編輯:關於android開發
1,android:orientation
布局方向。horizontal是讓所有的子元素按水平方向從左到右排列, vertical是讓所有的子元素按豎直方向從上到下排列。
2,android:gravity 與 android:layout_gravity的區別android:gravity是指定本元素的子元素相對它的對齊方式。
android:layout_gravity是指定本元素相對它的父元素的對齊方式。
例如:
下面這裡的linearlayout的android:gravity設為right,有兩個子元素Button01和Button02。
java代碼:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
android:orientation=”vertical”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”fill_parent”
android:gravity=”right”
>
<Button android:text=”button01″ android:id=”@+id/Button01″ android:layout_width=”wrap_content” android:layout_height=”wrap_content”></Button>
<Button android:text=”button02″ android:id=”@+id/Button02″ android:layout_width=”wrap_content” android:layout_height=”wrap_content”></Button>
</LinearLayout>
這個main.xml裡的LinearLayout也是有兩個子元素Button01和Button02。Button01的android:layout_gravity設為”left”,Button02的 android:layout_gravity設為”right”
java代碼:
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
android:orientation=”vertical”
android:layout_width=”fill_parent”
android:layout_height=”fill_parent”
>
<Button
android:layout_gravity=”left”
android:text=”button01″
android:id=”@+id/Button01″
android:layout_width=”wrap_content” a
ndroid:layout_height=”wrap_content”></Button>
<Button
android:layout_gravity=”right”
android:text=”button02″
android:id=”@+id/Button02″
android:layout_width=”wrap_content”
android:layout_height=”wrap_content”>
</Button>
</LinearLayout>
FameLayout布局
FrameLayout是最簡單的一個布局對象。它被定制為你屏幕上的一個空白備用區域,之後你可以在其中填充一個單一對象—比如,一張你要發布的圖片。所有的子元素將會固定在屏幕的左上角;你不能為FrameLayout中的一個子元素指定一個位置。後一個子元素將會直接在前一個子元素之上進行覆蓋填充,把它們部份或全部擋住(除非後 一個子元素是透明的)。
xml屬性
1,用xml文件來定義界面,然後Activity的setContentView方法根據xml文件裡的定義來創建真正的控件對象。好比說xml文件是設計圖紙,setContentView是生產機器,它依照圖紙生產出各種各樣的杯具和洗具。
2,FrameLayout的xml屬性來自三個地方:繼承下來的,嵌套類定義的,自身類定義的。
3,具的屬性可查閱官方文檔。下面是剛才遇到的幾個屬性。
java代碼:
android:id
//這個xml屬性是繼承自android.view類的xml屬性。它為framelayout提供一個唯一識別符號,之後,程序要用到它時可以用View.findViewById() 或Activity.findViewById()來找到它。
android:layout_width: 布局寬
android:layout_height: 布局高
//它們的取值是fill_parent或wrap_content。
fill_parent :在x軸或則y軸上充滿父容器的空間。
wrap_content :framelayout裡的元素有多少寬高就多少寬高,
//這兩個屬性都是定義在android.widget.FrameLayout的嵌套類android.widget.FrameLayout.LayoutParams裡。
android:background:背景
android:foreground :前景
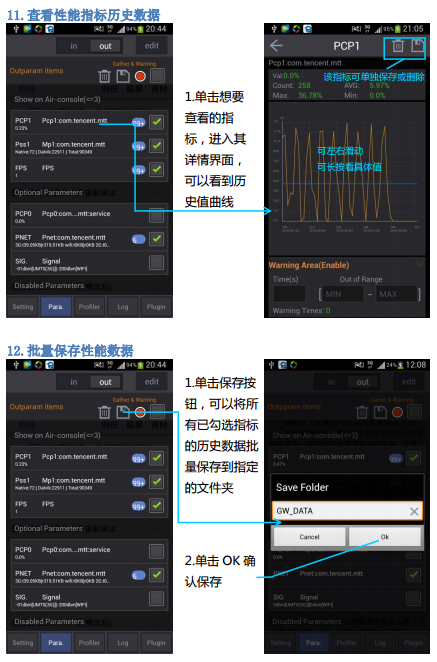 【Android性能工具】騰訊開源工具GT(隨身調),androidgt
【Android性能工具】騰訊開源工具GT(隨身調),androidgt
【Android性能工具】騰訊開源工具GT(隨身調),androidgt做App測試時監測使用期間的cpu,內存,流量,電量等指標時,發現的企鵝很好用的工具。 備份至此,
 安卓--shape簡單使用,安卓--shape
安卓--shape簡單使用,安卓--shape
安卓--shape簡單使用,安卓--shapeshape 先看下,系統自帶的EditText和Button的外形 下面看加了shape後的效
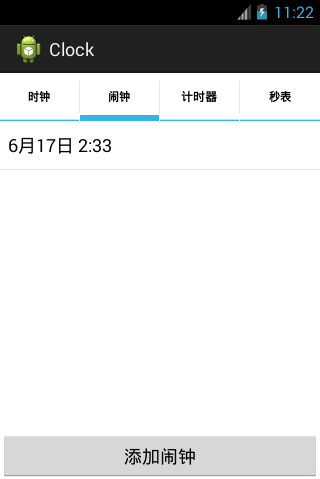 詳解安卓項目-鬧鐘,詳解安卓鬧鐘
詳解安卓項目-鬧鐘,詳解安卓鬧鐘
詳解安卓項目-鬧鐘,詳解安卓鬧鐘一.概述 * 鬧鐘功能概述:添加鬧鐘,刪除鬧鐘 * 思路: * 1.給一個button添加點擊監聽,用於添加鬧鐘 * 2.提供
 LeanCloud使用入門(android),leancloudandroid
LeanCloud使用入門(android),leancloudandroid
LeanCloud使用入門(android),leancloudandroidLeanCloud算是一個簡單易用的雲服務器,其中包含了強大的數據庫支持,我們只需要將此服務
 Android移動APP開發筆記——Cordova(PhoneGap)通過CordovaPlugin插件調用 Activity 實例,phonegapcordova
Android移動APP開發筆記——Cordova(PhoneGap)通過CordovaPlugin插件調用 Activity 實例,phonegapcordova
Android移動APP開發筆記——Cordova(PhoneGap)通
 運用安卓CreateOptionsMenu和onCreateContextMenu菜單,模擬微信聊天界面長按彈出菜單選項。,oncreateoptionsmenu
運用安卓CreateOptionsMenu和onCreateContextMenu菜單,模擬微信聊天界面長按彈出菜單選項。,oncreateoptionsmenu
運用安卓CreateOptionsMenu和onCreateContex