編輯:關於android開發
我們知道在android中,安裝應用是由PackageManager來管理的,但是我們發現PackageManager是一個抽象類,他的installPackage方法也沒有具體的實現。那在安裝過程中是怎麼執行的吶?
查看代碼可以知道ApplicationPackageManager是直接繼承自PackageManager的,所以最終代碼會調用ApplicationPackageManager下的installPackage(Uri packageURI, IPackageInstallObserver observer, int flags,String installerPackageName),而在installPackage裡面又調用了installCommon。
installCommon的實現如下:
private void installCommon(Uri packageURI,
PackageInstallObserver observer, int flags, String installerPackageName,
VerificationParams verificationParams, ContainerEncryptionParams encryptionParams) {
if (!"file".equals(packageURI.getScheme())) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Only file:// URIs are supported");
}
if (encryptionParams != null) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("ContainerEncryptionParams not supported");
}
final String originPath = packageURI.getPath();
try {
mPM.installPackage(originPath, observer.getBinder(), flags, installerPackageName,
verificationParams, null);
} catch (RemoteException ignored) {
}
}
可以看到在installCommon最終調用了mPm.installPackage那mPm又是什麼?可以發現mPM是一個IPackageManager,他在是ApplicationPackageManager的構造函數中傳入的,那是什麼時候調用構造函數的吶?在ContextImpl中調用getPackageManager時會進行調用,傳入的pm在是ActivityThread中創建的。
@Override
public PackageManager getPackageManager() {
if (mPackageManager != null) {
return mPackageManager;
}
IPackageManager pm = ActivityThread.getPackageManager();
if (pm != null) {
// Doesn't matter if we make more than one instance.
return (mPackageManager = new ApplicationPackageManager(this, pm));
}
return null;
}
ActivityThread.getPackageManager()的代碼如下:
public static IPackageManager getPackageManager() {
if (sPackageManager != null) {
//Slog.v("PackageManager", "returning cur default = " + sPackageManager);
return sPackageManager;
}
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("package");
//Slog.v("PackageManager", "default service binder = " + b);
sPackageManager = IPackageManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
//Slog.v("PackageManager", "default service = " + sPackageManager);
return sPackageManager;
}
從上面可以看到IPackageManager是進程間通信的客戶端, 首先是IPackageManager是通過IPackageManager.aidl文件生成,同時生成了存根類IPackageManager.Stub,代理類:IPackageManager.Stub.Proxy,他是IBinder類型,那遠端又是誰吶?遠端就是PackageManagerService,PackageManagerService繼承自IPackageManager.Stub,因此最終的調用都是通過aidl由PackageManagerService執行。因此我們主要來看看PackageManagerService中的執行過程。
主要有兩種方式:
1:系統啟動後掃描安裝,會調用PackageManagerService的scanPackageLI函數,
2:應用市場安裝,應用市場下載後會默認調用PackageManagerService的intallPackage函數,改函數最終也會調用到scanPackageLI,因此只需要分享第二種
我們可以大致看看代碼調用的過程,流程圖如下:
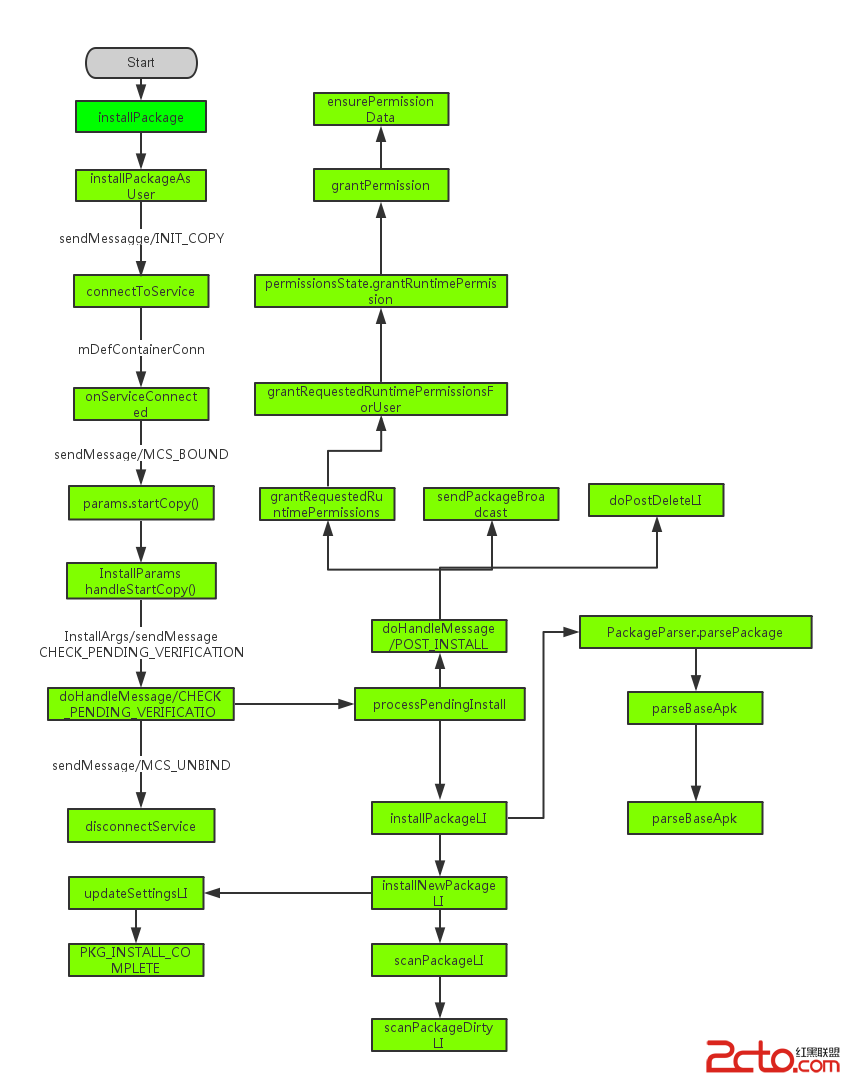
由於PackageManager最終是由PackageManagerService來執行的
@Override
public void installPackage(String originPath, IPackageInstallObserver2 observer,
int installFlags, String installerPackageName, VerificationParams verificationParams,
String packageAbiOverride) {
installPackageAsUser(originPath, observer, installFlags, installerPackageName,
verificationParams, packageAbiOverride, UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
主要傳遞了6個參數:
1,originPath,安裝包的位置,他必須是file類型活在content的URI類型。傳遞這裡的是一個string類型。
2,observer,是一個IPackageInstallObserver類型,回調通知調用者安裝完成
3,installFlags,他的值是INSTALL_FORWARD_LOCK,INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING,INSTALL_ALLOW_TEST三個中的一個,INSTALL_FORWARD_LOCK表示安裝過程中是否鎖定,INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING表示是否替換安裝包,INSTALL_ALLOW_TEST是否測試安裝包,如果有改標志,manifest必須配置android:testOnly
4,installerPackageName,安裝包包名
5,verificationParams,代表驗證參數用於驗證包安裝。
6,packageAbiOverride,一般傳null
該函數調用了installPackageAsUser函數,installPackageAsUser函數如下:
@Override
public void installPackageAsUser(String originPath, IPackageInstallObserver2 observer,
int installFlags, String installerPackageName, VerificationParams verificationParams,
String packageAbiOverride, int userId) {
mContext.enforceCallingOrSelfPermission(android.Manifest.permission.INSTALL_PACKAGES, null);
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
enforceCrossUserPermission(callingUid, userId, true, true, "installPackageAsUser");
if (isUserRestricted(userId, UserManager.DISALLOW_INSTALL_APPS)) {
try {
if (observer != null) {
observer.onPackageInstalled("", INSTALL_FAILED_USER_RESTRICTED, null, null);
}
} catch (RemoteException re) {
}
return;
}
if ((callingUid == Process.SHELL_UID) || (callingUid == Process.ROOT_UID)) {
installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_FROM_ADB;
} else {
// Caller holds INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, so we're less strict
// about installerPackageName.
installFlags &= ~PackageManager.INSTALL_FROM_ADB;
installFlags &= ~PackageManager.INSTALL_ALL_USERS;
}
UserHandle user;
if ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_ALL_USERS) != 0) {
user = UserHandle.ALL;
} else {
user = new UserHandle(userId);
}
// Only system components can circumvent runtime permissions when installing.
if ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_GRANT_RUNTIME_PERMISSIONS) != 0
&& mContext.checkCallingOrSelfPermission(Manifest.permission
.INSTALL_GRANT_RUNTIME_PERMISSIONS) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_DENIED) {
throw new SecurityException("You need the "
+ "android.permission.INSTALL_GRANT_RUNTIME_PERMISSIONS permission "
+ "to use the PackageManager.INSTALL_GRANT_RUNTIME_PERMISSIONS flag");
}
verificationParams.setInstallerUid(callingUid);
final File originFile = new File(originPath);
final OriginInfo origin = OriginInfo.fromUntrustedFile(originFile);
final Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(INIT_COPY);
msg.obj = new InstallParams(origin, null, observer, installFlags, installerPackageName,
null, verificationParams, user, packageAbiOverride, null);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
該函數主要做了以下操作,第一強制獲取權限,如果被拒絕則退出執行,接著設置installFlags參數,最後一步發送了一個what為INIT_COPY的message,參數為InstallParams,記住該參數,後面還會多次用到,看what的名稱INIT_COPY,看起來是表達初始化並且拷貝,那是不是真是這樣吶?我們去看看這個操作,這個操做是PackageHandler來執行的,PackageHandler繼續字Handler,那我們來具體看看執行代碼:
case INIT_COPY: {
HandlerParams params = (HandlerParams) msg.obj;
int idx = mPendingInstalls.size();
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "init_copy idx=" + idx + ": " + params);
// If a bind was already initiated we dont really
// need to do anything. The pending install
// will be processed later on.
if (!mBound) {
// If this is the only one pending we might
// have to bind to the service again.
if (!connectToService()) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to bind to media container service");
params.serviceError();
return;
} else {
// Once we bind to the service, the first
// pending request will be processed.
mPendingInstalls.add(idx, params);
}
} else {
mPendingInstalls.add(idx, params);
// Already bound to the service. Just make
// sure we trigger off processing the first request.
if (idx == 0) {
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_BOUND);
}
}
break;
}
可以看到首先取出參數params,這個params就是之前傳入的InstallParams,接著獲取等待安裝隊列的內容個數,由於初始mBound為false,因此會進入該判斷,之後執行了connectToService函數,如個返回false表示連接失敗,直接行使params的serviceError函數來結束當前執行,如果為這將paramsa添加到mPendingInstalls的最後一個位置,connectToService連接又是什麼吶?當前代碼也沒有執行任何與copy有段的操作啊?那我們去看看connectToService究竟干了什麼?
private boolean connectToService() {
if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG, "Trying to bind to" +
" DefaultContainerService");
Intent service = new Intent().setComponent(DEFAULT_CONTAINER_COMPONENT);
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT);
if (mContext.bindServiceAsUser(service, mDefContainerConn,
Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE, UserHandle.OWNER)) {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
mBound = true;
return true;
}
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
return false;
}
可以看到這裡bind到了一個service,service的名稱是DefaultContainerService,這又是個什麼service吶?並且在綁定之前先設置該進程的優先級為THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT,執行完成後再次設置為THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND,這裡我們也沒有看到有任何copy的操作,那copy操作究竟在什麼地方,綁定的這個服務又是什麼?我們來看看綁定的connection參數:
class DefaultContainerConnection implements ServiceConnection {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG, "onServiceConnected");
IMediaContainerService imcs =
IMediaContainerService.Stub.asInterface(service);
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(MCS_BOUND, imcs));
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG, "onServiceDisconnected");
}
}
可以看到當綁定成功後將一個service轉換成了一個IMediaContainerService,這個又是什麼吶?這個就是在onServiceConnected回調函數中根據參數傳進來的IMediaContainerService.Stub的對象引用創建一個遠程代理對象。以後PackageManagerService服務通過該代理對象訪問DefaultContainerService服務。DefaultContainerService是一個應用服務,具體負責實現APK等相關資源文件在內部或外部存儲器上的存儲工作,DefaultContainerService服務中提供了一個IMediaContainerService.Stub樁對象。
接下來我們看到這裡又發送了一個what為MCS_BOUND的message,參數為之前獲得的IMediaContainerService,這裡也沒有任何copy操作,那我們繼續跟進看看該what執行了什麼?
case MCS_BOUND: {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "mcs_bound");
if (msg.obj != null) {
mContainerService = (IMediaContainerService) msg.obj;
}
if (mContainerService == null) {
if (!mBound) {
// Something seriously wrong since we are not bound and we are not
// waiting for connection. Bail out.
Slog.e(TAG, "Cannot bind to media container service");
for (HandlerParams params : mPendingInstalls) {
// Indicate service bind error
params.serviceError();
}
mPendingInstalls.clear();
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Waiting to connect to media container service");
}
} else if (mPendingInstalls.size() > 0) {
HandlerParams params = mPendingInstalls.get(0);
if (params != null) {
if (params.startCopy()) {
// We are done... look for more work or to
// go idle.
if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG,
"Checking for more work or unbind...");
// Delete pending install
if (mPendingInstalls.size() > 0) {
mPendingInstalls.remove(0);
}
if (mPendingInstalls.size() == 0) {
if (mBound) {
if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG,
"Posting delayed MCS_UNBIND");
removeMessages(MCS_UNBIND);
Message ubmsg = obtainMessage(MCS_UNBIND);
// Unbind after a little delay, to avoid
// continual thrashing.
sendMessageDelayed(ubmsg, 10000);
}
} else {
// There are more pending requests in queue.
// Just post MCS_BOUND message to trigger processing
// of next pending install.
if (DEBUG_SD_INSTALL) Log.i(TAG,
"Posting MCS_BOUND for next work");
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_BOUND);
}
}
}
} else {
// Should never happen ideally.
Slog.w(TAG, "Empty queue");
}
break;
}
可以看到這裡首先獲取了傳入的參數,如果參數為空,則調用HandlerParams的serviceError,並且清空mPendingInstalls列表,否則獲取到等待安裝列表中的第一個對象,就是我們最初始添加進的InstallParams,這裡我們看到調用了InstallParams的startCopy函數,執行完成後移除該參數,如果等待安裝列表為空且當前綁定狀態為true,則發一個what為MCS_UNBIND的解綁操作,否則就繼續執行該操作,將等待列表中的一個一個執行,MCS_UNBIND與MCS_RECONNECT,這就不詳細說了,MCS_UNBIND主要是解綁之前的鏈接,MCS_RECONNECT是重新綁定鏈接,那我們繼續看看startCopy函數:
final boolean startCopy() {
boolean res;
try {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "startCopy " + mUser + ": " + this);
if (++mRetries > MAX_RETRIES) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to invoke remote methods on default container service. Giving up");
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_GIVE_UP);
handleServiceError();
return false;
} else {
handleStartCopy();
res = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.i(TAG, "Posting install MCS_RECONNECT");
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_RECONNECT);
res = false;
}
handleReturnCode();
return res;
}
這裡會重試多次,如果超過最大次數則發送一個what為MCS_GIVE_UP的message表示安裝失敗,否則調用handleStartCopy,我們來看看handleStartCopy,這裡調用的是InstallParams的handleStartCopy函數:
/*
* Invoke remote method to get package information and install
* location values. Override install location based on default
* policy if needed and then create install arguments based
* on the install location.
*/
public void handleStartCopy() throws RemoteException {
int ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED;
// If we're already staged, we've firmly committed to an install location
if (origin.staged) {
if (origin.file != null) {
installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_INTERNAL;
installFlags &= ~PackageManager.INSTALL_EXTERNAL;
} else if (origin.cid != null) {
installFlags |= PackageManager.INSTALL_EXTERNAL;
installFlags &= ~PackageManager.INSTALL_INTERNAL;
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid stage location");
}
}
final boolean onSd = (installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_EXTERNAL) != 0;
final boolean onInt = (installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_INTERNAL) != 0;
PackageInfoLite pkgLite = null;
if (onInt && onSd) {
// Check if both bits are set.
Slog.w(TAG, "Conflicting flags specified for installing on both internal and external");
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_INSTALL_LOCATION;
} else {
pkgLite = mContainerService.getMinimalPackageInfo(origin.resolvedPath, installFlags,
packageAbiOverride);
/*
* If we have too little free space, try to free cache
* before giving up.
*/
if (!origin.staged && pkgLite.recommendedInstallLocation
== PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE) {
// TODO: focus freeing disk space on the target device
final StorageManager storage = StorageManager.from(mContext);
final long lowThreshold = storage.getStorageLowBytes(
Environment.getDataDirectory());
final long sizeBytes = mContainerService.calculateInstalledSize(
origin.resolvedPath, isForwardLocked(), packageAbiOverride);
if (mInstaller.freeCache(null, sizeBytes + lowThreshold) >= 0) {
pkgLite = mContainerService.getMinimalPackageInfo(origin.resolvedPath,
installFlags, packageAbiOverride);
}
/*
* The cache free must have deleted the file we
* downloaded to install.
*
* TODO: fix the "freeCache" call to not delete
* the file we care about.
*/
if (pkgLite.recommendedInstallLocation
== PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INVALID_URI) {
pkgLite.recommendedInstallLocation
= PackageHelper.RECOMMEND_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE;
}
}
}
// 設置ret
final InstallArgs args = createInstallArgs(this);
mArgs = args;
if (ret == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
/*
* ADB installs appear as UserHandle.USER_ALL, and can only be performed by
* UserHandle.USER_OWNER, so use the package verifier for UserHandle.USER_OWNER.
*/
int userIdentifier = getUser().getIdentifier();
if (userIdentifier == UserHandle.USER_ALL
&& ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_FROM_ADB) != 0)) {
userIdentifier = UserHandle.USER_OWNER;
}
/*
* Determine if we have any installed package verifiers. If we
* do, then we'll defer to them to verify the packages.
*/
final int requiredUid = mRequiredVerifierPackage == null ? -1
: getPackageUid(mRequiredVerifierPackage, userIdentifier);
if (!origin.existing && requiredUid != -1
&& isVerificationEnabled(userIdentifier, installFlags)) {
final Intent verification = new Intent(
Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_NEEDS_VERIFICATION);
verification.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
verification.setDataAndType(Uri.fromFile(new File(origin.resolvedPath)),
PACKAGE_MIME_TYPE);
verification.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_GRANT_READ_URI_PERMISSION);
final List receivers = queryIntentReceivers(verification,
PACKAGE_MIME_TYPE, PackageManager.GET_DISABLED_COMPONENTS,
0 /* TODO: Which userId? */);
if (DEBUG_VERIFY) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Found " + receivers.size() + " verifiers for intent "
+ verification.toString() + " with " + pkgLite.verifiers.length
+ " optional verifiers");
}
final int verificationId = mPendingVerificationToken++;
verification.putExtra(PackageManager.EXTRA_VERIFICATION_ID, verificationId);、
.......
設置verification的參數
final PackageVerificationState verificationState = new PackageVerificationState(
requiredUid, args);
mPendingVerification.append(verificationId, verificationState);
final List sufficientVerifiers = matchVerifiers(pkgLite,
receivers, verificationState);
// Apps installed for "all" users use the device owner to verify the app
UserHandle verifierUser = getUser();
if (verifierUser == UserHandle.ALL) {
verifierUser = UserHandle.OWNER;
}
/*
* If any sufficient verifiers were listed in the package
* manifest, attempt to ask them.
*/
if (sufficientVerifiers != null) {
final int N = sufficientVerifiers.size();
if (N == 0) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Additional verifiers required, but none installed.");
ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_VERIFICATION_FAILURE;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
final ComponentName verifierComponent = sufficientVerifiers.get(i);
final Intent sufficientIntent = new Intent(verification);
sufficientIntent.setComponent(verifierComponent);
mContext.sendBroadcastAsUser(sufficientIntent, verifierUser);
}
}
}
final ComponentName requiredVerifierComponent = matchComponentForVerifier(
mRequiredVerifierPackage, receivers);
if (ret == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED
&& mRequiredVerifierPackage != null) {
/*
* Send the intent to the required verification agent,
* but only start the verification timeout after the
* target BroadcastReceivers have run.
*/
verification.setComponent(requiredVerifierComponent);
mContext.sendOrderedBroadcastAsUser(verification, verifierUser,
android.Manifest.permission.PACKAGE_VERIFICATION_AGENT,
new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
final Message msg = mHandler
.obtainMessage(CHECK_PENDING_VERIFICATION);
msg.arg1 = verificationId;
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, getVerificationTimeout());
}
}, null, 0, null, null);
/*
* We don't want the copy to proceed until verification
* succeeds, so null out this field.
*/
mArgs = null;
}
} else {
/*
* No package verification is enabled, so immediately start
* the remote call to initiate copy using temporary file.
*/
ret = args.copyApk(mContainerService, true);
}
}
mRet = ret;
}
@Override
void handleReturnCode() {
// If mArgs is null, then MCS couldn't be reached. When it
// reconnects, it will try again to install. At that point, this
// will succeed.
if (mArgs != null) {
processPendingInstall(mArgs, mRet);
}
}
首先設置installFlags參數,之後設置ret參數與verification參數,之後根據參數創建了InstallArgs參數,根據參數這裡實際返回的是AsecInstallArgs類型,如果該包需要被驗證,則發送一個廣播進行包驗證,否則直接拷貝apk,廣播的onReceive中發送了一個what為CHECK_PENDING_VERIFICATION的message,參數為verificationId,handleReturnCode中直接調用了processPendingInstall來進行安裝處理,我們先來看看CHECK_PENDING_VERIFICATION的處理,這裡最終也會調用到processPendingInstall。
case CHECK_PENDING_VERIFICATION: {
final int verificationId = msg.arg1;
final PackageVerificationState state = mPendingVerification.get(verificationId);
if ((state != null) && !state.timeoutExtended()) {
final InstallArgs args = state.getInstallArgs();
final Uri originUri = Uri.fromFile(args.origin.resolvedFile);
Slog.i(TAG, "Verification timed out for " + originUri);
mPendingVerification.remove(verificationId);
int ret = PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_VERIFICATION_FAILURE;
if (getDefaultVerificationResponse() == PackageManager.VERIFICATION_ALLOW) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Continuing with installation of " + originUri);
state.setVerifierResponse(Binder.getCallingUid(),
PackageManager.VERIFICATION_ALLOW_WITHOUT_SUFFICIENT);
broadcastPackageVerified(verificationId, originUri,
PackageManager.VERIFICATION_ALLOW,
state.getInstallArgs().getUser());
try {
ret = args.copyApk(mContainerService, true);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Could not contact the ContainerService");
}
} else {
broadcastPackageVerified(verificationId, originUri,
PackageManager.VERIFICATION_REJECT,
state.getInstallArgs().getUser());
}
processPendingInstall(args, ret);
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MCS_UNBIND);
}
break;
}
驗證完成後發送一個驗證完成的廣播,之後調用InstallArgs的copyApk函數拷貝包,這裡的InstallArgs是什麼類型吶?就是前面創建的AsecInstallArgs類型,因此執行的是AsecInstallArgs的copyApk函數,執行完成後調用processPendingInstall。copyApk主要是拷貝包到指定的目錄下。這裡就不詳述了。接著看看processPendingInstall函數:
private void processPendingInstall(final InstallArgs args, final int currentStatus) {
// Queue up an async operation since the package installation may take a little while.
mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
mHandler.removeCallbacks(this);
// Result object to be returned
PackageInstalledInfo res = new PackageInstalledInfo();
res.returnCode = currentStatus;
res.uid = -1;
res.pkg = null;
res.removedInfo = new PackageRemovedInfo();
if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
args.doPreInstall(res.returnCode);
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
installPackageLI(args, res);
}
args.doPostInstall(res.returnCode, res.uid);
}
// A restore should be performed at this point if (a) the install
// succeeded, (b) the operation is not an update, and (c) the new
// package has not opted out of backup participation.
final boolean update = res.removedInfo.removedPackage != null;
final int flags = (res.pkg == null) ? 0 : res.pkg.applicationInfo.flags;
boolean doRestore = !update
&& ((flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_ALLOW_BACKUP) != 0);
// Set up the post-install work request bookkeeping. This will be used
// and cleaned up by the post-install event handling regardless of whether
// there's a restore pass performed. Token values are >= 1.
int token;
if (mNextInstallToken < 0) mNextInstallToken = 1;
token = mNextInstallToken++;
PostInstallData data = new PostInstallData(args, res);
mRunningInstalls.put(token, data);
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "+ starting restore round-trip " + token);
if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED && doRestore) {
// Pass responsibility to the Backup Manager. It will perform a
// restore if appropriate, then pass responsibility back to the
// Package Manager to run the post-install observer callbacks
// and broadcasts.
IBackupManager bm = IBackupManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.BACKUP_SERVICE));
if (bm != null) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "token " + token
+ " to BM for possible restore");
try {
if (bm.isBackupServiceActive(UserHandle.USER_OWNER)) {
bm.restoreAtInstall(res.pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, token);
} else {
doRestore = false;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// can't happen; the backup manager is local
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Exception trying to enqueue restore", e);
doRestore = false;
}
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "Backup Manager not found!");
doRestore = false;
}
}
if (!doRestore) {
// No restore possible, or the Backup Manager was mysteriously not
// available -- just fire the post-install work request directly.
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "No restore - queue post-install for " + token);
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(POST_INSTALL, token, 0);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
});
}
這裡post一個Runnable來執行內部的邏輯,主要做了如下操作:
1,鎖定後安裝包,通過調用installPackageLI來進行的
2,接下來都是執行備份操作,備份是通過BackupManagerService來完成的。備份完成後,通過發送what為POST_INSTALL的message來繼續處理
我們先來看看installPackageLI的執行過程:
private void installPackageLI(InstallArgs args, PackageInstalledInfo res) {
//...... 初始化參數....
PackageParser pp = new PackageParser();
pp.setSeparateProcesses(mSeparateProcesses);
pp.setDisplayMetrics(mMetrics);
final PackageParser.Package pkg;
try {
pkg = pp.parsePackage(tmpPackageFile, parseFlags);
} catch (PackageParserException e) {
res.setError("Failed parse during installPackageLI", e);
return;
}
.................
String oldCodePath = null;
boolean systemApp = false;
synchronized (mPackages) {
// Check if installing already existing package
if ((installFlags & PackageManager.INSTALL_REPLACE_EXISTING) != 0) {
String oldName = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkgName);
if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null
&& pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(oldName)
&& mPackages.containsKey(oldName)) {
// This package is derived from an original package,
// and this device has been updating from that original
// name. We must continue using the original name, so
// rename the new package here.
pkg.setPackageName(oldName);
pkgName = pkg.packageName;
replace = true;
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Replacing existing renamed package: oldName="
+ oldName + " pkgName=" + pkgName);
} else if (mPackages.containsKey(pkgName)) {
// This package, under its official name, already exists
// on the device; we should replace it.
replace = true;
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Replace existing pacakge: " + pkgName);
}
// Prevent apps opting out from runtime permissions
if (replace) {
PackageParser.Package oldPackage = mPackages.get(pkgName);
final int oldTargetSdk = oldPackage.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion;
final int newTargetSdk = pkg.applicationInfo.targetSdkVersion;
if (oldTargetSdk > Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP_MR1
&& newTargetSdk <= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP_MR1) {
res.setError(PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_PERMISSION_MODEL_DOWNGRADE,
"Package " + pkg.packageName + " new target SDK " + newTargetSdk
+ " doesn't support runtime permissions but the old"
+ " target SDK " + oldTargetSdk + " does.");
return;
}
}
}
...............
// Check whether the newly-scanned package wants to define an already-defined perm
int N = pkg.permissions.size();
for (int i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {
PackageParser.Permission perm = pkg.permissions.get(i);
BasePermission bp = mSettings.mPermissions.get(perm.info.name);
if (bp != null) {
// If the defining package is signed with our cert, it's okay. This
// also includes the "updating the same package" case, of course.
// "updating same package" could also involve key-rotation.
final boolean sigsOk;
if (bp.sourcePackage.equals(pkg.packageName)
&& (bp.packageSetting instanceof PackageSetting)
&& (shouldCheckUpgradeKeySetLP((PackageSetting) bp.packageSetting,
scanFlags))) {
sigsOk = checkUpgradeKeySetLP((PackageSetting) bp.packageSetting, pkg);
} else {
sigsOk = compareSignatures(bp.packageSetting.signatures.mSignatures,
pkg.mSignatures) == PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH;
}
if (!sigsOk) {
// If the owning package is the system itself, we log but allow
// install to proceed; we fail the install on all other permission
// redefinitions.
if (!bp.sourcePackage.equals("android")) {
res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_DUPLICATE_PERMISSION, "Package "
+ pkg.packageName + " attempting to redeclare permission "
+ perm.info.name + " already owned by " + bp.sourcePackage);
res.origPermission = perm.info.name;
res.origPackage = bp.sourcePackage;
return;
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName
+ " attempting to redeclare system permission "
+ perm.info.name + "; ignoring new declaration");
pkg.permissions.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}
if (systemApp && onExternal) {
// Disable updates to system apps on sdcard
res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_INSTALL_LOCATION,
"Cannot install updates to system apps on sdcard");
return;
}
if (args.move != null) {
// We did an in-place move, so dex is ready to roll
scanFlags |= SCAN_NO_DEX;
scanFlags |= SCAN_MOVE;
synchronized (mPackages) {
final PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.get(pkgName);
if (ps == null) {
res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR,
"Missing settings for moved package " + pkgName);
}
// We moved the entire application as-is, so bring over the
// previously derived ABI information.
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi = ps.primaryCpuAbiString;
pkg.applicationInfo.secondaryCpuAbi = ps.secondaryCpuAbiString;
}
} else if (!forwardLocked && !pkg.applicationInfo.isExternalAsec()) {
// Enable SCAN_NO_DEX flag to skip dexopt at a later stage
scanFlags |= SCAN_NO_DEX;
try {
derivePackageAbi(pkg, new File(pkg.codePath), args.abiOverride,
true /* extract libs */);
} catch (PackageManagerException pme) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Error deriving application ABI", pme);
res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_INTERNAL_ERROR, "Error deriving application ABI");
return;
}
// Run dexopt before old package gets removed, to minimize time when app is unavailable
int result = mPackageDexOptimizer
.performDexOpt(pkg, null /* instruction sets */, false /* forceDex */,
false /* defer */, false /* inclDependencies */);
if (result == PackageDexOptimizer.DEX_OPT_FAILED) {
res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_DEXOPT, "Dexopt failed for " + pkg.codePath);
return;
}
}
if (!args.doRename(res.returnCode, pkg, oldCodePath)) {
res.setError(INSTALL_FAILED_INSUFFICIENT_STORAGE, "Failed rename");
return;
}
startIntentFilterVerifications(args.user.getIdentifier(), replace, pkg);
if (replace) {
replacePackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags | SCAN_REPLACING, args.user,
installerPackageName, volumeUuid, res);
} else {
installNewPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags | SCAN_DELETE_DATA_ON_FAILURES,
args.user, installerPackageName, volumeUuid, res);
}
synchronized (mPackages) {
final PackageSetting ps = mSettings.mPackages.get(pkgName);
if (ps != null) {
res.newUsers = ps.queryInstalledUsers(sUserManager.getUserIds(), true);
}
}
}
主要是執行了以下操作:
1,初始一些參數 2,調用PackageParser來解析包 3,判斷是否是當前已有應用升級還是全新安裝,這兩個都需要堅持簽名
4,檢測權限,檢測新掃描的權限是否是已經定義的權限 5,根據條件是否進行derivePackageAbi操作,這個操作的注釋為Derive
the ABI of a non-system package located at {@code scanFile}. This
information is derived purely on the basis of the contents of {@code
scanFile} and{@code cpuAbiOverride}. 6,開始intent filter驗證7,根據是否是已有應用進行升級還是全新安裝執行不同的操作
這裡重要的主要是第2點和第7點,但是由於這裡主要講述android過程,因此對第2點不做詳述,之後來詳解該內容,我們假設這裡是全新安裝著調用installNewPackageLI:
/*
* Install a non-existing package.
*/
private void installNewPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg, int parseFlags, int scanFlags,
UserHandle user, String installerPackageName, String volumeUuid,
PackageInstalledInfo res) {
// Remember this for later, in case we need to rollback this install
String pkgName = pkg.packageName;
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "installNewPackageLI: " + pkg);
final boolean dataDirExists = Environment
.getDataUserPackageDirectory(volumeUuid, UserHandle.USER_OWNER, pkgName).exists();
...........
try {
PackageParser.Package newPackage = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,
System.currentTimeMillis(), user);
updateSettingsLI(newPackage, installerPackageName, volumeUuid, null, null, res, user);
// delete the partially installed application. the data directory will have to be
// restored if it was already existing
if (res.returnCode != PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
// remove package from internal structures. Note that we want deletePackageX to
// delete the package data and cache directories that it created in
// scanPackageLocked, unless those directories existed before we even tried to
// install.
deletePackageLI(pkgName, UserHandle.ALL, false, null, null,
dataDirExists ? PackageManager.DELETE_KEEP_DATA : 0,
res.removedInfo, true);
}
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
res.setError("Package couldn't be installed in " + pkg.codePath, e);
}
}
主要是調用了scanPackageLI來進行包的安裝,之後調用了updateSettingsLI,updateSettingsLI主要是更新了包的PackageSetting對象,主要更新了權限信息與安裝完成信息。這裡我們繼續查看scanPackageLI的執行:
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(PackageParser.Package pkg, int parseFlags,
int scanFlags, long currentTime, UserHandle user) throws PackageManagerException {
boolean success = false;
try {
final PackageParser.Package res = scanPackageDirtyLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,
currentTime, user);
success = true;
return res;
} finally {
if (!success && (scanFlags & SCAN_DELETE_DATA_ON_FAILURES) != 0) {
removeDataDirsLI(pkg.volumeUuid, pkg.packageName);
}
}
}
scanPackageLI主要調用了scanPackageDirtyLI,如果調用失敗則調用removeDataDirsLI來移除安裝信息,scanPackageDirtyLI的代碼如下:
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageDirtyLI(PackageParser.Package pkg, int parseFlags,
int scanFlags, long currentTime, UserHandle user) throws PackageManagerException {
final File scanFile = new File(pkg.codePath);
............
if (pkg.packageName.equals("android")) {
.............
}
................
// Initialize package source and resource directories
File destCodeFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.getCodePath());
File destResourceFile = new File(pkg.applicationInfo.getResourcePath());
SharedUserSetting suid = null;
PackageSetting pkgSetting = null;
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
// Check if we are renaming from an original package name.
PackageSetting origPackage = null;
String realName = null;
if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null) {
// This package may need to be renamed to a previously
// installed name. Let's check on that...
final String renamed = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkg.mRealPackage);
if (pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(renamed)) {
// This package had originally been installed as the
// original name, and we have already taken care of
// transitioning to the new one. Just update the new
// one to continue using the old name.
realName = pkg.mRealPackage;
if (!pkg.packageName.equals(renamed)) {
// Callers into this function may have already taken
// care of renaming the package; only do it here if
// it is not already done.
pkg.setPackageName(renamed);
}
} else {
for (int i=pkg.mOriginalPackages.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
if ((origPackage = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(
pkg.mOriginalPackages.get(i))) != null) {
// We do have the package already installed under its
// original name... should we use it?
if (!verifyPackageUpdateLPr(origPackage, pkg)) {
// New package is not compatible with original.
origPackage = null;
continue;
} else if (origPackage.sharedUser != null) {
// Make sure uid is compatible between packages.
if (!origPackage.sharedUser.name.equals(pkg.mSharedUserId)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to migrate data from " + origPackage.name
+ " to " + pkg.packageName + ": old uid "
+ origPackage.sharedUser.name
+ " differs from " + pkg.mSharedUserId);
origPackage = null;
continue;
}
} else {
if (DEBUG_UPGRADE) Log.v(TAG, "Renaming new package "
+ pkg.packageName + " to old name " + origPackage.name);
}
break;
}
}
}
}
.........
// Just create the setting, don't add it yet. For already existing packages
// the PkgSetting exists already and doesn't have to be created.
pkgSetting = mSettings.getPackageLPw(pkg, origPackage, realName, suid, destCodeFile,
destResourceFile, pkg.applicationInfo.nativeLibraryRootDir,
pkg.applicationInfo.primaryCpuAbi,
pkg.applicationInfo.secondaryCpuAbi,
pkg.applicationInfo.flags, pkg.applicationInfo.privateFlags,
user, false);
...............
if ((parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
// Check all shared libraries and map to their actual file path.
// We only do this here for apps not on a system dir, because those
// are the only ones that can fail an install due to this. We
// will take care of the system apps by updating all of their
// library paths after the scan is done.
updateSharedLibrariesLPw(pkg, null);
}
pkg.applicationInfo.uid = pkgSetting.appId;
pkg.mExtras = pkgSetting;
if (shouldCheckUpgradeKeySetLP(pkgSetting, scanFlags)) {
if (checkUpgradeKeySetLP(pkgSetting, pkg)) {
// We just determined the app is signed correctly, so bring
// over the latest parsed certs.
pkgSetting.signatures.mSignatures = pkg.mSignatures;
} else {
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
throw new PackageManagerException(INSTALL_FAILED_UPDATE_INCOMPATIBLE,
"Package " + pkg.packageName + " upgrade keys do not match the "
+ "previously installed version");
} else {
pkgSetting.signatures.mSignatures = pkg.mSignatures;
String msg = "System package " + pkg.packageName
+ " signature changed; retaining data.";
reportSettingsProblem(Log.WARN, msg);
}
}
} else {
try {
verifySignaturesLP(pkgSetting, pkg);
// We just determined the app is signed correctly, so bring
// over the latest parsed certs.
pkgSetting.signatures.mSignatures = pkg.mSignatures;
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
}
}
// Verify that this new package doesn't have any content providers
// that conflict with existing packages. Only do this if the
// package isn't already installed, since we don't want to break
// things that are installed.
if ((scanFlags & SCAN_NEW_INSTALL) != 0) {
final int N = pkg.providers.size();
int i;
for (i=0; i
這裡主要做了以下操作:
1,檢測路徑代碼路徑是否存在不存在拋出異常
2,設置Package的applicationInfo信息
3,設置ResolverActivity信息
4,如果是系統程序則更改ResolverActivity信息
5,如果我們只安裝以及存在的包,則判斷他的PackageSetting信息,如果路徑不一致,測拋出異常
6,初始化包的代碼與資源目錄
7,檢測我們是否需要重命名一個原始包
8,檢測所有共享的libraries並且映射到真實的路徑
9,如個是升級包則檢測簽名,如果新安裝包則驗證簽名
10,檢測新包不含有與已經存在包沖突的provider
11,檢測當前包對於其他包所擁有的權限
12,創建包data目錄,並且重新調整uid,調用createDataDirsLI進行包的安裝
13,設置包的本地的Library路徑
14,創建包的用戶數據,調用createUserData
15,對包進行opt操作,調用performDexOpt,最終調用的還是Install的dexopt函數
16,如果是已存在的包,則調用ActivityManager殺死該進程
17,解析包的provider,並添加到ProviderIntentResolver,解析包的service,並添加到ServiceIntentResolver,解析包的receiver,並添加到ActivityIntentResolver,解析包的activity,並添加到ActivityIntentResolver,解析包的權利組與權限。最後解析instrumentation這個是測試用的,上述的解析主要是為了在應用中調用getPackageManager().resolveActivity等方法使用的。
上面主要是調用了createDataDirsLI來進行包的安裝:
private int createDataDirsLI(String volumeUuid, String packageName, int uid, String seinfo) {
int[] users = sUserManager.getUserIds();
int res = mInstaller.install(volumeUuid, packageName, uid, uid, seinfo);
if (res < 0) {
return res;
}
for (int user : users) {
if (user != 0) {
res = mInstaller.createUserData(volumeUuid, packageName,
UserHandle.getUid(user, uid), user, seinfo);
if (res < 0) {
return res;
}
}
}
return res;
}
這裡最終調用了mInstaller的intall函數,mInstaller是一個InstallerConnection,InstallerConnection裡面是通過輸入輸出流與一個LocalSocket進行安裝操作的,所以這裡最終調用的InstallerConnection的intall函數,執行完成後如果user不為空,創建用戶數據。
包的安裝過程到此就結束了,我們再回頭看看POST_INSTALL進行了什麼操作?
case POST_INSTALL: {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "Handling post-install for " + msg.arg1);
PostInstallData data = mRunningInstalls.get(msg.arg1);
mRunningInstalls.delete(msg.arg1);
boolean deleteOld = false;
if (data != null) {
InstallArgs args = data.args;
PackageInstalledInfo res = data.res;
if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
final String packageName = res.pkg.applicationInfo.packageName;
res.removedInfo.sendBroadcast(false, true, false);
Bundle extras = new Bundle(1);
extras.putInt(Intent.EXTRA_UID, res.uid);
// Now that we successfully installed the package, grant runtime
// permissions if requested before broadcasting the install.
if ((args.installFlags
& PackageManager.INSTALL_GRANT_RUNTIME_PERMISSIONS) != 0) {
grantRequestedRuntimePermissions(res.pkg, args.user.getIdentifier(),
args.installGrantPermissions);
}
// Determine the set of users who are adding this
// package for the first time vs. those who are seeing
// an update.
int[] firstUsers;
int[] updateUsers = new int[0];
if (res.origUsers == null || res.origUsers.length == 0) {
firstUsers = res.newUsers;
} else {
firstUsers = new int[0];
for (int i=0; i AVAILABLE");
}
int[] uidArray = new int[] { res.pkg.applicationInfo.uid };
ArrayList pkgList = new ArrayList(1);
pkgList.add(packageName);
sendResourcesChangedBroadcast(true, true,
pkgList,uidArray, null);
}
}
if (res.removedInfo.args != null) {
// Remove the replaced package's older resources safely now
deleteOld = true;
}
// If this app is a browser and it's newly-installed for some
// users, clear any default-browser state in those users
if (firstUsers.length > 0) {
// the app's nature doesn't depend on the user, so we can just
// check its browser nature in any user and generalize.
if (packageIsBrowser(packageName, firstUsers[0])) {
synchronized (mPackages) {
for (int userId : firstUsers) {
mSettings.setDefaultBrowserPackageNameLPw(null, userId);
}
}
}
}
// Log current value of "unknown sources" setting
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.UNKNOWN_SOURCES_ENABLED,
getUnknownSourcesSettings());
}
// Force a gc to clear up things
Runtime.getRuntime().gc();
// We delete after a gc for applications on sdcard.
if (deleteOld) {
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
res.removedInfo.args.doPostDeleteLI(true);
}
}
if (args.observer != null) {
try {
Bundle extras = extrasForInstallResult(res);
args.observer.onPackageInstalled(res.name, res.returnCode,
res.returnMsg, extras);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Observer no longer exists.");
}
}
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, "Bogus post-install token " + msg.arg1);
}
} break;
萬裡長征最後一步,這裡主要先將安裝信息從安裝列表中移除,這也是在之前processPendingInstall中添加的,包安裝成功之後,在發送安裝成功廣播之前先獲取運行時權限,獲取權限後發送ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED廣播,如果是更新包再發送ACTION_PACKAGE_REPLACED和ACTION_MY_PACKAGE_REPLACED廣播來通知其他應用,安裝的廣播發送完成後發送一個資源更改的廣播通知其他應用,如果該應用是一個浏覽器,則先清除默認的浏覽器設置,重新檢查浏覽器設置。
上訴幾步調用完成之後,強制調用gc,來觸發jvm進行垃圾回收操作。gc調用後刪除舊的安裝信息,如果初始傳入的IPackageInstallObserver2不為空,這回調調用方安裝包安裝完成。
總結到此大致分析了整個安裝過程,還有很多細節可以分析,比如parsePackage,之後可以在進行解析,整篇文字可能有理解錯誤的地方,望指出。
 Android自定義View入門(一),androidview
Android自定義View入門(一),androidview
Android自定義View入門(一),androidview最近在寫一個關於音樂播放的應用,寫到播放界面UI時,就想自己實現的一個播放界面。那麼如何實現自定義View呢
 Android SharedPreferences存儲,sharedpreferences
Android SharedPreferences存儲,sharedpreferences
Android SharedPreferences存儲,sharedpreferences一 概念 SharedPreferences存儲方式是Android中存儲輕
 Android開發學習——打電話應用,android開發打電話
Android開發學習——打電話應用,android開發打電話
Android開發學習——打電話應用,android開發打電話 打電話應用 system/app/phone.apk 這個是打電話應用,這個Jav
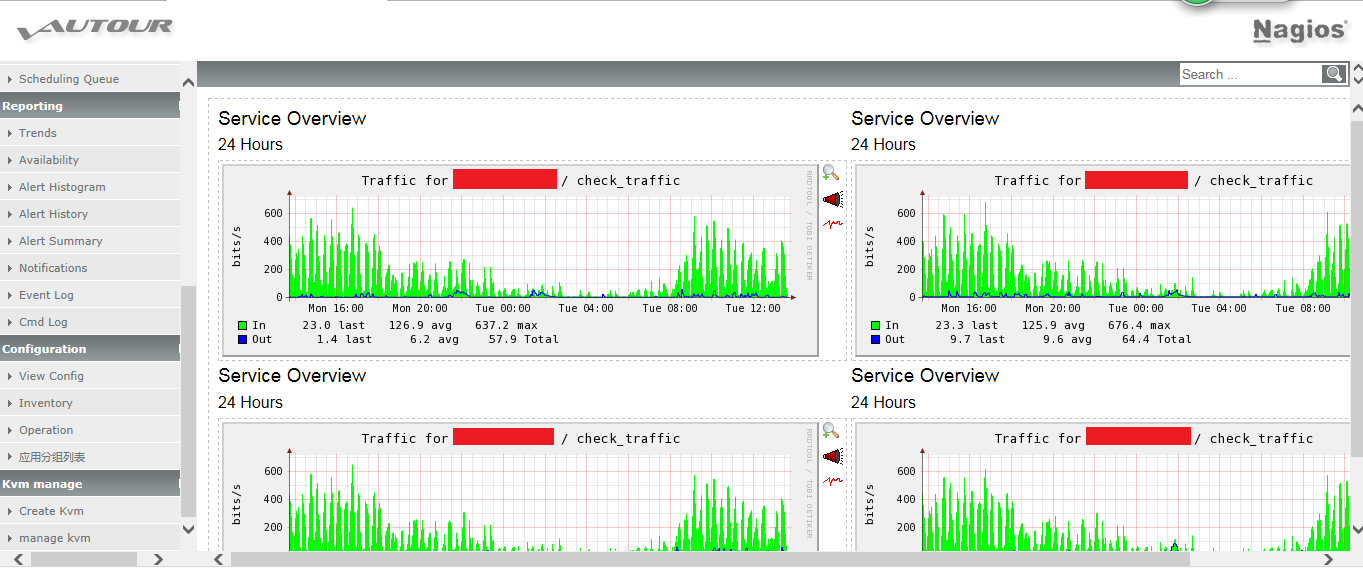 nagios二次開發之“依據分組繪制服務圖”
nagios二次開發之“依據分組繪制服務圖”
nagios二次開發之“依據分組繪制服務圖”背景: 在nagios3.2.0版本,曾將nagios、saltstack、Thinkphp進行整合。在整合的基礎之上,進行了