編輯:關於android開發
相關文章
Android View體系(一)視圖坐標系
Android View體系(二)實現View滑動的六種方法
Android View體系(三)屬性動畫
Android View體系(四)從源碼解析Scroller
Android View體系(五)從源碼解析View的事件分發機制
Android View體系(六)從源碼解析Activity的構成
在上一篇我們了解了Activity的構成後,開始了解一下View的工作流程,就是measure、layout和draw。measure用來測量View的寬高,layout用來確定View的位置,draw則用來繪制View。這一講我們來看看measure流程,measure流程分為View的measure流程和ViewGroup的measure流程,只不過ViewGroup的measure流程除了要完成自己的測量還要遍歷去調用子元素的measure()方法。
先來看看onMeasure()方法(View.java):
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
看看setMeasuredDimension()方法:
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
很顯然是用來設置View的寬高的,先來看看getDefaultSize()方法處理了什麼:
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
specMode是View的測量模式,而specSize是View的測量大小,看到這裡我們有必要先看看MeasureSpec類:
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
...省略
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
...省略
}
MeasureSpec類幫助我們來測量View,它是一個32位的int值,高兩位為specMode (測量的模式),低30位為specSize (測量的大小),測量模式分為三種:
UNSPECIFIED:未指定模式,View想多大就多大,父容器不做限制,一般用於系統內部的測量。 AT_MOST:最大模式,對應於wrap_comtent屬性,只要尺寸不超過父控件允許的最大尺寸就行。 EXACTLY:精確模式,對應於match_parent屬性和具體的數值,父容器測量出View所需要的大小,也就是specSize的值。讓我們回頭看看getDefaultSize()方法,很顯然在AT_MOST和EXACTLY模式下,都返回specSize這個值,也就是View測量後的大小,而在UNSPECIFIED模式返回的是getDefaultSize()方法的第一次個參數的值,這第一個參數從onMeasure()方法來看是getSuggestedMinimumWidth()方法和getSuggestedMinimumHeight()得到的,那我們來看看getSuggestedMinimumWidth()方法做了什麼,我們只需要弄懂getSuggestedMinimumWidth()方法,因為這兩個方法原理是一樣的:
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
如果View沒有設置背景則取值為mMinWidth,mMinWidth是可以設置的,它對應於android:minWidth這個屬性設置的值或者View的setMinimumWidth的值,如果不指定的話則默認為0:
public void setMinimumWidth(int minWidth) {
mMinWidth = minWidth;
requestLayout();
}
如果View設置了背景在取值為max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth()),取值mMinWidth和mBackground.getMinimumWidth()的最大值,上面我們說過了mMinWidth,那來看看mBackground.getMinimumWidth(),這個mBackground是Drawable類型的,看一下Drawable類的getMinimumWidth()方法(Drawable.java):
public int getMinimumWidth() {
final int intrinsicWidth = getIntrinsicWidth();
return intrinsicWidth > 0 ? intrinsicWidth : 0;
}
intrinsicWidth得到的是這個Drawable的固有的寬度,如果固有寬度大於0則返回固有寬度,否則返回0。
總結一下getSuggestedMinimumWidth()方法就是:如果View沒有設置背景則返回mMinWidth ,如果設置了背景就返回mMinWidth 和Drawable最小寬度兩個值的最大值。
講完了View的measure流程,接下來看看ViewGroup的measure流程,對於ViewGroup,它不只要measure自己本身,還要遍歷的調用子元素的measure()方法,ViewGroup中沒有定義onMeasure()方法,但他定義了measureChildren()方法(ViewGroup.java):
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
就是遍歷子元素並調用measureChild()方法:
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
調用child.getLayoutParams()方法來獲得子元素的LayoutParams屬性,並獲取到子元素的MeasureSpec並調用子元素的measure()方法進行測量。getChildMeasureSpec()方法裡寫了什麼呢?
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
很顯然這是根據父容器的MeasureSpec的模式再結合子元素的LayoutParams屬性來得出子元素的MeasureSpec屬性,有一點需要注意的是如果父容器的MeasureSpec屬性為AT_MOST,子元素的LayoutParams屬性為WRAP_CONTENT,那根據代碼我們會發現子元素的MeasureSpec屬性也為AT_MOST,它的specSize值為父容器的specSize減去padding的值,也就是說跟這個子元素設置LayoutParams屬性為MATCH_PARENT效果是一樣的,為了解決這個問題需要在LayoutParams屬性為WRAP_CONTENT時指定一下默認的寬和高。
ViewGroup並沒有提供onMeasure()方法,而是讓其子類來各自實現測量的方法,究其原因就是ViewGroup有不同的布局的需要很難統一,接下來我們來簡單分析一下ViewGroup的子類LinearLayout的measure流程,先來看看它的onMeasure()方法(LinearLayout.java):
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
來看看垂直measureVertical()方法的部分源碼:
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mTotalLength = 0;
mTotalLength = 0;
...省略
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
if (hasDividerBeforeChildAt(i)) {
mTotalLength += mDividerHeight;
}
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
totalWeight += lp.weight;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
// Optimization: don't bother measuring children who are going to use
// leftover space. These views will get measured again down below if
// there is any leftover space.
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
skippedMeasure = true;
} else {
int oldHeight = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if (lp.height == 0 && lp.weight > 0) {
// heightMode is either UNSPECIFIED or AT_MOST, and this
// child wanted to stretch to fill available space.
// Translate that to WRAP_CONTENT so that it does not end up
// with a height of 0
oldHeight = 0;
lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
// Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or
// previous children have given a weight, then we allow it to
// use all available space (and we will shrink things later
// if needed).
measureChildBeforeLayout(
child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec,
totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
if (oldHeight != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
lp.height = oldHeight;
}
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin +
lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
...省略
if (useLargestChild &&
(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED)) {
mTotalLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) {
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
continue;
}
final LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)
child.getLayoutParams();
// Account for negative margins
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + largestChildHeight +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
}
}
// Add in our padding
mTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
int heightSize = mTotalLength;
// Check against our minimum height
定義了mTotalLength用來存儲LinearLayout在垂直方向的高度,然後遍歷子元素,根據子元素的MeasureSpec模式分別計算每個子元素的高度,如果是wrap_content則將每個子元素的高度和margin垂直高度等值相加並賦值給mTotalLength得出整個LinearLayout的高度。如果布局高度設置為match_parent者具體數值則和View的測量方法一樣。
 硅谷新聞8--TabLayout替換ViewPagerIndicator,tablayoutindicator
硅谷新聞8--TabLayout替換ViewPagerIndicator,tablayoutindicator
硅谷新聞8--TabLayout替換ViewPagerIndicator,tablayoutindicator 1.關聯庫 compile com.android.sup
 Android Studio中使用AIDL進行進程間通信
Android Studio中使用AIDL進行進程間通信
Android Studio中使用AIDL進行進程間通信 什麼是AIDL aidl是 Android Interface definition language的縮寫,也
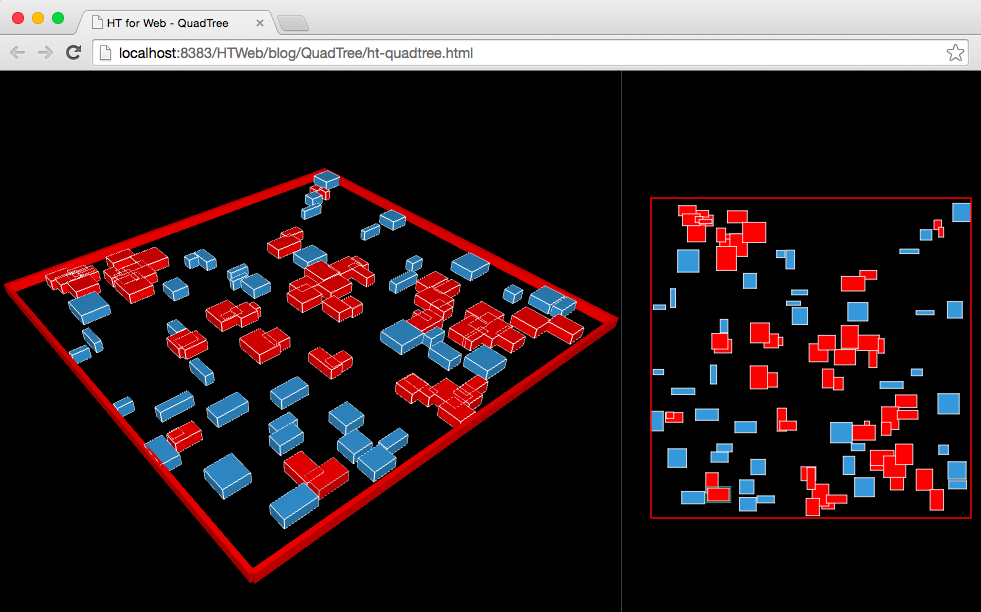 HTML5實現3D和2D可視化QuadTree四叉樹碰撞檢測
HTML5實現3D和2D可視化QuadTree四叉樹碰撞檢測
HTML5實現3D和2D可視化QuadTree四叉樹碰撞檢測QuadTree四叉樹顧名思義就是樹狀的數據結構,其每個節點有四個孩子節點,可將二維平面遞歸分割子區域。Qua
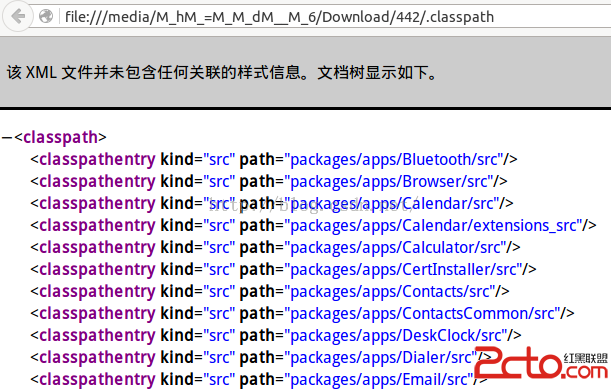 使用Eclipse開發Android源碼
使用Eclipse開發Android源碼
使用Eclipse開發Android源碼 1.把eclipse工程配置文件復制到Android源碼根目錄下 cp development/ide/eclipse/.c