開始今天的主題,控件渲染Shade(也可以叫著色器)的使用,一直都有在關注這方面的東西,網上也有部分文章寫得不錯,但是還是覺得不過瘾,往往都是寫一點點自己在工作中使用過的,有看到過很多人經典問這個邊框那個邊框的,呵呵,今天就總結下這方面的東西,希望對這塊知識有興趣的帥果、美驢們有所幫助或提高,也備自己不時之用,果斷先看效果再一步步看代碼!希望大家仔細看看我在XML及.java中添加的注釋,相信你不會後悔花時間在這文章上的,今天的DEMO效果圖如下:
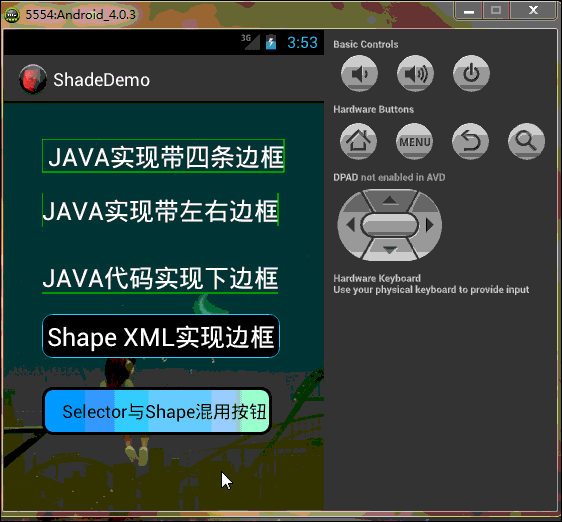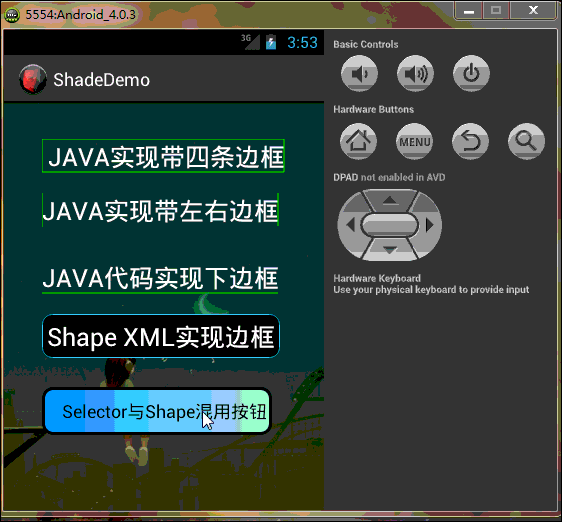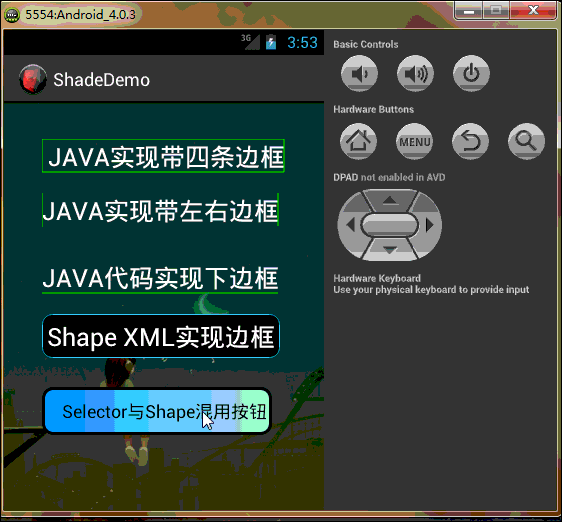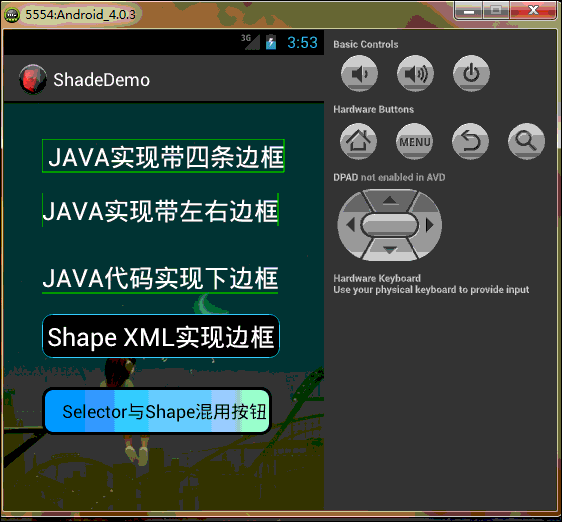
工程目錄結構如下,由於太長的原因,部分已縮進:
好了,效果看完了,下一步開始看代碼吧,親…….靜下心….一步步來!!! PS:模擬器與eclipse效果中
預覽的以下部分有點不一樣,可能是eclipse與模擬器二者之前存在Bug吧…吼吼….
首先,先做個小小的鋪墊:
Android提供的Shader類主要是渲染圖像以及一些幾何圖形。
Shader有幾個直接子類:
BitmapShader : 主要用來渲染圖像
LinearGradient :用來進行線性渲染
RadialGradient : 用來進行環形渲染
SweepGradient : 掃描漸變—圍繞一個中心點掃描漸變就像電影裡那種雷達掃描,用來梯度渲染。
ComposeShader : 組合渲染,可以和其他幾個子類組合起來使用。
小記:Android控件渲染Shade的實現方式有兩種,(一、JAVA代碼實現;二、XML配置來實現),
自己比較偏向XML實現,原因很簡單:
1.你代碼實現寫得再經典,不跑起來效果看不到!
2.跑一遍Android模擬器,思路可以斷一大節!(我很笨,經常這樣 T_T)!
3.JAVA代碼的每個函數參數你也得一個個去啃(老板管效率,不管怎麼實現,等你啃完參數時,XML已經看到效果了 O_o ……走起…..)!
4.這是最主要的一點,Eclipse或者I/O大會剛推出的Android Studio,實時顯示,我就特別喜歡 立竿見影 ^_^ !
5.二者各有利弊,JAVA代碼實現可以動態且靈活滴,XML配置的統一但不雜亂 @_@!!
Now…….. Ladies and 鄉親們,看舉一種JAVA代碼excmple,其余類型的與之類似,親們自己“度娘 、谷哥 ”:
LinearGradient是線性漸變,用法如下:
Gradient是基於Shader類,所以我們通過Paint的setShader方法來設置這個漸變,代碼如下:
Paint p=new Paint();
LinearGradient lg=newLinearGradien(0,0,100,100,Color.RED,Color.BLUE,Shader.TileMode.MIRROR);
Gradient是基於Shader類,所以我們通過Paint的setShader方法來設置這個漸變,代碼如下:
p.setShader(lg);
canvas.drawCicle(0,0,200,p); //參數3為畫圓的半徑,類型為float型。
先不說效果了,PS:看著上面的代碼,有沒有想哭的沖動啊 ? ? ?感覺亂亂的,不知道是什麼,然後單詞gradient不懂,一查如下(暈),看著挺牛,還是只是個渲染!不管了,繼續往下看…
再看XML布局文件代碼:
一:主布局文件代碼如下(為了方便,布局是直接拖的,大家不用太關注):
XML/HTML代碼
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:background="@drawable/background"
- android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
- android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
- android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
- android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
- tools:context=".MainActivity" >
-
- <com.xiaoma.shadedemo.TextViewBorder
- android:id="@+id/textView1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
- android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
- android:layout_marginLeft="22dp"
- android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
- android:text=" JAVA實現帶四條邊框"
- android:textColor="@android:color/white"
- android:textSize="25sp" />
-
- <com.xiaoma.shadedemo.TextViewBorderLeftRight
- android:id="@+id/TextViewBorder01"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:textColor="@android:color/white"
- android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/textView1"
- android:layout_below="@+id/textView1"
- android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
- android:text="JAVA實現帶左右邊框"
- android:textSize="25sp" />
-
- <com.xiaoma.shadedemo.TextViewBorderUnder
- android:id="@+id/TextViewBorder02"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/TextViewBorder01"
- android:textColor="@android:color/white"
- android:layout_below="@+id/TextViewBorder01"
- android:layout_marginTop="33dp"
- android:text="JAVA代碼實現下邊框"
- android:textSize="25sp" />
-
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/TextViewBorderUnder01"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button1"
- android:layout_below="@+id/TextViewBorder02"
- android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
- android:text="Shape XML實現邊框"
- android:background="@drawable/shape_test"
- android:textColor="@android:color/white"
- android:textSize="25sp" />
-
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/button1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/TextViewBorder02"
- android:layout_below="@+id/TextViewBorderUnder01"
- android:layout_marginTop="29dp"
- android:background="@drawable/shape_selector"
- android:text="Selector與Shape混用按鈕"
- android:textColor="@android:color/black" />
-
- </RelativeLayout>
二:上面布局中使用的自定義控件代碼及Shape渲染代碼分別如下:
2.1:JAVA實現帶四條邊框(自定義TextView JAVA代碼一)
Java代碼
- package com.xiaoma.shadedemo;
-
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.graphics.Canvas;
- import android.graphics.Color;
- import android.graphics.Paint;
- import android.util.AttributeSet;
- import android.widget.TextView;
-
- public class TextViewBorder extends TextView
- {
-
- /**
- * 下面兩個方法在構造時需注意: 一:如果是XML文件加載的方式使用自定義控件到布局中是用以下方式, 二:如果是用純代碼的方式加載自定義的控制到而已中時用第二種方式
- */
-
- // 方式一:
- public TextViewBorder(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
- {
- super(context, attrs);
- }
-
- // 方式二:
- /*
- * public TextViewBorder(Context context) { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub super(context); }
- */
-
- /**
- * 1. Rect對象 一個區域對象Rect(left, top, right, bottom) , 是一個左閉右開的區域, 即是說使用 Rect.contains(left, top)為true,
- * Rect.contains(right, bottom)為false 2. drawLine方法 drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY,
- * Paint paint) 也是一個左閉右開的區間,只會繪制到stopX-1,stopY-1 3. drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint) 當繪制空心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右閉的區域
- * 驗證方法:下面就是可以驗證左閉右開的區間方法,現在知道為什麼要-1 了
- */
-
- @Override
- protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
- {
- super.onDraw(canvas);
-
- Paint paint = new Paint();
-
- paint.setAntiAlias(true);
-
- paint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
-
- canvas.drawLine(0, 0, this.getWidth() - 1, 0, paint);// 繪制上邊框
-
- canvas.drawLine(0, 0, 0, this.getHeight() - 1, paint); // 繪制左邊框
-
- canvas.drawLine(this.getWidth() - 1, 0, this.getWidth() - 1, this.getHeight() - 1, paint); // 繪制右邊框
-
- canvas.drawLine(0, this.getHeight() - 1, this.getWidth() - 1, this.getHeight() - 1, paint);// 繪制下邊框
-
- }
-
- /*
- * 1. Rect對象
- *
- * 一個區域對象Rect(left, top, right, bottom) , 是一個左閉右開的區域,即是說使用 Rect.contains(left, top)為true, Rect.contains(right,
- * bottom)為false
- *
- * 2.drawLine方法
- *
- * drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY, Paint paint) 也是一個左閉右開的區間,只會繪制到stopX-1,stopY-1
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * Canvas c = canvas; paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+c.getWidth()-1, y, paint); c.drawLine(x,
- * y+height-1, x+c.getWidth(), y+height-1, paint); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawPoint(x+c.getWidth()-1, y,
- * paint); 說明drawLine是沒有繪制到右邊最後一個點的
- *
- * 3.drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint)
- *
- * 當繪制空心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右閉的區域
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * rect.set(x, y, x+width, y+height); paint.setStyle(Style.STROKE); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawRect(rect,
- * paint); paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+width, y, paint); c.drawLine(x, y+height, x+width,
- * y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x, y, x, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x+width, y, x+width, y+height, paint);
- * 當繪制實心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右開的區域
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * rect.set(x, y, x+width, y+height); paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+width, y, paint); c.drawLine(x,
- * y+height, x+width, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x, y, x, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x+width, y, x+width,
- * y+height, paint); paint.setStyle(Style.FILL); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawRect(rect, paint);
- * 這個規則跟j2me也是一樣的,在j2me裡,drawRect長寬會多畫出1px。SDK的說明是:
- *
- * The resulting rectangle will cover an area (width + 1) pixels wide by (height + 1) pixels tall. If either width
- * or height is less than zero, nothing is drawn.
- *
- * 例如drawRect(10,10,100,1)繪制,結果是一個2px高的矩形,用fillRect(10,10,100,1),結果是一個1px高的矩形
- *
- * 以上就是對Android繪圖的具體介紹。
- */
-
- }
-
- /**
- * 在布局文件中引用 這樣引用就行了..吼吼 <com.xiaoma.shadedemo.TextViewBorder android:id="@+id/a02_txtKSSJ" android:textColor="#000000"
- * android:layout_marginLeft="10dip" android:layout_width="100dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- */
2.2:JAVA實現帶左右邊框(自定義TextView JAVA代碼二)
Java代碼
- package com.xiaoma.shadedemo;
-
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.graphics.Canvas;
- import android.graphics.Color;
- import android.graphics.Paint;
- import android.util.AttributeSet;
- import android.widget.TextView;
-
- public class TextViewBorderLeftRight extends TextView
- {
-
- /**
- * 下面兩個方法在構造時需注意: 一:如果是XML文件加載的方式使用自定義控件到布局中是用以下方式, 二:如果是用純代碼的方式加載自定義的控制到而已中時用第二種方式
- */
-
- // 方式一:
- public TextViewBorderLeftRight(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
- {
- super(context, attrs);
- }
-
- // 方式二:
- /*
- * public TextViewBorder(Context context) { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub super(context); }
- */
-
- /**
- * 1. Rect對象 一個區域對象Rect(left, top, right, bottom) , 是一個左閉右開的區域, 即是說使用 Rect.contains(left, top)為true,
- * Rect.contains(right, bottom)為false 2. drawLine方法 drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY,
- * Paint paint) 也是一個左閉右開的區間,只會繪制到stopX-1,stopY-1 3. drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint) 當繪制空心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右閉的區域
- * 驗證方法:下面就是可以驗證左閉右開的區間方法,現在知道為什麼要-1 了
- */
-
- @Override
- protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
- {
- super.onDraw(canvas);
-
- Paint paint = new Paint();
-
- paint.setAntiAlias(true);
-
- paint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
-
- canvas.drawLine(0, 0, 0, getHeight(), paint);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(getWidth(), 0, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1, paint);
- canvas.drawLine(this.getWidth() - 1, 0, this.getWidth() - 1, this.getHeight() - 1, paint);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(0, 0, 0, this.getHeight() - 1, paint);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(this.getWidth() - 1, 0, this.getWidth() - 1, this.getHeight() - 1, paint);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(0, this.getHeight() - 1, this.getWidth() - 1, this.getHeight() - 1, paint);
-
- }
- /*
- * 1. Rect對象
- *
- * 一個區域對象Rect(left, top, right, bottom) , 是一個左閉右開的區域,即是說使用 Rect.contains(left, top)為true, Rect.contains(right,
- * bottom)為false
- *
- * 2.drawLine方法
- *
- * drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY, Paint paint) 也是一個左閉右開的區間,只會繪制到stopX-1,stopY-1
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * Canvas c = canvas; paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+c.getWidth()-1, y, paint); c.drawLine(x,
- * y+height-1, x+c.getWidth(), y+height-1, paint); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawPoint(x+c.getWidth()-1, y,
- * paint); 說明drawLine是沒有繪制到右邊最後一個點的
- *
- * 3.drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint)
- *
- * 當繪制空心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右閉的區域
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * rect.set(x, y, x+width, y+height); paint.setStyle(Style.STROKE); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawRect(rect,
- * paint); paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+width, y, paint); c.drawLine(x, y+height, x+width,
- * y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x, y, x, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x+width, y, x+width, y+height, paint);
- * 當繪制實心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右開的區域
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * rect.set(x, y, x+width, y+height); paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+width, y, paint); c.drawLine(x,
- * y+height, x+width, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x, y, x, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x+width, y, x+width,
- * y+height, paint); paint.setStyle(Style.FILL); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawRect(rect, paint);
- * 這個規則跟j2me也是一樣的,在j2me裡,drawRect長寬會多畫出1px。SDK的說明是:
- *
- * The resulting rectangle will cover an area (width + 1) pixels wide by (height + 1) pixels tall. If either width
- * or height is less than zero, nothing is drawn.
- *
- * 例如drawRect(10,10,100,1)繪制,結果是一個2px高的矩形,用fillRect(10,10,100,1),結果是一個1px高的矩形
- *
- * 以上就是對Android繪圖的具體介紹。
- */
-
- }
-
- /**
- * 在布局文件中引用 這樣引用就行了..吼吼 <com.xiaoma.shadedemo.TextViewBorder android:id="@+id/a02_txtKSSJ" android:textColor="#000000"
- * android:layout_marginLeft="10dip" android:layout_width="100dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- */
2.3:JAVA代碼實現下邊框(自定義TextView JAVA代碼三)
Java代碼
- package com.xiaoma.shadedemo;
-
- import android.content.Context;
- import android.graphics.Canvas;
- import android.graphics.Color;
- import android.graphics.Paint;
- import android.util.AttributeSet;
- import android.widget.TextView;
-
- public class TextViewBorderUnder extends TextView
- {
-
- /**
- * 下面兩個方法在構造時需注意: 一:如果是XML文件加載的方式使用自定義控件到布局中是用以下方式, 二:如果是用純代碼的方式加載自定義的控制到而已中時用第二種方式
- */
-
- // 方式一:
- public TextViewBorderUnder(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
- {
- super(context, attrs);
- }
-
- // 方式二:
- /*
- * public TextViewBorder(Context context) { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub super(context); }
- */
-
- /**
- * 1. Rect對象 一個區域對象Rect(left, top, right, bottom) , 是一個左閉右開的區域, 即是說使用 Rect.contains(left, top)為true,
- * Rect.contains(right, bottom)為false 2. drawLine方法 drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY,
- * Paint paint) 也是一個左閉右開的區間,只會繪制到stopX-1,stopY-1 3. drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint) 當繪制空心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右閉的區域
- * 驗證方法:下面就是可以驗證左閉右開的區間方法,現在知道為什麼要-1 了
- */
-
- @Override
- protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
- {
- super.onDraw(canvas);
-
- Paint paint = new Paint();
-
- paint.setAntiAlias(true);
-
- paint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(0, 0, this.getWidth() - 1, 0, paint);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(0, getHeight(), getWidth() - 1, getHeight(), paint);
-
- // canvas.drawLine(this.getWidth() - 1, 0, this.getWidth() - 1, this.getHeight() - 1, paint);
-
- canvas.drawLine(0, getHeight() - 1, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1, paint);
-
- }
-
- /*
- * 1. Rect對象
- *
- * 一個區域對象Rect(left, top, right, bottom) , 是一個左閉右開的區域,即是說使用 Rect.contains(left, top)為true, Rect.contains(right,
- * bottom)為false
- *
- * 2.drawLine方法
- *
- * drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY, Paint paint) 也是一個左閉右開的區間,只會繪制到stopX-1,stopY-1
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * Canvas c = canvas; paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+c.getWidth()-1, y, paint); c.drawLine(x,
- * y+height-1, x+c.getWidth(), y+height-1, paint); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawPoint(x+c.getWidth()-1, y,
- * paint); 說明drawLine是沒有繪制到右邊最後一個點的
- *
- * 3.drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint)
- *
- * 當繪制空心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右閉的區域
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * rect.set(x, y, x+width, y+height); paint.setStyle(Style.STROKE); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawRect(rect,
- * paint); paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+width, y, paint); c.drawLine(x, y+height, x+width,
- * y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x, y, x, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x+width, y, x+width, y+height, paint);
- * 當繪制實心矩形時,繪制的是一個左閉右開的區域
- *
- * 驗證方法:
- *
- * rect.set(x, y, x+width, y+height); paint.setColor(Color.RED); c.drawLine(x, y, x+width, y, paint); c.drawLine(x,
- * y+height, x+width, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x, y, x, y+height, paint); c.drawLine(x+width, y, x+width,
- * y+height, paint); paint.setStyle(Style.FILL); paint.setColor(Color.BLUE); c.drawRect(rect, paint);
- * 這個規則跟j2me也是一樣的,在j2me裡,drawRect長寬會多畫出1px。SDK的說明是:
- *
- * The resulting rectangle will cover an area (width + 1) pixels wide by (height + 1) pixels tall. If either width
- * or height is less than zero, nothing is drawn.
- *
- * 例如drawRect(10,10,100,1)繪制,結果是一個2px高的矩形,用fillRect(10,10,100,1),結果是一個1px高的矩形
- *
- * 以上就是對Android繪圖的具體介紹。
- */
-
- }
-
- /**
- * 在布局文件中引用 這樣引用就行了..吼吼 <com.xiaoma.shadedemo.TextViewBorder android:id="@+id/a02_txtKSSJ" android:textColor="#000000"
- * android:layout_marginLeft="10dip" android:layout_width="100dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- */
2.4:Shape XML實現邊框(XML代碼)
XML/HTML代碼
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
-
- <!-- <solid android:color="#cceeff"/> 直接寫這個的話,可以給控制添加一個整體的背景哦 -->
- <stroke
- android:width="0.5dp"
- android:color="#22ccff" />
-
- <padding android:left="5dp" android:top="5dp" android:right="5dp" android:bottom="5dp"/>
-
- <size
- android:height="0.5dp"
- android:width="5dp" />
- <!-- 目前沒有什麼用,可刪除,留在這個地方防止亂猜 -->
-
- <corners android:radius="10dp" />
- <!-- 這個radius裡面的值需要個整型,單位用dp,用其它單位亦無影響 -->
-
- </shape>
2.5:Selector與Shape混用控件效果實現
XML/HTML代碼
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
-
- <!-- 今天主要講的是shape渲染,shape主要類型分四種,效果如下,我們常用rectangle,也就是矩形渲染,其它的都太丑了!! -->
-
- <item android:state_pressed="true"> <!--按鈕按下時的渲染效果 -->
- <shape android:shape="oval">
-
- <corners android:radius="10dp" /> <!-- 四個角的角度 -->
-
- <!--gradient就是梯度渲染,簡單說就是顏色漸變,type為漸變方式,總共三種 linear sweep ridial,常用linear-->
- <gradient android:endColor="#eebbbb" android:startColor="#9900ee" android:type="linear" />
-
- <!-- padding屬性是指定內容與控件邊距,這個地方小馬專門將距左邊距設置較大,方便觀察 -->
- <padding android:bottom="5dp" android:left="20dp" android:right="5dp" android:top="5dp" />
-
- <!-- solid填充整個區域,顏色為FFDDFF,如果使用整個區域填充的話,上面的gradient梯度會失效,即:覆蓋 -->
- <!-- <solid android:color="#FFDDFF"/> -->
-
- <!-- stroke為需要填充的邊框,指定顏色及邊框寬度 -->
- <stroke android:width="3dp" android:color="#000000" />
- </shape>
-
- <!-- <clip android:clipOrientation="vertical" android:gravity="right" android:drawable="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> --><!-- 試了下沒用 -->
- <!-- <color android:color="#223344"/> -->
- <!-- <scale android:scaleWidth="15dp" android:scaleHeight=" 5dp" android:scaleGravity="center" /> -->
-
- </item>
-
- <item> <!-- 默認 -->
- <shape android:shape="rectangle">
-
- <corners android:radius="10dp" /> <!-- 四個角的角度 -->
-
- <!--gradient就是梯度渲染,簡單說就是顏色漸變,type為漸變方式,總共三種 linear sweep ridial,常用linear-->
- <!-- 這個地方一定注意,在使用gradient標簽中使用android:type的前提是必須android:gradientRadius="20dp"已經設置,否則會報錯 -->
- <gradient android:endColor="#acefda" android:startColor="#0099ff" android:type="linear" />
-
- <!-- padding屬性是指定內容與控件邊距,這個地方小馬專門將距左邊距設置較大,方便觀察 -->
- <padding android:bottom="5dp" android:left="20dp" android:right="5dp" android:top="5dp" />
-
- <!-- solid填充整個區域,顏色為FFDDFF,如果使用整個區域填充的話,上面的gradient梯度會失效,即:覆蓋 -->
- <!-- <solid android:color="#FFDDFF"/> -->
-
- <!-- stroke為需要填充的邊框,指定顏色及邊框寬度 -->
- <stroke android:width="3dp" android:color="#000000" />
- </shape>
- </item>
-
- </selector>
怎麼樣?看著JAVA自定義TextView代碼是不是覺得特別的繁瑣?今天的主題就是來解決這個問題的….…^_^………下面著重來講一下Selector與Shape混用控件效果Selector實現的細節,(請仔細看下XML裡面的注釋 O_O)
每個Item過是由Shape來進行渲染生成最終的效果,首先來看根Shape節點的常用屬性<shape android:shape=”rectangle”>:
這個shape屬性總共分三種 rectangle(矩形)、oval(橢圓) 、line(刪除線)、ring(鈴,這個存在不知道有什麼意義),其效果分別如下:
1.rectangle

2.oval

3.line

4.ring

其中,gradient標簽中的type為漸變方式,總共三種 linear sweep ridial,常用linear,其效果分別為(注意:ridial試了無任何效果 T_T)
1.linear效果

2.sweep效果

好了,代碼及整體效果已經分解完畢了,如果認真從頭到尾的看一邊的話,肯定有所收獲的,對了,以上的Shape渲染寫好了,可以在任意控件上使用…不限於TextView,上面的例子只是拿TextView來開刀用的…大家別誤會,呵呵….^_^…. ,最後,希望在文章中有什麼不清楚或不明白或有錯誤的地方,請大家直接指出…有錯必改的….這個源碼已經上傳到http://mzh3344258.blog.51cto.com/1823534/1215749最下面附件中,有興趣或有用的朋友可以直接下載來跑跑改改看,有批評才有進步,希望有什麼不好的,直接指出….在此先謝謝大家啦….
官網參考鏈接如下(只是沒效果圖,所以大家也懶得去看這個東西)
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/resources/drawable-resource.html








 Android中的普通對話框、單選對話框、多選對話框、帶Icon的對話框、以及自定義Adapter和自定義View對話框詳解
Android中的普通對話框、單選對話框、多選對話框、帶Icon的對話框、以及自定義Adapter和自定義View對話框詳解
 Android7.0 Phone應用源碼分析(三) phone拒接流程分析,android7.0拒接
Android7.0 Phone應用源碼分析(三) phone拒接流程分析,android7.0拒接
 Android Tab,androidtab
Android Tab,androidtab
 Android實現批量照片上傳至服務器,拍照或者從相冊選擇
Android實現批量照片上傳至服務器,拍照或者從相冊選擇