編輯:關於android開發
1, 是否是 64 bit apk,在對應的 full_sky828_8s70.mk 裡面,這裡主要包含64 bit apk的支持, 還有zygote的啟動方式,64 bit apk fork的簡要過程
$(call inherit-product, device/skyworth/sky828_8s70/device.mk)
$(call inherit-product-if-exists, vendor/google/products/gms.mk)
這個裡面主要的內容是:
PRODUCT_COPY_FILES += system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64_32.rc:root/init.zygote64_32.rc
PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES += ro.zygote=zygote64_32
TARGET_SUPPORTS_32_BIT_APPS := true
TARGET_SUPPORTS_64_BIT_APPS := true
這裡主要是表明編譯系統support 32 , 64 apk, 還有把zygote 名字ro.zygote設置為 zygote64_32,
在L之前啟動zygote 是直接在 init.rc 裡面通過
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin –zygote –start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
這個來啟動的, 但L上由於可能有2個zygote, 所以把zygote的啟動腳本抽象到一個單獨的rc文件裡面, 根據ro.zygote來區分。
這個單獨的腳本是在init rc裡面include的。 具體如下
import /init.environ.rc
import /init.usb.rc
import /init.
import /init.trace.rc
同時在 zygote64_32 腳本這個裡面做了什麼了?
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin –zygote –start-system-server –socket-name=zygote
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
service zygote_secondary /system/bin/app_process32 -Xzygote /system/bin –zygote –socket-name=zygote_secondary
class main
socket zygote_secondary stream 660 root system
onrestart restart zygote
這裡啟動了2個zygote, 其中一個是bin是 32bit的, 一個bin是64 bit的, 注意這裡的socket的名字 , 一個是zygote, 一個是zygote_secondary,第一個是primary zygote。我們之前知道, 在啟動apk的時候, 是從zygote出來的, 所以在L上, 啟動一個process之前, 會判斷是多少bit,然後向對應的zygote請求fork 子進程出來, 我們知道fork 子進程會集成父進程的屬性, 所以子 進程的位數跟父進程一致,從而如果我們要看一個 apk是多少bit, 可以通過看父進程是32bit的zygote,還是 64 bit的zygote
下面我們看一下啟動 process的時候, 是如何判斷 apk的 指令集的, 最終start 一個app的process 都是call到activitymanagerservice裡面去的,startProcessLocked
String requiredAbi = (abiOverride != null) ? abiOverride : app.info.primaryCpuAbi;==》 這個值是在安裝 apk的時候拿出來的,這裡這個值對於按照正常規范寫的有native code的apk, 這個值就是有值的,不是空, 但是對於沒有nativelib的,比如是pure java 的apk, 這個就是null。
if (requiredAbi == null) {
requiredAbi = Build.SUPPORTED_ABIS[0];
}
==》這裡的意思是系統無法根據lib 來判斷apk是多少bit的, 就會用系統support的 第一個 abi 來作為這個apk的 指令集, 這就是為什麼在 系統上, 如果有pure java的 apk , 肯定會跑 64 bit,而不是32 bit。在以64 系統為主的 系統上,系統support的 abi 如下:
shell@sky828_8s70:/ # getprop ro.product.cpu.abilist
arm64-v8a,armeabi-v7a,armeabi
String instructionSet = null;
if (app.info.primaryCpuAbi != null) {
instructionSet = VMRuntime.getInstructionSet(app.info.primaryCpuAbi);
}
我說一下 這裡 abi 跟 instructionset的關系, 對於64 為主, 也只是 32 bit 的系統, abi就是 arm64-v8a,armeabi-v7a,armeabi
,
那instructionset了, 其實 是根據 abi算過來的, arm64-v8a 對應的 指令集就是 arm64, 而 armeabi-v7a,armeabi 對應的就是 arm
然後才會開始真的startprocess,這裡會傳進入 abi, 跟 instructionset,
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = “android.app.ActivityThread”;
checkTime(startTime, “startProcess: asking zygote to start proc”);
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
在往後看, 會call到
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote); 我們看 openZygoteSocketIfNeeded , 這個裡面, 由此可以看出 判斷apk 跑哪個進程,還是根據前面的 abi來的。
private static ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(ZYGOTE_SOCKET);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(“Error connecting to primary zygote”, ioe);
}
}
if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return primaryZygoteState;
}
// The primary zygote didn't match. Try the secondary.
if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
secondaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_SOCKET);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote", ioe);
}
}
if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return secondaryZygoteState;
}
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
}
這裡的 primaryZygoteState 就是連接到名字叫zygote的 primary zygote, secondaryZygoteState 代表的是第二個,
這裡首先會判斷apk需要的abi是否在primary zygote支持的abi裡面, 如果不在 才會去secondary zygote去看。最終會根據找到對應的。
那系統是如何判斷primary zygote 支持哪些 abi的了?
Matches方法主要是
boolean matches(String abi) {
return abiList.contains(abi);
} 我們看 abilist是如何獲得到 ,
public static ZygoteState connect(String socketAddress) throws IOException {
DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = null;
BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = null;
final LocalSocket zygoteSocket = new LocalSocket();
try {
zygoteSocket.connect(new LocalSocketAddress(socketAddress,
LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED));
zygoteInputStream = new DataInputStream(zygoteSocket.getInputStream());
zygoteWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
zygoteSocket.getOutputStream()), 256);
} catch (IOException ex) {
try {
zygoteSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ignore) {
}
throw ex;
}
String abiListString = getAbiList(zygoteWriter, zygoteInputStream);
Log.i("Zygote", "Process: zygote socket opened, supported ABIS: " + abiListString);
return new ZygoteState(zygoteSocket, zygoteInputStream, zygoteWriter,
Arrays.asList(abiListString.split(",")));
}
然後getAbiList又是如何的了?
private static String getAbiList(BufferedWriter writer, DataInputStream inputStream)
throws IOException {
// Each query starts with the argument count (1 in this case)
writer.write(“1”);
// … followed by a new-line.
writer.newLine();
// … followed by our only argument.
writer.write(“–query-abi-list”);
writer.newLine();
writer.flush();
// The response is a length prefixed stream of ASCII bytes.
int numBytes = inputStream.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[numBytes];
inputStream.readFully(bytes);
return new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
}
發現這個是還是通過socket 去查詢結果的。 我們去看看server端的東西。
static const char ABI_LIST_PROPERTY[] = “ro.product.cpu.abilist64”;
static const char ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME[] = “zygote64”;
static const char ABI_LIST_PROPERTY[] = “ro.product.cpu.abilist32”;
static const char ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME[] = “zygote”;
在以 64 位為主的系統上,這兩個屬性的結果如下:
127|shell@sky828_8s70:/ # getprop ro.product.cpu.abilist64
arm64-v8a
shell@sky828_8s70:/ # getprop ro.product.cpu.abilist32
armeabi-v7a,armeabi
shell@sky828_8s70:/ #
在zygote 啟動的main 函數裡面, 會根據這兩個屬性獲取到自己支持的abi
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if (prctl(PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS, 1, 0, 0, 0) < 0) {
// Older kernels don’t understand PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS and return
// EINVAL. Don’t die on such kernels.
if (errno != EINVAL) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL(“PR_SET_NO_NEW_PRIVS failed: %s”, strerror(errno));
return 12;
}
}
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
// Everything up to '--' or first non '-' arg goes to the vm.
//
// The first argument after the VM args is the "parent dir", which
// is currently unused.
//
// After the parent dir, we expect one or more the following internal
// arguments :
//
// --zygote : Start in zygote mode
// --start-system-server : Start the system server.
// --application : Start in application (stand alone, non zygote) mode.
// --nice-name : The nice name for this process.
//
// For non zygote starts, these arguments will be followed by
// the main class name. All remaining arguments are passed to
// the main method of this class.
//
// For zygote starts, all remaining arguments are passed to the zygote.
// main function.
//
// Note that we must copy argument string values since we will rewrite the
// entire argument block when we apply the nice name to argv0.
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
if (argv[i][0] != '-') {
break;
}
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0) {
++i; // Skip --.
break;
}
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
}
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) {
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
Vector args;
if (!className.isEmpty()) {
// We're not in zygote mode, the only argument we need to pass
// to RuntimeInit is the application argument.
//
// The Remainder of args get passed to startup class main(). Make
// copies of them before we overwrite them with the process name.
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i);
} else {
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
if (startSystemServer) {
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
}
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
}
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string());
set_process_name(niceName.string());
}
if (zygote) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
return 10;
}
}
Native裡面最後通過 runtime.start(“com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit”, args); call到 java層上面,也就是com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit 這個類的main方法
在java裡面就會把這裡放到args裡面的 指令集取出來,
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
registerZygoteSocket(socketName);
我們再客戶端通過socket 請求對應的socket 拿到的 abi,其實就是這裡拿出來的 指,
2,apk的安裝過程, 主要是packagemanagerservice裡面 判斷 apk 跑多少bit的這段邏輯。
Pms 是在systemserver裡面啟動起來的,
// Start the package manager.
Slog.i(TAG, “Package Manager”);
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, mInstaller,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();//這裡的isFirstBoot 就是判斷系統是否是第一次啟動,恢復出廠設置, 然後再啟動,也認為是第一次,為什麼第一次啟動 apk 做優化,沒有轉圈圈,就與這個有關系
try {
mPackageManagerService.performBootDexOpt();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf(“performing boot dexopt”, e);
}
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().showBootMessage(
context.getResources().getText(
com.android.internal.R.string.android_upgrading_starting_apps),
false);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
我們看一下scan system app下的大概過程
// Collect ordinary system packages.
final File systemAppDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), “app”);
scanDirLI(systemAppDir, PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM
| PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR, scanFlags, 0);
注意下這裡的scanFlags,是下面這個值, 主要注意第二個參數 SCAN_DEFER_DEX,這個表示是推遲dex動作, 也就是說在在掃描這個目錄的時候,並不是掃描一個apk,就優化一個apk, 而是放到一個待優化列表,等掃描結束之後, 一起來做優化動作。
// Set flag to monitor and not change apk file paths when
// scanning install directories.
final int scanFlags = SCAN_NO_PATHS | SCAN_DEFER_DEX | SCAN_BOOTING;
通過這個函數會call到下面這個function
private void scanDirLI(File dir, int parseFlags, int scanFlags, long currentTime) {
final File[] files = dir.listFiles(); 列出這個目錄下的所有file,注意其實這裡不是file,而是目錄, 因為L上 apk的形式多了一級目錄,eg/system/app/helloworld/helloworld.apk 是這種形式
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(files)) {
Log.d(TAG, “No files in app dir ” + dir);
return;
}
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) {
Log.d(TAG, "Scanning app dir " + dir + " scanFlags=" + scanFlags
+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(parseFlags));
}
循環安裝這個目錄下的每個 apk
for (File file : files) {
final boolean isPackage = (isApkFile(file) || file.isDirectory())
&& !PackageInstallerService.isStageName(file.getName());
if (!isPackage) {
// Ignore entries which are not packages
continue;
}
try {
scanPackageLI(file, parseFlags | PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK,
scanFlags, currentTime, null);
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to parse " + file + ": " + e.getMessage());
// Delete invalid userdata apps
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0 &&
e.error == PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK) {
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Deleting invalid package at " + file);
if (file.isDirectory()) {
FileUtils.deleteContents(file);
}
file.delete();
}
}
}
}
我們根據這個scanPackageLI(file, parseFlags | PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK,
scanFlags, currentTime, null);
在往下走,
* Scan a package and return the newly parsed package.
* Returns null in case of errors and the error code is stored in mLastScanError
*/
private PackageParser.Package scanPackageLI(File scanFile, int parseFlags, int scanFlags,
long currentTime, UserHandle user) throws PackageManagerException {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, “Parsing: ” + scanFile);
parseFlags |= mDefParseFlags;
PackageParser pp = new PackageParser(); 主要用來解析apk裡面AndroidManifest.xml 文件的
pp.setSeparateProcesses(mSeparateProcesses);
pp.setOnlyCoreApps(mOnlyCore);
pp.setDisplayMetrics(mMetrics);
if ((scanFlags & SCAN_TRUSTED_OVERLAY) != 0) {
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_TRUSTED_OVERLAY;
}
final PackageParser.Package pkg;
try {
pkg = pp.parsePackage(scanFile, parseFlags);真正開始解析 apk裡面AndroidManifest.xml 文件的,這個過程請看後面的流程 parsePackage, 這裡主要是解析mafifest文件, 把信息記錄到package對象裡面
} catch (PackageParserException e) {
throw PackageManagerException.from(e);
}
PackageSetting ps = null;
PackageSetting updatedPkg;
// reader
synchronized (mPackages) {
// Look to see if we already know about this package.
String oldName = mSettings.mRenamedPackages.get(pkg.packageName);
if (pkg.mOriginalPackages != null && pkg.mOriginalPackages.contains(oldName)) {
// This package has been renamed to its original name. Let's
// use that.
ps = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(oldName);
}
// If there was no original package, see one for the real package name.
if (ps == null) {
ps = mSettings.peekPackageLPr(pkg.packageName);
}
// Check to see if this package could be hiding/updating a system
// package. Must look for it either under the original or real
// package name depending on our state.
updatedPkg = mSettings.getDisabledSystemPkgLPr(ps != null ? ps.name : pkg.packageName);
if (DEBUG_INSTALL && updatedPkg != null) Slog.d(TAG, "updatedPkg = " + updatedPkg);
}
boolean updatedPkgBetter = false;
// First check if this is a system package that may involve an update
if (updatedPkg != null && (parseFlags&PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) != 0) {
if (ps != null && !ps.codePath.equals(scanFile)) {
// The path has changed from what was last scanned... check the
// version of the new path against what we have stored to determine
// what to do.
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Slog.d(TAG, "Path changing from " + ps.codePath);
if (pkg.mVersionCode < ps.versionCode) {
// The system package has been updated and the code path does not match
// Ignore entry. Skip it.
logCriticalInfo(Log.INFO, "Package " + ps.name + " at " + scanFile
+ " ignored: updated version " + ps.versionCode
+ " better than this " + pkg.mVersionCode);
if (!updatedPkg.codePath.equals(scanFile)) {
Slog.w(PackageManagerService.TAG, "Code path for hidden system pkg : "
+ ps.name + " changing from " + updatedPkg.codePathString
+ " to " + scanFile);
updatedPkg.codePath = scanFile;
updatedPkg.codePathString = scanFile.toString();
// This is the point at which we know that the system-disk APK
// for this package has moved during a reboot (e.g. due to an OTA),
// so we need to reevaluate it for privilege policy.
if (locationIsPrivileged(scanFile)) {
updatedPkg.pkgFlags |= ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED;
}
}
updatedPkg.pkg = pkg;
throw new PackageManagerException(INSTALL_FAILED_DUPLICATE_PACKAGE, null);
} else {
// The current app on the system partition is better than
// what we have updated to on the data partition; switch
// back to the system partition version.
// At this point, its safely assumed that package installation for
// apps in system partition will go through. If not there won't be a working
// version of the app
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
// Just remove the loaded entries from package lists.
mPackages.remove(ps.name);
}
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Package " + ps.name + " at " + scanFile
+ " reverting from " + ps.codePathString
+ ": new version " + pkg.mVersionCode
+ " better than installed " + ps.versionCode);
InstallArgs args = createInstallArgsForExisting(packageFlagsToInstallFlags(ps),
ps.codePathString, ps.resourcePathString, ps.legacyNativeLibraryPathString,
getAppDexInstructionSets(ps));
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
args.cleanUpResourcesLI();
}
synchronized (mPackages) {
mSettings.enableSystemPackageLPw(ps.name);
}
updatedPkgBetter = true;
}
}
}
if (updatedPkg != null) {
// An updated system app will not have the PARSE_IS_SYSTEM flag set
// initially
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM;
// An updated privileged app will not have the PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED
// flag set initially
if ((updatedPkg.pkgFlags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_PRIVILEGED) != 0) {
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_IS_PRIVILEGED;
}
}
// Verify certificates against what was last scanned
collectCertificatesLI(pp, ps, pkg, scanFile, parseFlags);
/*
* A new system app appeared, but we already had a non-system one of the
* same name installed earlier.
*/
boolean shouldHideSystemApp = false;
if (updatedPkg == null && ps != null
&& (parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) != 0 && !isSystemApp(ps)) {
/*
* Check to make sure the signatures match first. If they don't,
* wipe the installed application and its data.
*/
if (compareSignatures(ps.signatures.mSignatures, pkg.mSignatures)
!= PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH) {
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Package " + ps.name + " appeared on system, but"
+ " signatures don't match existing userdata copy; removing");
deletePackageLI(pkg.packageName, null, true, null, null, 0, null, false);
ps = null;
} else {
/*
* If the newly-added system app is an older version than the
* already installed version, hide it. It will be scanned later
* and re-added like an update.
*/
if (pkg.mVersionCode < ps.versionCode) {
shouldHideSystemApp = true;
logCriticalInfo(Log.INFO, "Package " + ps.name + " appeared at " + scanFile
+ " but new version " + pkg.mVersionCode + " better than installed "
+ ps.versionCode + "; hiding system");
} else {
/*
* The newly found system app is a newer version that the
* one previously installed. Simply remove the
* already-installed application and replace it with our own
* while keeping the application data.
*/
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Package " + ps.name + " at " + scanFile
+ " reverting from " + ps.codePathString + ": new version "
+ pkg.mVersionCode + " better than installed " + ps.versionCode);
InstallArgs args = createInstallArgsForExisting(packageFlagsToInstallFlags(ps),
ps.codePathString, ps.resourcePathString, ps.legacyNativeLibraryPathString,
getAppDexInstructionSets(ps));
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
args.cleanUpResourcesLI();
}
}
}
}
// The apk is forward locked (not public) if its code and resources
// are kept in different files. (except for app in either system or
// vendor path).
// TODO grab this value from PackageSettings
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM_DIR) == 0) {
if (ps != null && !ps.codePath.equals(ps.resourcePath)) {
parseFlags |= PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK;
}
}
// TODO: extend to support forward-locked splits
String resourcePath = null;
String baseResourcePath = null;
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_FORWARD_LOCK) != 0 && !updatedPkgBetter) {
if (ps != null && ps.resourcePathString != null) {
resourcePath = ps.resourcePathString;
baseResourcePath = ps.resourcePathString;
} else {
// Should not happen at all. Just log an error.
Slog.e(TAG, "Resource path not set for pkg : " + pkg.packageName);
}
} else {
resourcePath = pkg.codePath;
baseResourcePath = pkg.baseCodePath;
}
// Set application objects path explicitly.
pkg.applicationInfo.setCodePath(pkg.codePath);
pkg.applicationInfo.setBaseCodePath(pkg.baseCodePath);
pkg.applicationInfo.setSplitCodePaths(pkg.splitCodePaths);
pkg.applicationInfo.setResourcePath(resourcePath);
pkg.applicationInfo.setBaseResourcePath(baseResourcePath);
pkg.applicationInfo.setSplitResourcePaths(pkg.splitCodePaths);
// Note that we invoke the following method only if we are about to unpack an application
PackageParser.Package scannedPkg = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags
| SCAN_UPDATE_SIGNATURE, currentTime, user);
/*
* If the system app should be overridden by a previously installed
* data, hide the system app now and let the /data/app scan pick it up
* again.
*/
if (shouldHideSystemApp) {
synchronized (mPackages) {
/*
* We have to grant systems permissions before we hide, because
* grantPermissions will assume the package update is trying to
* expand its permissions.
*/
grantPermissionsLPw(pkg, true, pkg.packageName);
mSettings.disableSystemPackageLPw(pkg.packageName);
}
}
return scannedPkg;
}
parsePackage:
public Package parsePackage(File packageFile, int flags) throws PackageParserException {
if (packageFile.isDirectory()) {
return parseClusterPackage(packageFile, flags);
} else {
return parseMonolithicPackage(packageFile, flags);
}
}
注意,我們這裡是目錄, 而不是文件, 所以會走return parseClusterPackage(packageFile, flags); 再往下走
private Package parseClusterPackage(File packageDir, int flags) throws PackageParserException {
final PackageLite lite = parseClusterPackageLite(packageDir, 0);
if (mOnlyCoreApps && !lite.coreApp) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED,
"Not a coreApp: " + packageDir);
}
final AssetManager assets = new AssetManager();
try {
// Load the base and all splits into the AssetManager
// so that resources can be overriden when parsing the manifests.
loadApkIntoAssetManager(assets, lite.baseCodePath, flags);
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(lite.splitCodePaths)) {
for (String path : lite.splitCodePaths) {
loadApkIntoAssetManager(assets, path, flags);
}
}
final File baseApk = new File(lite.baseCodePath);
final Package pkg = parseBaseApk(baseApk, assets, flags);
if (pkg == null) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NOT_APK,
"Failed to parse base APK: " + baseApk);
}
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(lite.splitNames)) {
final int num = lite.splitNames.length;
pkg.splitNames = lite.splitNames;
pkg.splitCodePaths = lite.splitCodePaths;
pkg.splitFlags = new int[num];
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
parseSplitApk(pkg, i, assets, flags);
}
}
pkg.codePath = packageDir.getAbsolutePath();
return pkg;
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(assets);
}
}
這裡主要看兩個函數,一個是 parseClusterPackageLite, 一個是 parseBaseApk, 其中要明白兩個class的含義, 其中packagelite是一個輕量級的package的信息, 主要只包含下面的信息
public static class PackageLite {
public final String packageName;
public final int versionCode;
public final int installLocation;
public final VerifierInfo[] verifiers;
/** Names of any split APKs, ordered by parsed splitName */
public final String[] splitNames;
/**
* Path where this package was found on disk. For monolithic packages
* this is path to single base APK file; for cluster packages this is
* path to the cluster directory.
*/
public final String codePath;
/** Path of base APK */
public final String baseCodePath;
/** Paths of any split APKs, ordered by parsed splitName */
public final String[] splitCodePaths;
public final boolean coreApp;
public final boolean multiArch;
但是Package 就是一個apk的詳細信息, 比如這個apk 裡面的activity,service,broadcast,contentprovider 列表, 內容比較多。我只貼一部分
public final static class Package {
public String packageName;
/** Names of any split APKs, ordered by parsed splitName */
public String[] splitNames;
// TODO: work towards making these paths invariant
/**
* Path where this package was found on disk. For monolithic packages
* this is path to single base APK file; for cluster packages this is
* path to the cluster directory.
*/
public String codePath;
/** Path of base APK */
public String baseCodePath;
/** Paths of any split APKs, ordered by parsed splitName */
public String[] splitCodePaths;
/** Flags of any split APKs; ordered by parsed splitName */
public int[] splitFlags;
public boolean baseHardwareAccelerated;
// For now we only support one application per package.
public final ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = new ApplicationInfo();
public final ArrayList permissions = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList permissionGroups = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList activities = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList receivers = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList providers = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList services = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList instrumentation = new ArrayList(0);
public final ArrayList requestedPermissions = new ArrayList();
public final ArrayList requestedPermissionsRequired = new ArrayList();
public ArrayList protectedBroadcasts;
然後來看函數 final PackageLite lite = parseClusterPackageLite(packageDir, 0);
private static PackageLite parseClusterPackageLite(File packageDir, int flags)
throws PackageParserException {
final File[] files = packageDir.listFiles();
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(files)) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_NOT_APK,
“No packages found in split”);
}
String packageName = null;
int versionCode = 0;
final ArrayMap apks = new ArrayMap<>();
for (File file : files) {
if (isApkFile(file)) {
final ApkLite lite = parseApkLite(file, flags);
// Assert that all package names and version codes are
// consistent with the first one we encounter.
if (packageName == null) {
packageName = lite.packageName;
versionCode = lite.versionCode;
} else {
if (!packageName.equals(lite.packageName)) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST,
"Inconsistent package " + lite.packageName + " in " + file
+ "; expected " + packageName);
}
if (versionCode != lite.versionCode) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST,
"Inconsistent version " + lite.versionCode + " in " + file
+ "; expected " + versionCode);
}
}
// Assert that each split is defined only once
if (apks.put(lite.splitName, lite) != null) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST,
"Split name " + lite.splitName
+ " defined more than once; most recent was " + file);
}
}
}
final ApkLite baseApk = apks.remove(null);
if (baseApk == null) {
throw new PackageParserException(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_BAD_MANIFEST,
"Missing base APK in " + packageDir);
}
// Always apply deterministic ordering based on splitName
final int size = apks.size();
String[] splitNames = null;
String[] splitCodePaths = null;
if (size > 0) {
splitNames = new String[size];
splitCodePaths = new String[size];
splitNames = apks.keySet().toArray(splitNames);
Arrays.sort(splitNames, sSplitNameComparator);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
splitCodePaths[i] = apks.get(splitNames[i]).codePath;
}
}
final String codePath = packageDir.getAbsolutePath();
return new PackageLite(codePath, baseApk, splitNames, splitCodePaths);
}
其中paseapklite 就是拿到了如下信息
return new ApkLite(codePath, packageSplit.first, packageSplit.second, versionCode,
installLocation, verifiers, signatures, coreApp, multiArch);
其中這兩個packageSplit.first, packageSplit.second對於一般的apk 都是 null, 是沒有拆分的,這些信息都是從manifest 文件裡面parse 出來的,最後返回的 是return new PackageLite(codePath, baseApk, splitNames, splitCodePaths);
其中codepath就是 /system/app/helloworld 這個目錄, baseapk就是上面的 apklite, 另外splitNames, splitCodePaths 都是null, 這裡parseapklite就講完了。
然後我們看 final Package pkg = parseBaseApk(baseApk, assets, flags); 這裡裡面對四大組件的詳細 解析, 最後會走到這個函數
private Package parseBaseApk(Resources res, XmlResourceParser parser, int flags,
String[] outError) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
這裡我不多講, 會解析manefest裡面的很多東西, 主要包括權限, 四大組件等信息,
最後解析application裡面四大組件的地方再這裡
private boolean parseBaseApplication(Package owner, Resources res,
XmlPullParser parser, AttributeSet attrs, int flags, String[] outError)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
基本的位置在下面
String tagName = parser.getName();
if (tagName.equals(“activity”)) {
Activity a = parseActivity(owner, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError, false,
owner.baseHardwareAccelerated);
if (a == null) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return false;
}
owner.activities.add(a);
} else if (tagName.equals("receiver")) {
Activity a = parseActivity(owner, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError, true, false);
if (a == null) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return false;
}
owner.receivers.add(a);
} else if (tagName.equals("service")) {
Service s = parseService(owner, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError);
if (s == null) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return false;
}
owner.services.add(s);
} else if (tagName.equals("provider")) {
Provider p = parseProvider(owner, res, parser, attrs, flags, outError);
if (p == null) {
mParseError = PackageManager.INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED;
return false;
}
owner.providers.add(p);
}
這裡這四個過程就是分別解析manifest裡面 四大組件, 然後加到我們的package對象裡面對應的四個list裡面去。記錄這些信息。
這樣子解析manefest的大致過程就說完了。
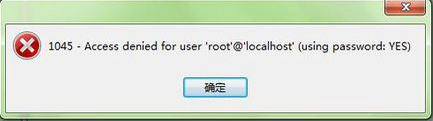 如何解決Linux系統中的Navicat for MySQL 1045錯誤
如何解決Linux系統中的Navicat for MySQL 1045錯誤
如何解決Linux系統中的Navicat for MySQL 1045錯誤Navicat連接MySQL數據庫時難免會遇到1045錯誤,主要是因為用戶輸入的用戶名或密碼錯誤
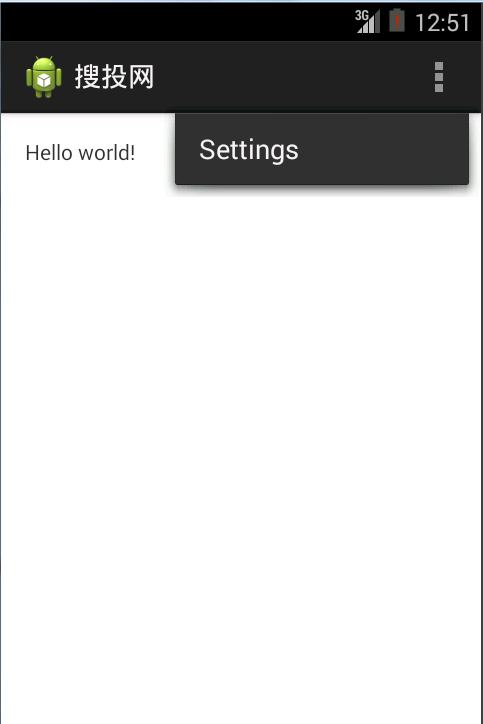 第四篇 Android應用程序詳細解析,第四篇android
第四篇 Android應用程序詳細解析,第四篇android
第四篇 Android應用程序詳細解析,第四篇android我們繼續的沿用上一篇所建立的應用。 Android應用程序可以分為:應用程序源代碼(.java),應用程序描
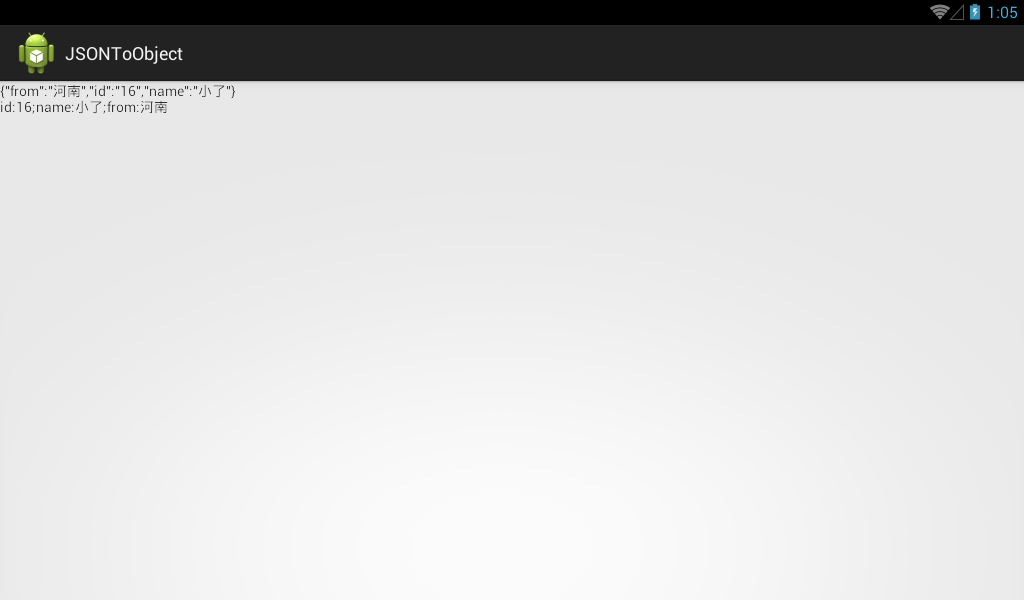 Android之JSON解析,androidjson
Android之JSON解析,androidjson
Android之JSON解析,androidjson 做個Android網絡編程的同學一定對於JSON解析一點都不陌生,因為現在我們通過手機向服務器請求資源,服務器給我
 Android新手入門2016(10)--GridView
Android新手入門2016(10)--GridView
Android新手入門2016(10)--GridView GridView跟ListView一樣是多控件布局。實現九宮圖是最方便的。 還是先看看圖,沒圖說個雞雞是不是