueOf(str);
switch (index)
{
//獲取到藍牙傳輸過來的數據
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP:
m_receive_data_up=msg.getData().getFloatArray("Data");
break;
//實際只用到這個case ,因為demo只連接了一個硬件設備
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN:
m_receive_data_down=msg.getData().getFloatArray("Data");
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_CENTER:
m_receive_data_center=msg.getData().getFloatArray("Data");
break;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
break;
case MESSAGE_STATE_CHANGE:
// 連接狀態
switch (msg.arg1) {
case BluetoothService.STATE_CONNECTED:
break;
case BluetoothService.STATE_CONNECTING:
break;
case BluetoothService.STATE_LISTEN:
break;
case BluetoothService.STATE_NONE:
break;
}
break;
case MESSAGE_DEVICE_NAME:
mConnectedDeviceName = msg.getData().getString("device_name");
Log.i("bluetooth","成功連接到:"+mConnectedDeviceName);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"成功連接到設備" + mConnectedDeviceName,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case MESSAGE_TOAST:
int index=msg.getData().getInt("device_id");
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),msg.getData().getString("toast"), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
//當失去設備或者不能連接設備時,重新連接
Log.d("Magikare","當失去設備或者不能連接設備時,重新連接");
//重新連接硬件設備
if(mBluetoothService!=null)
{
switch (index) {
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN:
//根據你的硬件的MAC地址寫參數,每一個硬件設備都有一個MAC地址,此方法是根據MAC地址得到藍牙設備
BluetoothDevice sensor_down = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice("20:16:06:15:78:76");
if (sensor_down != null)
mBluetoothService.connect(sensor_down, MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN);
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP:
BluetoothDevice sensor_up = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(""); //參數寫你這個設備的MAC碼
if (sensor_up != null)
mBluetoothService.connect(sensor_up, MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP);
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_CENTER:
BluetoothDevice center = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(""); //參數寫你這個設備的MAC碼
if (center != null)
mBluetoothService.connect(center, MAGIKARE_SENSOR_CENTER);
break;
}
}
break;
}
return false;
}
});
public synchronized void onResume() {
super.onResume();
if (mBluetoothService != null) {
if (mBluetoothService.getState() == BluetoothService.STATE_NONE) {
mBluetoothService.start();
}
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (mBluetoothService != null) mBluetoothService.stop();
}
// 硬件通過藍牙傳輸的byte類型已經轉換為float類型,並且通過handler傳輸到 m_receive_data_down[]數組中,一下操作是獲取這個數據,根據個人情況使用
//獲取角度
public float[] GetAngle(int index)
{
float[] angles=new float[3];
if(m_receive_data_up==null
||m_receive_data_down==null
)
{
return angles;
}
switch (index)
{
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN:
angles[0]=m_receive_data_down[6];
angles[1]=m_receive_data_down[7];
angles[2]=m_receive_data_down[8];
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP:
angles[0]=m_receive_data_up[6];
angles[1]=m_receive_data_up[7];
angles[2]=m_receive_data_up[8];
Log.d("安卓 Up 角度",angles[0]+","+angles[1]+","+angles[2]);
break;
}
return angles;
}
//獲取角速度
public static float[] GetAngleSpeed(int index)
{
float [] anglespeed=new float[3];
if(m_receive_data_down==null)
{
return anglespeed;
}
switch (index)
{
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN:
anglespeed[0]=m_receive_data_down[3];
anglespeed[1]=m_receive_data_down[4];
anglespeed[2]=m_receive_data_down[5];
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP:
anglespeed[0]=m_receive_data_up[3];
anglespeed[1]=m_receive_data_up[4];
anglespeed[2]=m_receive_data_up[5];
break;
}
return anglespeed;
}
public float[] GetQuaternion(int index)
{
float[] quaternion=new float[4];
if(m_receive_data_down==null)
{
return quaternion;
}
switch (index)
{
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_DOWN:
quaternion[0]=m_receive_data_down[23];
quaternion[1]=m_receive_data_down[24];
quaternion[2]=m_receive_data_down[25];
quaternion[3]=m_receive_data_down[26];
Log.i("saveinfo","m_receive_data_down23"+m_receive_data_down[23]);
Log.i("saveinfo","m_receive_data_down24"+m_receive_data_down[24]);
Log.i("saveinfo","m_receive_data_down25"+m_receive_data_down[25]);
Log.i("saveinfo","m_receive_data_down26"+m_receive_data_down[26]);
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_UP:
quaternion[0]=m_receive_data_up[23];
quaternion[1]=m_receive_data_up[24];
quaternion[2]=m_receive_data_up[25];
quaternion[3]=m_receive_data_up[26];
break;
case MAGIKARE_SENSOR_CENTER:
quaternion[0]=m_receive_data_center[23];
quaternion[1]=m_receive_data_center[24];
quaternion[2]=m_receive_data_center[25];
quaternion[3]=m_receive_data_center[26];
}
return quaternion;
}
}
二、BluetoothService
public class BluetoothService {
private static final UUID MY_UUID = UUID.fromString("00001101-0000-1000-8000-00805F9B34FB");
private Context context;
//藍牙適配器
private BluetoothAdapter mAdapter;
private Handler mHandler;
//當前傳感器設備的個數,即要開啟的線程個數,用於設置線程數組的大小
//這裡默認為1,因為我們目前只需要和一個傳感器連接, 比如:你要連接兩個硬件設備,那就設置值為2,這樣就會開啟兩個線程,分別去執行想要操作
public static final int SENSEOR_NUM=1;
private AcceptThread mAcceptThread;// 請求連接的監聽進程
private ConnectThread mConnectThread;// 連接一個設備的進程
public ConnectedThread[] mConnectedThread=new ConnectedThread[SENSEOR_NUM];// 已經連接之後的管理進程
private int mState;// 當前狀態
// 指明連接狀態的常量
public static final int STATE_NONE = 0; //沒有連接
public static final int STATE_LISTEN = 1; //等待連接
public static final int STATE_CONNECTING = 2; //正在連接
public static final int STATE_CONNECTED = 3; //已經連接
public BluetoothService(Context context, Handler mHandler) {
this.context = context;
this.mHandler = mHandler;
mAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();//獲取藍牙適配器
mState = STATE_NONE ; //當前連接狀態:未連接
}
// 參數 index 是 硬件設備的id ,隨便設的,目的在於當 同時連接多個硬件設備的時候,根據此id進行區分
public synchronized void connect(BluetoothDevice device, int index) {
//連接一個藍牙時,將該設備 的藍牙連接線程關閉,如果有的話
//demo 就只有一個硬件設備,默認該設備id 取值index=1;
if (mConnectedThread[index-1] != null) {
mConnectedThread[index-1].cancel();
mConnectedThread[index-1]=null;
}
mConnectThread=new ConnectThread(device,index);
mConnectThread.start();
setState(STATE_CONNECTING);
}
private class ConnectThread extends Thread{
private final BluetoothSocket mmSocket;
private final BluetoothDevice mmDevice;
private int index;
public ConnectThread(BluetoothDevice device,int index) {
mmDevice = device;
this.index=index;
BluetoothSocket tmp = null;
try {
tmp = device.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(MY_UUID);// Get a BluetoothSocket for a connection with the given BluetoothDevice
}
catch (IOException e) {}
mmSocket = tmp;
}
public void run() {
setName("ConnectThread");
//當連接成功,取消藍牙適配器搜索藍牙設備的操作,因為搜索操作非常耗時
mAdapter.cancelDiscovery();// Always cancel discovery because it will slow down a connection
try {
mmSocket.connect();// This is a blocking call and will only return on a successful connection or an exception
}
catch (IOException e) {
connectionFailed(this.index);
try {
mmSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e2) {}
BluetoothService.this.start();// 引用來說明要調用的是外部類的方法 run
return;
}
synchronized (BluetoothService.this) {// Reset the ConnectThread because we're done
mConnectThread = null;
}
connected(mmSocket, mmDevice,index);// Start the connected thread
}
public void cancel() {
try {
mmSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
class ConnectedThread extends Thread{
private BluetoothSocket mmSocket;
private InputStream mmInStream;
private OutputStream mmOutStream;
private int index;
private Queue<Byte> queueBuffer = new LinkedList<Byte>();
private byte[] packBuffer = new byte[11];
//構造方法
public ConnectedThread(BluetoothSocket socket,int index) {
mmSocket = socket;
InputStream tmpIn = null;
OutputStream tmpOut = null;
this.index=index;
// Get the BluetoothSocket input and output streams
try {
tmpIn = socket.getInputStream();
tmpOut = socket.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {}
mmInStream = tmpIn;
mmOutStream = tmpOut;
}
// 數組大小看你的數據需求,這裡存的是你處理藍牙傳輸來的字節數據之後實際要用到的數據
private float [] fData=new float[31];
@Override
public void run() {
byte[] tempInputBuffer = new byte[1024];
int acceptedLen = 0; //記錄每次讀取數據的數據長度
byte sHead;
long lLastTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //獲取開始時間
while(true){
try {
acceptedLen = mmInStream.read(tempInputBuffer);//返回接收的長度
//從緩沖區中讀取數據
for (int i = 0; i < acceptedLen; i++) {
queueBuffer.add(tempInputBuffer[i]);
}
// 這裡需要按個人硬件數據的情況自行修改了
// 如果你的硬件藍牙傳輸 一個包有11個字節,那queueBuffer.size()>=11
// 如果你的硬件藍牙傳輸 一個包有21個字節,那queueBuffer.size()>=21
while (queueBuffer.size()>=11){
//返回隊首並刪除,判斷隊首是不是0x55,如果不是,說明不是一個包的數據,跳過,
//注意這裡的0x55是你的包的首字節
if (queueBuffer.poll()!=0x55)
continue;
// 進入到這裡,說明得到一個包的數據了,然後就要根據個人硬件的數據情況,將byte類型的數據轉換為float類型的數據
sHead = queueBuffer.poll(); //返回隊首並刪除
// 現在得到的就是你數據部分了,如果有9位字節代表數據,j<9 ,如果有19位字節代表數據,j<19
//將字節數組存到packBuffer[]數據中,用於byte-->float數據的轉換
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
packBuffer[j] = queueBuffer.poll();
}
switch (sHead) {//
case 0x52://角速度
fData[3] = ((((short) packBuffer[1]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[0] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f * 2000;
fData[4] = ((((short) packBuffer[3]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[2] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f * 2000;
fData[5] = ((((short) packBuffer[5]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[4] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f * 2000;
fData[17] = ((((short) packBuffer[7]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[6] & 0xff)) / 100.0f;
break;
case 0x53://角度
fData[6] = ((((short) packBuffer[1]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[0] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f * 180;
fData[7] = ((((short) packBuffer[3]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[2] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f * 180;
fData[8] = ((((short) packBuffer[5]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[4] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f * 180;
fData[17] = ((((short) packBuffer[7]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[6] & 0xff)) / 100.0f;
break;
case 0x59://四元數
fData[23] = ((((short) packBuffer[1]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[0] & 0xff)) / 32768.0f;
fData[24] = ((((short) packBuffer[3]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[2] & 0xff))/32768.0f;
fData[25] = ((((short) packBuffer[5]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[4] & 0xff))/32768.0f;
fData[26] = ((((short) packBuffer[7]) << 8) | ((short) packBuffer[6] & 0xff))/32768.0f;
break;
}
}
long lTimeNow = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 獲取收據轉換之後的時間
// 如果數據處理後的時間 與 接收到數據的時間 的時間差>80 則發送消息傳輸數據,
// 這個時間需要看你硬件一秒鐘發送的包的個數
if (lTimeNow - lLastTime > 80) {
lLastTime = lTimeNow;
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MainActivity.MESSAGE_READ);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("index",String.valueOf(this.index));
bundle.putFloatArray("Data", fData);
msg.setData(bundle);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
connectionLost(this.index);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void cancel() {
try {
mmSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
//連接失敗
private void connectionFailed(int index) {
setState(STATE_LISTEN);
// Send a failure message back to the Activity
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MainActivity.MESSAGE_TOAST);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("toast", "未能連接設備"+index);
bundle.putInt("device_id",index);
msg.setData(bundle);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
// 連接丟失
private void connectionLost(int index) {
setState(STATE_LISTEN);
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MainActivity.MESSAGE_TOAST);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("toast", "設備丟失"+index);
bundle.putInt("device_id",index);
msg.setData(bundle);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
//用於 藍牙連接的Activity onResume()方法
public synchronized void start() {
// Cancel any thread attempting to make a connection
if (mConnectThread != null) {
mConnectThread.cancel();
mConnectThread = null;
}
if (mAcceptThread == null) {
mAcceptThread = new AcceptThread();
mAcceptThread.start();
}
setState(STATE_LISTEN);
}
public synchronized void connected(BluetoothSocket socket,BluetoothDevice device,int index) {
Log.d("MAGIKARE","連接到線程"+index);
// Cancel the thread that completed the connection
if (mConnectThread != null) {
mConnectThread.cancel();
mConnectThread = null;
}
// Cancel the accept thread because we only want to connect to one device
if (mAcceptThread != null) {
mAcceptThread.cancel();
mAcceptThread = null;
}
// Start the thread to manage the connection and perform transmissions
mConnectedThread[index-1] = new ConnectedThread(socket,index);
mConnectedThread[index-1].start();
// Send the name of the connected device back to the UI Activity
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MainActivity.MESSAGE_DEVICE_NAME);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("device_name", device.getName()+" "+index);
msg.setData(bundle);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
setState(STATE_CONNECTED);
}
private synchronized void setState(int state) {
mState = state;
// Give the new state to the Handler so the UI Activity can update
mHandler.obtainMessage(MainActivity.MESSAGE_STATE_CHANGE, state, -1).sendToTarget();
}
private class AcceptThread extends Thread {
// The local server socket
private final BluetoothServerSocket mmServerSocket;
//private int index;
public AcceptThread() {
BluetoothServerSocket tmp = null;
// this.index=index;
// Create a new listening server socket
try {
tmp = mAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord("BluetoothData", MY_UUID);
}
catch (IOException e) {}
mmServerSocket = tmp;
}
public void run() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
}
}).start();
}
public void cancel() {
try {
if(mmServerSocket!=null) {
mmServerSocket.close();
}
}
catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
public synchronized int getState() {
return mState;
}
public synchronized void stop() {
if (mConnectedThread != null) {
for(int i=0;i<mConnectedThread.length;i++)
{
mConnectedThread[i].cancel();
}
mConnectedThread = null;
}
if (mAcceptThread != null) {
mAcceptThread.cancel();
mAcceptThread = null;
}
setState(STATE_NONE);
}
}
三、自定義即時變化的折線圖:
public class MyView extends View {
/*http://www.cnblogs.com/aibuli/p/950c34f2bc0d02cbd290dd6a8339d42a.html*/
//坐標軸原點的位置
private int xPoint=60;
private int yPoint=260;
//刻度長度
private int xScale=8; //8個單位構成一個刻度
private int yScale=40;
//x與y坐標軸的長度
private int xLength=580;
private int yLength=480;
private int MaxDataSize=xLength/xScale; //橫坐標 最多可繪制的點
private List<Float> data=new ArrayList<Float>(); //存放 縱坐標 所描繪的點
private String[] yLabel=new String[yLength/yScale]; //Y軸的刻度上顯示字的集合
private Handler mh=new Handler(){
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
if(msg.what==0){ //判斷接受消息類型
MyView.this.invalidate(); //刷新View
}
};
};
public MyView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
for (int i = 0; i <yLabel.length; i++) {
yLabel[i]=(i+1)+"M/s";
}
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){ //在線程中不斷往集合中增加數據
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(data.size()>MaxDataSize){ //判斷集合的長度是否大於最大繪制長度
data.remove(0); //刪除頭數據
}
// 這裡得到藍牙設備得到的數據
float[] floats = MainActivity.GetAngleSpeed(1);
data.add(floats[0]);
mh.sendEmptyMessage(0); //發送空消息通知刷新
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Paint paint=new Paint();
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setColor(Color.RED);
//繪制Y軸
canvas.drawLine(xPoint, yPoint-yLength, xPoint, yPoint, paint);
//繪制Y軸左右兩邊的箭頭
canvas.drawLine(xPoint, yPoint-yLength, xPoint-3,yPoint-yLength+6, paint);
canvas.drawLine(xPoint, yPoint-yLength, xPoint+3,yPoint-yLength+6, paint);
//Y軸上的刻度與文字
for (int i = 0; i * yScale< yLength; i++) {
canvas.drawLine(xPoint, yPoint-i*yScale, xPoint+5, yPoint-i*yScale, paint); //刻度
canvas.drawText(yLabel[i], xPoint-50, yPoint-i*yScale, paint);//文字
}
//X軸
canvas.drawLine(xPoint, yPoint, xPoint+xLength, yPoint, paint);
//如果集合中有數據
if(data.size()>1){
for (int i = 1; i < data.size(); i++) { //依次取出數據進行繪制
canvas.drawLine(xPoint+(i-1)*xScale, yPoint-data.get(i-1)*yScale, xPoint+i*xScale, yPoint-data.get(i)*yScale, paint);
}
}
}
}
相關知識:淺談Bluetooth藍牙開發
有問題歡迎留言交流!
 MultiTouch————多點觸控,伸縮圖片,變換圖片位置,
MultiTouch————多點觸控,伸縮圖片,變換圖片位置,
MultiTouch————多點觸控,伸縮圖片,變換圖片位置,前言:當今的手機都支持多點觸控功能(可以進行圖片伸縮,變換位置),但是我們程序員要怎樣結合硬件去實現這個功能
 Android 塗鴉最佳實踐
Android 塗鴉最佳實踐
Android 塗鴉最佳實踐 Android中實現手勢畫圖一般都兩種方式,一是直接在View上繪制,而是使用SurfaceView。 兩者還是有一些差別的。簡介下。
 Android應用開發教程之六:ListView詳解
Android應用開發教程之六:ListView詳解
ListView是Android軟件開發中非常重要組件之一,基本上是個軟件基本都會使用ListView ,今天我通過一個demo來教大家怎麼樣使用L
 Linux內核系列—操作系統開發之HelloWorld,linuxhelloworld
Linux內核系列—操作系統開發之HelloWorld,linuxhelloworld
Linux內核系列—操作系統開發之HelloWorld,linuxhelloworld org 07c00h ;偽指令,告訴編譯器程序會被加載到7c00處