編輯:關於android開發
天氣說變就變,馬上又變冷了,還好空氣不錯,陽光也不錯,早起上班的車上的人也不多,公司來的同事和昨天一樣一樣的,可能明天會多一些吧,那就再來學習android吧。學了兩個android的組件,這裡學習下第三個android的組件,Content Provider內容提供器。
Content Provider向我們提供了在不同應用程序之間的數據共享,比如微信啊,支付寶啊,想要獲取手機聯系人的信息,而手機聯系人是另一個應用程序,那麼這時候就需要用到Content Provider了。Content Provider為存儲和獲取數據提供了統一的接口,對數據進行了封裝,我們不用關心數據存儲的細節,使用表的形式來組織數據。Android提供了一些默認的ContentProvider,比如音頻,視頻,圖片和通訊錄等。
類似於文件,SharedPreferences或者SQLiteDataBase都有一個路徑,那麼ContentProvider也是有路徑的,它的路徑由Uri表示,Uri主要包含了兩部分的信息,一個是需要操作的ContentProvider,另一個就是對ContentProvider中的什麼數據進行操作。一個簡單的Uri:
content://com.example.contentprovidertest.provider/person/2
主機名或者authority:com.example.contentprovidertest.provider表示,唯一的,一般指的是包名,
路徑:person,表示的是person這個表,2表示id為2。
如果要把上面的字符串轉變為uri,那麼就要使用Uri類中的parse()方法,如下:
Uri uri=Uri.parse("content://com.example.contentprovidertest.provider/person/2");
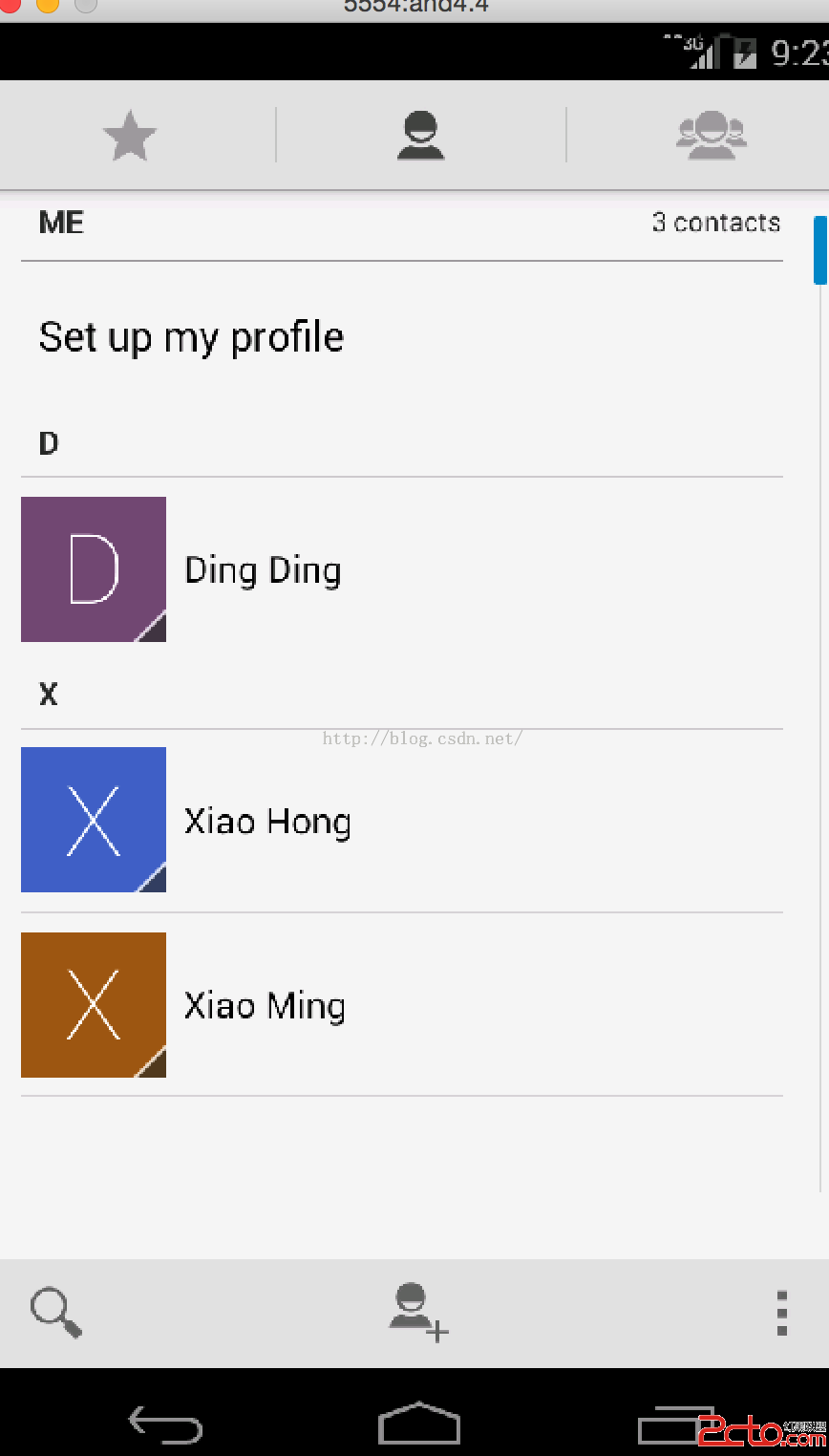
這裡先來寫個例子,用來獲取通訊錄中的信息吧。新建ContentProviderTest工程,因為模擬器的聯系人還沒有創建,這裡先添加幾個好友:
接著我們繼續編寫代碼,先在layout中添加listview,因為通訊錄一般都是用listview來實現的。代碼如下:
<!--{cke_protected}{C}%3C!%2D%2D%3Fxml%20version%3D%221.0%22%20encoding%3D%22utf-8%22%3F%2D%2D%3E-->
<linearlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.example.jared.contentprovidertest.MainActivity">
<listview android:id="@+id/contacts" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_width="match_parent">
</listview></linearlayout>
package com.example.jared.contentprovidertest;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.provider.ContactsContract;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ListView contactViews;
ArrayAdapter adapter;
List contactList = new ArrayList();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
contactViews = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.contacts);
adapter = new ArrayAdapter(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, contactList);
contactViews.setAdapter(adapter);
readContacts();
}
public void readContacts() {
Cursor cursor = null;
try {
cursor = getContentResolver().query(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI,
null, null, null, null);
while(cursor.moveToNext()) {
String ContactName = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.DISPLAY_NAME));
String ContactPhoneNum = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER));
contactList.add(ContactName+'\n'+ContactPhoneNum);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(cursor != null){
cursor.close();
}
}
}
}
String DISPLAY_NAME = "display_name";
String NUMBER = "number";這個和數據庫的存取很類似,接著在AndroidManifest中添加權限:
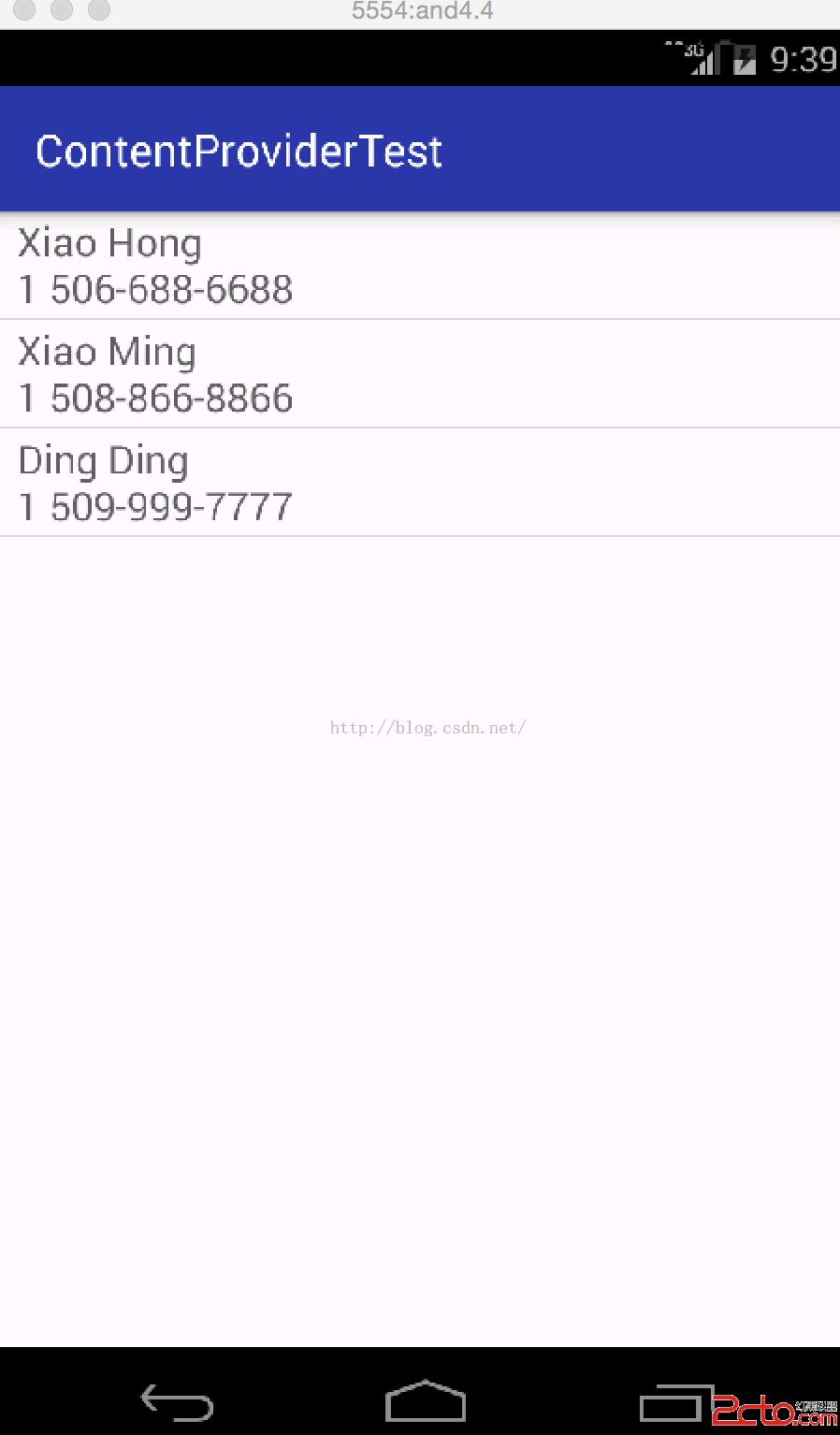
由上可知,獲得了三個聯系人的信息,也就是我們剛保存的信息。
接著學習自定義的ContentProvider,這裡借用了dbtest中的MyDBHelper類,新建myContenProvider類,代碼如下:
package com.example.jared.contentprovidertest;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
/**
* Created by jared on 16/2/15.
*/
public class myContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
public static final int PERSON_DIR = 0;
public static final int PERSON_ITEM = 1;
public static final int TEACHER_DIR = 2;
public static final int TEACHER_ITEM = 3;
private static UriMatcher uriMatcher;
private static final String AUTHORITY = "com.example.jared.contentprovidertest.provider";
private MyDBHelper myDBHelper;
static {
uriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "person", PERSON_DIR);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "person/#", PERSON_ITEM);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "teacher", TEACHER_DIR);
uriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "teacher/#", TEACHER_DIR);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
myDBHelper = new MyDBHelper(getContext(), "PersonStore.db", null, 2);
return true;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues contentValues, String s, String[] strings) {
SQLiteDatabase db = myDBHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int updateRows = 0;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
case PERSON_DIR:
updateRows = db.update("person", contentValues, s, strings);
break;
case PERSON_ITEM:
String personId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
updateRows = db.update("person", contentValues, "id = ?", new String[]{personId});
break;
case TEACHER_DIR:
updateRows = db.update("teacher", contentValues, s, strings);
break;
case TEACHER_ITEM:
String teacherId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
updateRows = db.update("teacher", contentValues, "id = ?", new String[]{teacherId});
break;
default:
break;
}
return updateRows;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String s, String[] strings) {
SQLiteDatabase db = myDBHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int deleteRows = 0;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
case PERSON_DIR:
deleteRows = db.delete("person", s, strings);
break;
case PERSON_ITEM:
String personId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
deleteRows = db.delete("person", "id = ?", new String[]{personId});
break;
case TEACHER_DIR:
deleteRows = db.delete("teacher", s, strings);
break;
case TEACHER_ITEM:
String teacherId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
deleteRows = db.delete("teacher", "id = ?", new String[]{teacherId});
break;
default:
break;
}
return deleteRows;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
case PERSON_DIR:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd."+AUTHORITY+".person";
//break;
case TEACHER_DIR:
return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd."+AUTHORITY+".teacher";
//break;
case PERSON_ITEM:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd."+AUTHORITY+".person";
//break;
case TEACHER_ITEM:
return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd."+AUTHORITY+".teacher";
//break;
default:
break;
}
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] strings, String s, String[] strings1, String s1) {
SQLiteDatabase db = myDBHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = null;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
case PERSON_DIR:
cursor = db.query("person", strings, s, strings1, null, null, s1);
break;
case PERSON_ITEM:
String personId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
cursor = db.query("person", strings, "id = ?", new String[]{personId}, null, null, s1);
break;
case TEACHER_DIR:
cursor = db.query("teacher", strings, s, strings1, null, null, s1);
break;
case TEACHER_ITEM:
String teacherId = uri.getPathSegments().get(1);
cursor = db.query("teacher", strings, "id = ?", new String[]{teacherId}, null, null, s1);
break;
default:
break;
}
return cursor;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues contentValues) {
SQLiteDatabase db = myDBHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Uri uriReturn = null;
switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) {
case PERSON_DIR:
case PERSON_ITEM:
long newPersonId = db.insert("person", null, contentValues);
uriReturn = Uri.parse("content://"+AUTHORITY+"/person/"+newPersonId);
break;
case TEACHER_DIR:
case TEACHER_ITEM:
long newTeacherId = db.insert("teacher", null, contentValues);
uriReturn = Uri.parse("content://"+AUTHORITY+"teacher"+newTeacherId);
break;
default:
break;
}
return uriReturn;
}
}
通過UriMatcher來匹配uri,然後通過Uri.parse解析uri。此外這裡又重寫了onCreate方法,update方法,delete方法。getType方法,query方法,insert方法。其中onCreate方法主要是創建數據庫,update為更新數據,delete是刪除數據,query是查詢數據,insert為插入數據,基本和數據庫的操作很類似。
getType方法主要是獲取Uri對象的MIME類型
如果以路徑結尾的話,那麼就是:vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.+authoriry+.path;
如果以id結尾的話,那麼就是:vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.+authoriry+.path;
接著就是AndroidManifest了,代碼如下:
<!--{cke_protected}{C}%3C!%2D%2D%3Fxml%20version%3D%221.0%22%20encoding%3D%22utf-8%22%3F%2D%2D%3E-->
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.jared.contentprovidertest">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS">
<application android:allowbackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:supportsrtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN">
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER">
</category></action></intent-filter>
</activity>
<provider android:name=".myContentProvider" android:exported="true" android:authorities="com.example.jared.contentprovidertest.provider">
</provider>
</application>
</uses-permission></manifest>
接著我們創建一個ContentProviderTest2工程,用來獲取,操作ContentProviderTest的內容。layout就參考了dbtest的工程的代碼:
<!--{cke_protected}{C}%3C!%2D%2D%3Fxml%20version%3D%221.0%22%20encoding%3D%22utf-8%22%3F%2D%2D%3E-->
<linearlayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"><button android:id="@+id/createDB" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="創建數據庫">
<linearlayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</linearlayout></button><button android:id="@+id/addData" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="添加數據"></button><button android:id="@+id/updateData" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="更新數據"></button><button android:id="@+id/delData" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="刪除數據"></button><button android:id="@+id/queryData" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="查詢數據"></button></linearlayout>
package com.example.jared.contentprovidertest2;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAB = "MainActivity";
private Button addDataBtn;
private Button deleteDataBtn;
private Button updateDataBtn;
private Button queryDataBtn;
public String id1, id2;
private static final String PERSON_URI = "content://com.example.jared.contentprovidertest.provider/person";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
addDataBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.addData);
addDataBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
deleteDataBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.delData);
deleteDataBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
updateDataBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.updateData);
updateDataBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
queryDataBtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.queryData);
queryDataBtn.setOnClickListener(new myOnClickListener());
}
private class myOnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.addData:
id1 = setAddDataBtn("xiao ming", 20, 172.5, "man");
id2 = setAddDataBtn("xiao hong", 22, 162.5, "woman");
break;
case R.id.delData:
setDeleteDataBtn(id1);
break;
case R.id.updateData:
setUpdateDataBtn(id1, 175.0);
break;
case R.id.queryData:
setQueryDataBtn();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
public void setQueryDataBtn() {
Uri uri = Uri.parse(PERSON_URI);
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, null, null, null, null);
if(cursor != null) {
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String personName = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));
int personAge = cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("age"));
double personHeight = cursor.getDouble(cursor.getColumnIndex("height"));
String personSex = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("sex"));
Log.d(TAB, "name:"+personName + " |age:"+personAge + " |height:"
+personHeight + " |sex:"+personSex);
}
cursor.close();
}
}
public void setUpdateDataBtn(String id, double height) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse(PERSON_URI+"/"+id);
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("height", height);
getContentResolver().update(uri, values, null, null);
}
public void setDeleteDataBtn(String id) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse(PERSON_URI+"/"+id);
getContentResolver().delete(uri, null, null);
}
public String setAddDataBtn(String name, int age, double height, String sex) {
Uri uri = Uri.parse(PERSON_URI);
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("name", name);
values.put("age", age);
values.put("height", height);
values.put("sex", sex);
Uri newUri = getContentResolver().insert(uri, values);
return newUri.getPathSegments().get(1);
}
}
這裡基本上都是先把字符串轉換為Uri,然後通過getContentResolver()類的方法來實現各個功能,准備好代碼後,我們繼續運行看下效果:
首先是添加功能:按添加按鈕再按查詢,查看log信息如下:
02-15 03:47:53.730 17319-17319/com.example.jared.contentprovidertest2 D/MainActivity: name:xiao ming |age:20 |height:172.5 |sex:man 02-15 03:47:53.780 17319-17319/com.example.jared.contentprovidertest2 D/MainActivity: name:xiao hong |age:22 |height:162.5 |sex:woman已經添加了數據,然後是更新功能:按更新按鈕再按查詢,查看log信息如下:
02-15 03:49:33.210 17319-17319/com.example.jared.contentprovidertest2 D/MainActivity: name:xiao ming |age:20 |height:175.0 |sex:man 02-15 03:49:33.210 17319-17319/com.example.jared.contentprovidertest2 D/MainActivity: name:xiao hong |age:22 |height:162.5 |sex:woman已經更新身高為175.0了,然後是刪除功能:按刪除按鈕再按查詢,查看log信息如下:
02-15 03:50:46.650 17319-17319/com.example.jared.contentprovidertest2 D/MainActivity: name:xiao hong |age:22 |height:162.5 |sex:woman查詢功能已經在上面的多次操作中用過了,基本上訪問另外一個app數據的功能也實現了。ContentProvider就先學到這裡了,繼續學習別的內容!
 ORB_SLAM2在Android上的移植過程
ORB_SLAM2在Android上的移植過程
ORB_SLAM2在Android上的移植過程 一直沒時間寫博客,最近抽時間寫了些關於在ORB_SLAM2在Android上的移植過程,也算是點經驗吧。 寫完後一個手
 生命不息,折騰不止
生命不息,折騰不止
生命不息,折騰不止截止到今天,我個人已經折騰了四個小玩意兒:高歌一曲(音樂播放器)、LMOS(x86_64體系的操作系統內核)、LMOSEM(ARM體系的操作系統內核),
 Android 手機衛士7--黑名單攔截,android7--
Android 手機衛士7--黑名單攔截,android7--
Android 手機衛士7--黑名單攔截,android7-- 1,黑名單數據庫創建 三個字段(_id 自增長字段 phone 黑名單號碼 mode 攔截類型) 創建表
 ListView初探,初探網
ListView初探,初探網
ListView初探,初探網一、ListView介紹 在Android開發中ListView是比較常用的控件,常用於以列表的形式顯示數據集及根據數據的長度自適應顯示。 L