編輯:關於android開發
---恢復內容開始---
Service的意義就在於當軟件停止之後還可以在背景中進行運行,換句話也就是說,比如一個音樂播放器,當我們退出音樂播放器的時候,還是希望它在背景中運行,也就是一直播放著音樂,這時候Service就派上了大的用途。
Service的生命周期和Activity的生命周期差不多。也有開啟和停止。onCreate()方法是初始化配置,onDestroy()是釋放所有剩余的資源。Service周期是發生在onCreate()和onDestroy()之間的。
startService()方法是啟動Service。
StopService()方法是停止Service。
bindService()方法是啟動Service的激活生命周期始於onBind()調用,在onUnbind()返回時結束。
當一個組件啟動Service時,是通過startService()進行啟動Service,當Service被啟動之後,onStartCommand()方法被調用,並且接收startService()方法中傳遞的Intent值。
onStartServiceCommand()方法必修返回一個整形值。這個整形值是說明了Service在系統中如何執行。其中三個比較常用的解釋如下:
START_NOT_STICKY:如果系統在onStartServiceCommand()返回後殺死Service,那麼不會重新創建Service,除非有等待的Intent要傳遞。
START_STICKY 如果系統在onStartServiceCommand()返回後殺死Service,重啟Service,並且重新調用onStartServiceCommand(),但不重新傳遞最新的Intent。
START_REDELIVER_INTENT 如果系統在onStartServiceCommand()返回後殺死Service,那麼重新創建Service,並且最近傳給Service的Intent調用onStartServiceCommand()。
創建一個Service啟動周期的實例
1 public class MyService extends Service{
2
3 //必須實現的方法,作用是用來返回binder對象
4
5
6 //重寫onBind()方法,返回Service實例,使Service支持綁定,實現onBind()方法,並且返回MyService實例
7 @Override
8 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
10 System.out.println("--onBind--");
11 return null;
12 }
13
14
15 //用於創建Service的方法,只能調用一次
16 public void onCreate(){
17 super.onCreate();
18 System.out.println("--onCreate--");
19
20 //每次啟動Service時都會調用這個方法
21 @Override
22 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
23 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
24 System.out.println("--onStartCommand--");
25 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
26 }
27
28 //解綁的時候使用的這個方法
29 @Override
30 public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
31 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
32 System.out.println("--onUnbind--");
33 return super.onUnbind(intent);
34 }
35
36 //退出或者銷毀的時候使用這個方法
37 @Override
38 public void onDestroy() {
39 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
40 serviceRunning = false;
41 System.out.println("--onDestroy--");
42 super.onDestroy();
43
44 }
45
46 }
注意:在測試的時候一定要在onCreate()方法中寫一個多線程,以便輸出,讓我們更加的明白。如下:
1 //用於創建Service的方法,只能調用一次
2 public void onCreate(){
3 super.onCreate();
4 System.out.println("--onCreate--");
5 serviceRunning = true;
6 new Thread(){
7 public void run(){
8 while(serviceRunning){
9 System.out.println("--Service運行中--");
10 try{
11 sleep(1000);
12 }catch(Exception e){
13 e.printStackTrace();
14 }
15 }
16 }
17 }.start();
18 }
綁定Service
綁定Service的時候會比較的復雜,其中,看綁定方法bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags)時大家就可以看出。其中Intent需要傳遞Intent的值,conn是ServiceConnection的實例,flags是所需要的一個標示。下面就為大家解析綁定Service所需要的三個步驟:
第一步:需要在Service中創建一個Binder接口,並且實現:
包含客戶端可以調用public方法
或返回當前Service的實例--也包含客戶端可以調用的Public方法
或返回Service持有的其他類型的實例--也包含客戶端可以調用的Public方法
代碼如下:
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
MyService getService(){
return MyService.this;
}
}
第二步:在onBind()中返回Binder實例。
代碼如下:
1 //必須實現的方法,作用是用來返回binder對象
2 //重寫onBind()方法,返回Service實例,使Service支持綁定,實現onBind()方法,並且返回MyService實例
3 @Override
4 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
5 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
6 System.out.println("--onBind--");
7 return null;
8 }
第三步:在客戶端中,從onServiceConnected()回調方法中接收這個Binder,並且使用Binder包含的Service提供的方法。
比如:
1 public class MyServiceConn implements ServiceConnection{
2
3 MyService.MyBinder binder = null;
4
5 @Override
6 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
8 binder = (MyService.MyBinder)service;
9 }
10
11 @Override
12 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
13 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
14 binder = null;
15 }
16
17 }
注意:一定要在客戶端中聲明這個實例:
1 final MyServiceConn myserviceconn = new MyServiceConn();
客戶端在合適的時候也可以進行解綁:
1 //解除綁定的Service
2 unbind.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
3
4 @Override
5 public void onClick(View v) {
6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
7 unbindService(myserviceconn);
8 }
9 });
上述就把Service的啟動、停止、綁定、解綁就完成了,下面的則是客戶端的一些的代碼:
1 import android.app.Activity;
2 import android.content.ComponentName;
3 import android.content.Context;
4 import android.content.Intent;
5 import android.content.ServiceConnection;
6 import android.os.Bundle;
7 import android.os.IBinder;
8 import android.view.View;
9 import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
10 import android.widget.Button;
11
12 public class MainActivity extends Activity {
13
14 private Button start;
15 private Button stop;
16 private Button bind;
17 private Button unbind;
18 private Intent intent;
19
20 @Override
21 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
22 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
23 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
24 start = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn1);
25 stop = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn2);
26 bind = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn3);
27 unbind = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn4);
28
29 final MyServiceConn myserviceconn = new MyServiceConn();
30
31 //給按鈕設置事件,以便監聽Service中的變化
32 //開啟service
33 start.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
34
35 @Override
36 public void onClick(View v) {
37 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
38 intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),MyService.class);
39 startService(intent);
40 }
41 });
42
43 //結束Service
44 stop.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
45
46 @Override
47 public void onClick(View v) {
48 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
49 stopService(intent);
50 }
51 });
52
53 //綁定service服務
54 bind.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
55
56 @Override
57 public void onClick(View v) {
58 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
59 bindService(intent,myserviceconn,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
60 }
61 });
62
63 //解除綁定的Service
64 unbind.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
65
66 @Override
67 public void onClick(View v) {
68 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
69 unbindService(myserviceconn);
70 }
71 });
72 }
73
74
75 }
XML文件的代碼(只是一些簡單的按鈕,就不解釋了):
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" 3 android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical" 7 tools:context=".MainActivity" > 8 9 <TextView 10 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 11 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 12 android:text="@string/service" /> 13 14 <Button 15 android:id="@+id/btn1" 16 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 17 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 18 android:text="StartService" /> 19 20 <Button 21 android:id="@+id/btn2" 22 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 23 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 24 android:text="StopService" /> 25 26 <Button 27 android:id="@+id/btn3" 28 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 29 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 30 android:text="bindService" /> 31 32 <Button 33 android:id="@+id/btn4" 34 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
35 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 36 android:text="unBindService" /> 37 38 </LinearLayout>
一定要注意在AndroidManifest.xml文件中加上權限:
1 <service android:name="com.example.servicetest.MyService"> 2 </service>
到這裡就完了,有什麼不懂或者不對的地方可以留言,至於截圖,上述的代碼比較詳細,我這裡就不貼出了。
---恢復內容結束---
 Activity啟動過程源碼分析
Activity啟動過程源碼分析
Activity啟動過程源碼分析 其實寫分析源碼文章總會顯得很復雜很乏味,但是梳理自己看源碼時的一些總結也是一種提高。這篇博客分析下Activity啟動過程源碼,我會盡量
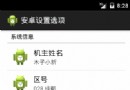 安卓系統設置選項的框架。,安卓系統設置框架
安卓系統設置選項的框架。,安卓系統設置框架
安卓系統設置選項的框架。,安卓系統設置框架首先在res文件中創建一個xml文件夾,創建preference.xml文件,然後寫布局: 1 <?xml versi
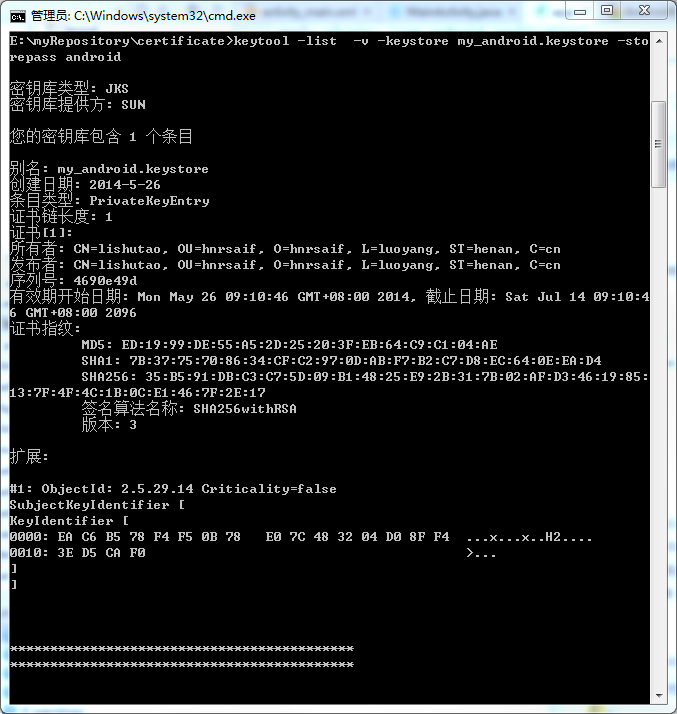 Android 查看自己的keystore的別名及相關信息,androidkeystore
Android 查看自己的keystore的別名及相關信息,androidkeystore
Android 查看自己的keystore的別名及相關信息,androidkeystore1.在DOS窗口下進入自己的keystore所在位置,輸入 &nb
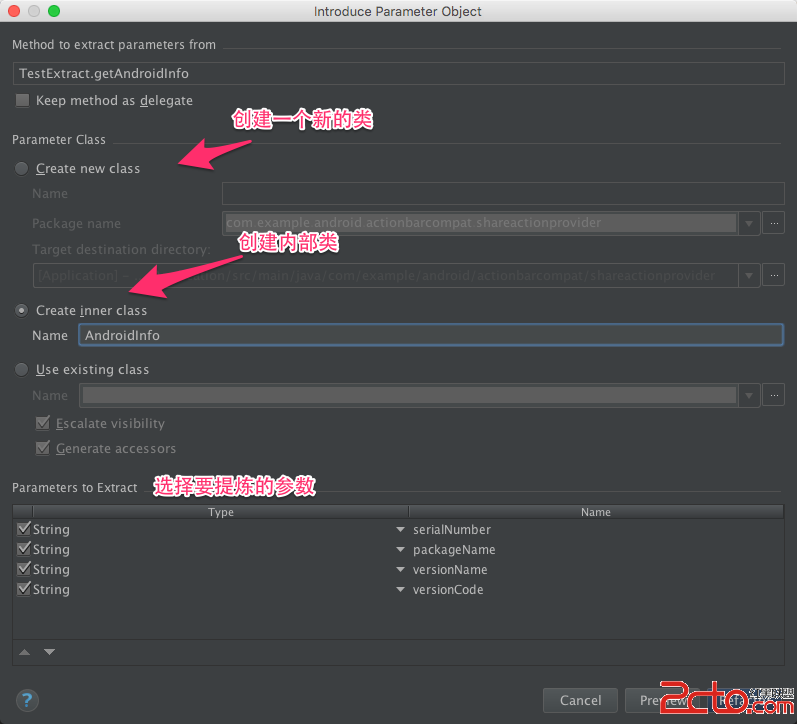 (Android Studio實用指南)8.16 提煉參數對象
(Android Studio實用指南)8.16 提煉參數對象
(Android Studio實用指南)8.16 提煉參數對象 某些參數總是同時出現,可能好幾個方法都使用這樣一組參數,為了避免參數列表過長,同時也為了避免重復代碼,
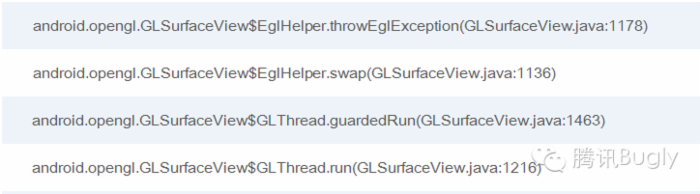 [轉]File Descriptor洩漏導致Crash: Too many open files,descriptorcrash
[轉]File Descriptor洩漏導致Crash: Too many open files,descriptorcrash
[轉]File Descriptor洩漏導致Crash: Too man