編輯:關於android開發
Fragment是activity的界面中的一部分或一種行為。可以把多個Fragment組合到一個activity中來創建一個多界面並且可以在多個activity中重用一個Fragment。可以把Fragment任務模塊化的一段activity,它具有自己的生命周期,接收它自己的事件,並可以在activity運行時被添加或刪除。
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wuyudong/p/5893804.html,轉載請注明源地址。
Fragment不能獨立存在,它必須嵌入到activity中,而且Fragment的生命周期直接受所在的activity的影響。例如:當activity暫停時,他擁有的所有的Fragment都暫停了,當activity銷毀時,他擁有的所有Fragment都被銷毀。然而,當activity運行時(在onResume()之後,onPause()之前),可以單獨地操作每個Fragment,比如添加或刪除它們。當中執行上述針對Fragment的事務時,可以將事務添加到一個棧中,這個棧被activity管理,棧中的每一條都是一個Fragment的一次事務。有了這個棧,就可以反向執行Fragment的事務,這樣就可以在Fragment級支持“返回”鍵(向後導航)。
當向activity中添加一個Fragment時,它須置於ViewGroup控件中,並且需定義Fragment自己的界面。可以在layout.xml布局文件中聲明Fragment,元素為:<fragment>;也可以在代碼中創建Fragment,然後把它加入到ViewGroup控件中。然而,Fragment不一定非要放在activity的界面中,它可以隱藏在後台為activity工作。
實戰一下
項目布局文件代碼:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment1"
android:name="com.wuyudong.fragment.Fragment1"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" >
</fragment>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragment2"
android:name="com.wuyudong.fragment.Fragment2"
android:layout_width="0dip"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1" >
</fragment>
</LinearLayout>
接著在layout文件夾下新建兩個fragment.xml文件
fragment1.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#0000ff"
android:orientation="vertical" >
</LinearLayout>
fragment2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ff00"
android:orientation="vertical" >
</LinearLayout>
接著在項目源代碼文件夾下新建兩個java文件
Fragment1.java
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
/**
* 當fragment被創建的時候,調用的方法,返回當前fragment顯示的內容
*/
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment1, null);
}
}
Fragment2.java
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
/**
* 當fragment被創建的時候,調用的方法,返回當前fragment顯示的內容
*/
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, null);
}
}
運行項目
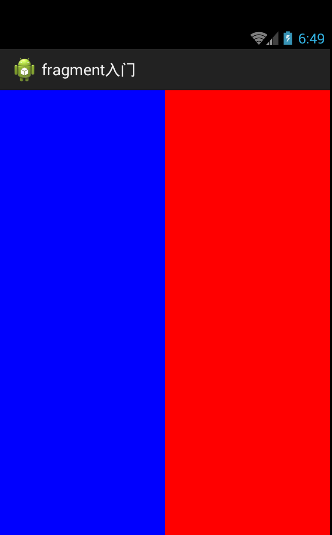
接下來實現動態創建Fragment
在剛才的項目的基礎上,新建一個項目。刪除原來activity_main.xml代碼中的fragment1與fragment2代碼段,其他的代碼不變
接下來在MainActivity中添加下面的代碼:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// 1、判斷當前手機的朝向
int width = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int height = getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
Fragment1 fragment1 = new Fragment1();
Fragment2 fragment2 = new Fragment2();
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction ft = fm.beginTransaction();
if (width > height) {
// 水平方向
ft.replace(android.R.id.content, fragment1);
} else {
ft.replace(android.R.id.content, fragment2);
}
ft.commit();
}
}
上面的代碼實現了當手機不同朝向的時候,顯示的不同的fragment
 Android 代碼動態改變View的屬性
Android 代碼動態改變View的屬性
Android 代碼動態改變View的屬性 設置Android View的長寬和位置我們平時都會在Layout的XML中定義,那麼什麼時候需要動態在代碼中設置View
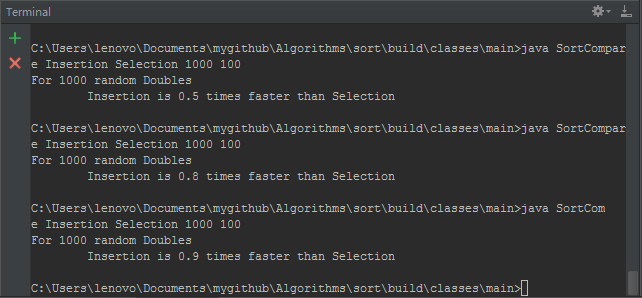 算法—比較兩種排序算法:選擇排序和插入排序,排序算法
算法—比較兩種排序算法:選擇排序和插入排序,排序算法
算法—比較兩種排序算法:選擇排序和插入排序,排序算法現在我們已經實現了兩種排序算法,我們很自然地想知道選擇排序和插入排序哪種更快。這裡我們第一次用實踐說明我們解決這個問題
 Android 在C代碼中調用logcat,androidlogcat
Android 在C代碼中調用logcat,androidlogcat
Android 在C代碼中調用logcat,androidlogcat本文給《Android java傳遞int類型數組給C》中添加C代碼中調用logcat的功能 And
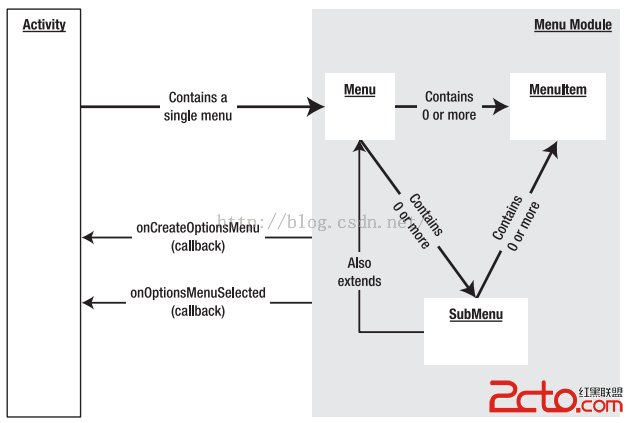 Android開發之Menu:OptionMenu(選項菜單)、ContextMenu(上下文菜單)、SubMenu(子菜單)
Android開發之Menu:OptionMenu(選項菜單)、ContextMenu(上下文菜單)、SubMenu(子菜單)
Android開發之Menu:OptionMenu(選項菜單)、ContextMenu(上下文菜單)、SubMenu(子菜單) 菜單的概念,現在已經很普及了。 W