編輯:關於android開發
ContentProvider為存儲和獲取數據提供統一的接口,它可以在不同的應用程序之間共享數據,本身就是適合進程間通信的。ContentProvider底層實現也是Binder,但是使用起來比AIDL要容易許多。系統也預制了很多的ContentProvider,例如通訊錄,音視頻等,這些操作本身就是跨進程進行通信。這篇文章主要是我們來自己實現用ContentProvider來進行進程間通信,而非介紹ContentProvider怎麼使用。
1. 建立數據庫,方便ContentProvider使用
我們創建數據庫,並創建表”game_provider.db”,裡面有兩個字段分別存儲游戲的名字和游戲的描述。(DbOpenHelper.java)
package com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovider;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class DbOpenHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private static final String DB_NAME="game_provider.db";
static final String GAME_TABLE_NAME="game";
private static final int DB_VERSION=1;
private String CREATE_GAME_TABLE="create table if not exists " + GAME_TABLE_NAME +"(_id integer primary key," + "name TEXT, "+"describe TEXT)";
public DbOpenHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DB_NAME, null, DB_VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL(CREATE_GAME_TABLE);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}
2. 使用ContentProvider對數據庫進行操作
在initProvoder方法中,我們開啟線程來對數據庫進行操作,刪除表的所有數據,再添加數據,並實現了query和insert方法。(GameProvider.java)
package com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovider;
import android.content.ContentProvider;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.UriMatcher;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.net.Uri;
public class GameProvider extends ContentProvider {
public static final String AUTHORITY = "com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovide.GameProvider";
public static final Uri GAME_CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse("content://" + AUTHORITY + "/game");
private static final UriMatcher mUriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH);
private SQLiteDatabase mDb;
private Context mContext;
private String table;
static {
mUriMatcher.addURI(AUTHORITY, "game", 0);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
table = DbOpenHelper.GAME_TABLE_NAME;
mContext = getContext();
initProvoder();
return false;
}
private void initProvoder() {
mDb = new DbOpenHelper(mContext).getWritableDatabase();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mDb.execSQL("delete from " + DbOpenHelper.GAME_TABLE_NAME);
mDb.execSQL("insert into game values(1,'九陰真經ol','最好玩的武俠網游');");
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) {
String table = DbOpenHelper.GAME_TABLE_NAME;
Cursor mCursor = mDb.query(table, projection, selection, selectionArgs, null, sortOrder, null);
return mCursor;
}
@Override
public String getType(Uri uri) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
mDb.insert(table, null, values);
mContext.getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null);
return null;
}
@Override
public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
}
在manifest文件中,我們要讓ContentProvider運行在另一個進程,如果不大了解如何開啟進程,可以查看本系列的第一篇文章Android IPC機制(一)開啟多進程
3. 在Activity中調用另一個進程的GameProvider的方法
在Activity中我們在GameProvider再插入一條數據(此前GameProvider初始化時已經插入了一條數據),然後調用GameProvider的query方法來查詢數據庫中有幾條數據並打印出來。
package com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovider;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class ContentProviderActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private final static String TAG = "ContentProviderActivity";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_content_provider);
Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovide.GameProvider");
ContentValues mContentValues = new ContentValues();
mContentValues.put("_id", 2);
mContentValues.put("name", "大航海時代ol");
mContentValues.put("describe", "最好玩的航海網游");
getContentResolver().insert(uri, mContentValues);
Cursor gameCursor = getContentResolver().query(uri, new String[]{"name", "describe"}, null, null, null);
while (gameCursor.moveToNext()) {
Game mGame = new Game(gameCursor.getString(0), gameCursor.getString(1));
Log.i(TAG, mGame.gameName + "---" + mGame.gameDescribe);
}
}
}
Bean文件 Game.java在Android IPC機制(三)在Android Studio中使用AIDL實現跨進程方法調用這篇文章中用過,直接拿過來用:
package com.example.liuwangshu.mooncontentprovider;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Game implements Parcelable {
public String gameName;
public String gameDescribe;
public Game(String gameName, String gameDescribe) {
this.gameName = gameName;
this.gameDescribe = gameDescribe;
}
protected Game(Parcel in) {
gameName = in.readString();
gameDescribe = in.readString();
}
public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
@Override
public Game createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new Game(in);
}
@Override
public Game[] newArray(int size) {
return new Game[size];
}
};
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(gameName);
dest.writeString(gameDescribe);
}
}
我們運行程序,發現GameProvider運行在另一個線程
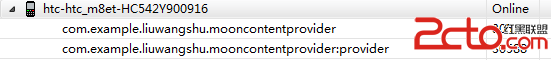
log中也打印出了我們想要的結果,打出了兩條游戲信息:

 Android開發4: Notification編程基礎、Broadcast的使用及其靜態注冊、動態注冊方式,靜態庫與動態庫編程
Android開發4: Notification編程基礎、Broadcast的使用及其靜態注冊、動態注冊方式,靜態庫與動態庫編程
Android開發4: Notification編程基礎、Broadcast的使用及其靜態注冊、動態注冊方式,靜態庫與動態庫編程前言 啦啦啦~(博主每次開篇都要賣個萌
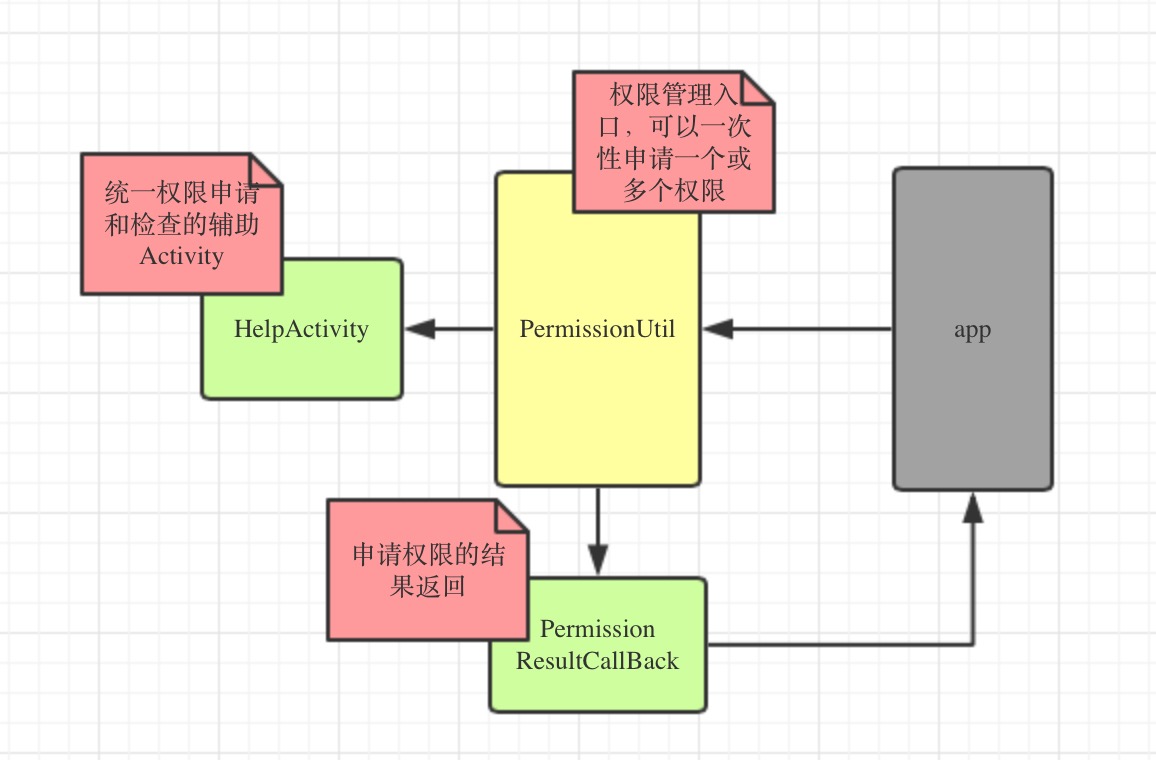 android6.0權限管理工具EasyPermissionUtil
android6.0權限管理工具EasyPermissionUtil
android6.0權限管理工具EasyPermissionUtil 前言 android6.0開始,權限的申請發生了改變,申請變的動態化,也就是運行時權限,和iOS相仿
 自定義可點擊的ImageSpan並在TextView中內置“View“,imagespantextview
自定義可點擊的ImageSpan並在TextView中內置“View“,imagespantextview
自定義可點擊的ImageSpan並在TextView中內置“View“,imagespantextview有的時候可能想在TextView中添加一些圖片,比如下圖,發短信
 Android 對程序異常崩潰的捕捉,android崩潰捕捉
Android 對程序異常崩潰的捕捉,android崩潰捕捉
Android 對程序異常崩潰的捕捉,android崩潰捕捉轉載博客:http://blog.csdn.net/i_lovefish/article/details/17