編輯:關於android開發
public class UserSqliteOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final int versionNo = 1;
public UserSqliteOpenHelper(Context context) {
super(context, "user.db", null, versionNo);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
Log. i("" , "sqlite onCreate" );
db.execSQL( "create table user (id Integer primary key autoincrement, name varchar(20))");
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
Log. i("" , "sqlite onUpgrade" );
db.execSQL( "insert into user(name) values(?)", new Object[]{"version"+versionNo });
}
}
從代碼中我們可以看出,UserSqliteOpenHelper重寫了SQLiteOpenHelper的onCreate和onUpgrade兩個方法 說明: onCreate:數據庫被建立的時候調用,一般執行創建數據庫語句 onUpgrade:當版本號(versionNo)增加時執行此方法,一般用於對表結構的更改、添加或刪除 *第一次創建數據庫時執行onCreate,不執行onUpgrade;更改版本號之後,執行onUpgrade,不執行onCreate 操作說明: 當 private static final int versionNo = 1 時結果如下
 當 private static final int versionNo = 2 時結果如下
當 private static final int versionNo = 2 時結果如下
 2.創建dao文件對sqlite數據庫進行操作
2.創建dao文件對sqlite數據庫進行操作
public class UserDao {
private UserSqliteOpenHelper tsoh;
public UserDao(Context context) {
tsoh = new UserSqliteOpenHelper(context);
}
public void insert(String name){
SQLiteDatabase db = tsoh.getWritableDatabase();
db. execSQL("insert into user(name) values(?)", new Object[]{name});
db.close();
}
public boolean find(String name){
SQLiteDatabase db = tsoh.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery( "select * from user where name = ?", new String[]{name});
boolean result = cursor.moveToNext();
cursor.close();
db.close();
return result;
}
public void update(String name, String newName){
SQLiteDatabase db = tsoh.getWritableDatabase();
db. execSQL("update user set name = ? where name = ?", new Object[]{newName, name});
db.close();
}
public void delete(String name){
SQLiteDatabase db = tsoh.getWritableDatabase();
db. execSQL("delete from user where name = ?", new Object[]{name});
db.close();
}
public List<User> findAll(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
SQLiteDatabase db = tsoh.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery( "select * from user", null);
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
int id = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("id" ));
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name" ));
User user = new User(id, name);
users.add(user);
}
cursor.close();
db.close();
return users;
}
}
user類的定義
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User() {
super();
}
public User(int id, String name) {
super();
this. id = id;
this. name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this. id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this. name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "info:"+ id+ ","+ name;
}
}
代碼很簡單,不做過多解釋。需要注意的是,每次在操作數據庫的時候記得將cursor和database關閉,釋放資源。項目級的代碼應該使用try catch finally來操作,這裡為了演示簡單操作。這裡還是沿用了拼接字符串的方式執行sql語句,其實android還為我們提供封裝好了的API(最終還是將參數拼接成字符串,不過對於調用者來說新的API簡單明了,用戶不用考慮單引號雙引號的麻煩了),這裡不做過多介紹。 3.調用代碼
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout. activity_main);
UserDao testDao = new UserDao( this);
testDao.insert( "name1");
testDao.insert( "name2");
testDao.insert( "name3");
testDao.update( "name1", "name4");
boolean result = testDao.find("name2" );
testDao.delete( "name3");
List<User> users = testDao.findAll();
for(User user:users){
Log. i("MainActivity" , user.toString());
}
}
基本操作介紹完畢。 二:推薦sqlite界面工具:sqlite expert professional 前兩天有個同事問我,sqlite中Integer能存儲最大的數值是多少,當時我也不知道,於是就當場測試了一下,測試的結果:-9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 也就是-2^63到2^63-1 這就是我通過 sqlite工具實驗的結果


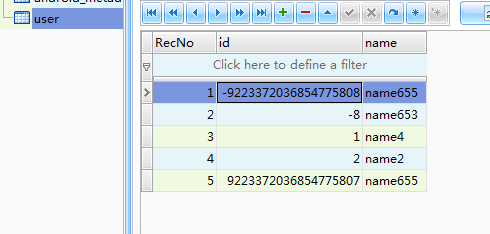
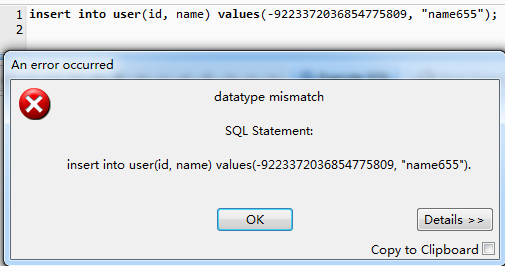
INTEGER: 用來存儲一個整數,根據大小可以使用1,2,3,4,6,8個字節來存儲(網絡抄錄,從我實驗的結果上來看上限是8個字節的整數)
 Linux內核系列—操作系統開發之HelloWorld,linuxhelloworld
Linux內核系列—操作系統開發之HelloWorld,linuxhelloworld
Linux內核系列—操作系統開發之HelloWorld,linuxhelloworld org 07c00h ;偽指令,告訴編譯器程序會被加載到7c00處
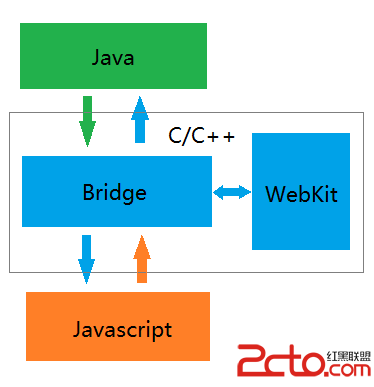 React-Native系列Android——Native與Javascript通信原理(二)
React-Native系列Android——Native與Javascript通信原理(二)
React-Native系列Android——Native與Javascript通信原理(二) 前一篇博客分析了Native端向Javascript端通信的全流程,這
 硅谷社交15--群詳情,硅谷社交15--
硅谷社交15--群詳情,硅谷社交15--
硅谷社交15--群詳情,硅谷社交15-- 1)頁面布局 <?xml version=1.0 encoding=utf-8?> <LinearLayou
 【React Native開發】React Native For Android環境配置以及第一個實例
【React Native開發】React Native For Android環境配置以及第一個實例
【React Native開發】React Native For Android環境配置以及第一個實例 (一)前言 FaceBook早期開源發布了React Nati