編輯:關於android開發
Handler想必在大家寫Android代碼過程中已經運用得爐火純青,特別是在做阻塞操作線程到UI線程的更新上.Handler用得恰當,能防止很多多線程異常.
而Looper大家也肯定有接觸過,只不過寫應用的代碼一般不會直接用到Looper.但實際Handler處理Message的關鍵之處全都在於Looper.
以下是我看了<深入理解Android>的有關章節後,寫的總結.
Handler
先來看看Handler的構造函數.
public Handler() {
this(null, false);
}
public Handler(Looper looper) {
this(looper, null, false);
}
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
klass.getCanonicalName());
}
}
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
主要關注Handler的2個成員變量mQueue,mLooper
mLooper可以從構造函數傳入.如果構造函數不傳的話,則直接取當前線程的Looper:mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
mQueue就是mLooper.mQueue.
把Message插入消息隊列
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue == null) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
return false;
}
return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);
}
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this;
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
上面兩個正是把Message插入消息隊列的方法.
從中能看出,Message是被插入到mQueue裡面,實際是mLooper.mQueue.
每個Message.target = this,也就是target被設置成了當前的Handler實例.
到此,我們有必要看看Looper是做一些什麼的了.
Looper
這是Looper一個標准的使用例子.
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
......
Looper.loop();
}
}
我們再看看Looper.prepare()和Looper.loop()的實現.
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
}
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
public static Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
}
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
}
msg.recycleUnchecked();
}
}
prepare()方法給sThreadLocal設置了一個Looper實例.
sThreadLocal是Thread Local Variables,線程本地變量.
每次調用myLooper()方法就能返回prepare()設置的Looper實例.
Looper()方法裡面有一個很顯眼的無限For循環,它就是用來不斷的處理messageQueue中的Message的.
最終會調用message.target.dispatchMessage(msg)方法.前面介紹過,target是handler的實例.下面看看handler.dispatchMessage()方法的實現.
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
}
實現非常簡單,如果callback不為空則用handleCallback(msg)來處理message.
而大多數情況下,我們實例化Handler的時候都沒有傳callback,所以都會走到handler.handleMessage()方法了.這方法用過Handler的人,都在再熟悉不過了.
這就是Handler和Looper協同工作的原理.消息隊列的實現都在Looper,Handler更像是一個輔助類.
HandlerThread
多數情況下,我們都是用Handler來處理UI界面的更新,這時我們要保證handler的Looper是UI線程的Looper.
只需要這樣子實例化Handler就能保證在UI線程處理Message了:Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
而當我們不希望Handler在UI線程去處理Message時候,就需要新建一個線程然後把線程的Looper傳給Handler做實例化.
也許我們會寫出下面類似的代碼(樣例代碼引用<深入理解Android>)
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Looper myLooper = null;
// 定義一個public 的成員myLooper,初值為空。
public void run() {
// 假設run 在線程2 中執行
Looper.prepare();
// myLooper 必須在這個線程中賦值
myLooper = Looper.myLooper();
Looper.loop();
}
}
// 下面這段代碼在線程1 中執行,並且會創建線程2
{
LooperThread lpThread= new LooperThread;
lpThread.start();//start 後會創建線程2
Looper looper = lpThread.myLooper;//<====== 注意
// thread2Handler 和線程2 的Looper 掛上鉤
Handler thread2Handler = new Handler(looper);
//sendMessage 發送的消息將由線程2 處理
threadHandler.sendMessage(...)
}
細心的你們可能已經一眼看穿,new Handler(looper);傳進來的looper可能為空.
原因是Looper looper = lpThread.myLooper時候,lpThread.myLooper可能為空,因為lpThread還沒有開始執行run()方法.
那要怎麼樣才能保證handler實例化時候,looper不為空呢.
Android給我們提供了完美的解決方案,那就是HandlerThread.
public class HandlerThread extends Thread{
// 線程1 調用getLooper 來獲得新線程的Looper
public Looper getLooper() {
......
synchronized (this) {
while (isAlive() && mLooper == null) {
try {
wait();// 如果新線程還未創建Looper,則等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
return mLooper;
}
// 線程2 運行它的run 函數,looper 就是在run 線程裡創建的。
public void run() {
mTid = Process.myTid();
Looper.prepare(); // 創建這個線程上的Looper
synchronized (this) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
notifyAll();// 通知取Looper 的線程1,此時Looper 已經創建好了。
}
Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority);
onLooperPrepared();
Looper.loop();
mTid = -1;
}
}
HandlerThread.getLooper()方法會等待mLooper被賦值了才返回.
在handler實例化調用handlerThread.getLooper()方法的時候,就能保證得到的Looper一定不為空了.
HandlerThread handlerThread = new HandlerThread(); handlerThread.start(); Handler handler = new Handler(handlerThread.getLooper());
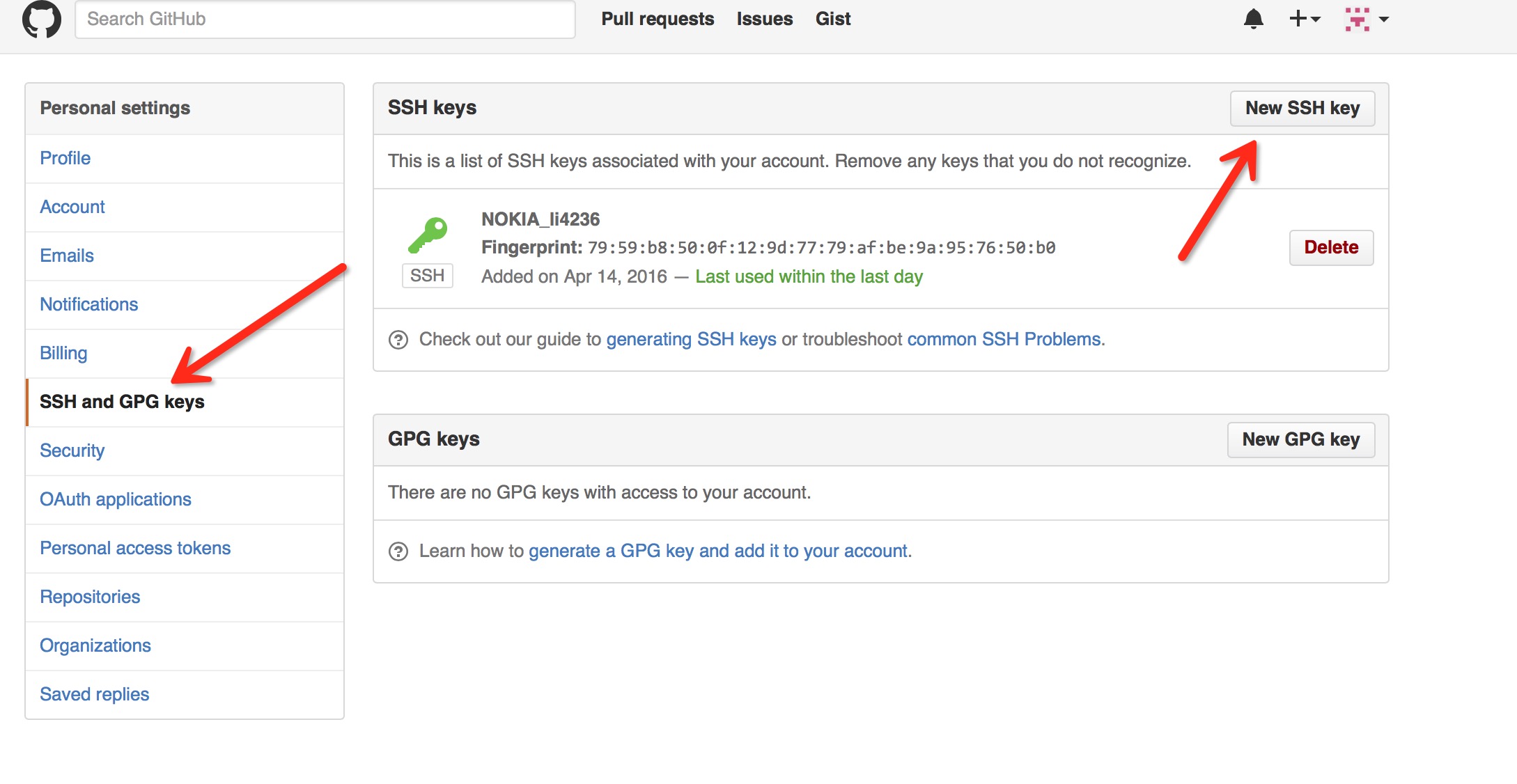 Mac Android studio提交本地項目到Github 已經配置 SSH KEY
Mac Android studio提交本地項目到Github 已經配置 SSH KEY
Mac Android studio提交本地項目到Github 已經配置 SSH KEY 注冊賬號 https://github.com 在本地配置ssh key秘鑰
 百度地圖定位簽到功能,百度地圖簽到
百度地圖定位簽到功能,百度地圖簽到
百度地圖定位簽到功能,百度地圖簽到 1. 注意 key 一定要在activity 前面 <application android:allowBackup=tr
 Activity與Service進行數據交互,activityservice
Activity與Service進行數據交互,activityservice
Activity與Service進行數據交互,activityserviceAndroid啟動Service有兩種方法,一種是startService,一種是bindSe
 通過jni調用OpenCv跟直接調用android版openCv對圖片進行簡單的變換
通過jni調用OpenCv跟直接調用android版openCv對圖片進行簡單的變換
通過jni調用OpenCv跟直接調用android版openCv對圖片進行簡單的變換 看看效果圖,如果運行時提示需要安裝xxxx.mamager,那麼就去現在Opencv
 ErrorExecution failed for task 'apptransformClassesWithDexForDebug',classes.dex
ErrorExecution failed for task 'apptransformClassesWithDexForDebug',classes.dex
ErrorExecution failed for task '