編輯:Android編程入門
發現我對Thread和Runable有錯誤的理解,看過源碼後進行區分這兩者。
其一:Runable只是一個接口,不會開啟一個線程,依舊是運行在UI線程中。
public interface Runnable {
/**
* Starts executing the active part of the class' code. This method is
* called when a thread is started that has been created with a class which
* implements {@code Runnable}.
*/
public void run();
}
可以看到,Runable在源碼中只有run方法,並且Runable可以在主線程執行修改UI的代碼,並且“OK”的執行一定是在輸出10個“runable”後,所以,Runable並沒有開啟線程,依舊是運行在UI線程中。
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
runnable.run();
Log.d("hello", "OK");
}
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) {
textView.setText("runable");
Log.d("hello", "runable");
}
}
};
其二:Thread如何開啟的線程,和Runable什麼關系?
源碼部分:
public class Thread implements Runnable {
最直接的一部分,實現Runable的接口。下面看看Thread的構造函數。
public Thread() {
create(null, null, null, 0);
}
這是其中之一的夠著函數,調用了create()方法,其他構造函數依然調用該方法。下面看看create()方法。
private void create(ThreadGroup group, Runnable runnable, String threadName, long stackSize) {
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
if (group == null) {
group = currentThread.getThreadGroup();
}
if (group.isDestroyed()) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException("Group already destroyed");
}
this.group = group;
synchronized (Thread.class) {
id = ++Thread.count;
}
if (threadName == null) {
this.name = "Thread-" + id;
} else {
this.name = threadName;
}
this.target = runnable;
this.stackSize = stackSize;
this.priority = currentThread.getPriority();
this.contextClassLoader = currentThread.contextClassLoader;
// Transfer over InheritableThreadLocals.
if (currentThread.inheritableValues != null) {
inheritableValues = new ThreadLocal.Values(currentThread.inheritableValues);
}
// add ourselves to our ThreadGroup of choice
this.group.addThread(this);
}
雖然比較多,但是只需要看這一行代碼,this.taeget = runable;而在Thread類的run()方法和start()方法中,
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}
/**
* Starts the new Thread of execution. The <code>run()</code> method of
* the receiver will be called by the receiver Thread itself (and not the
* Thread calling <code>start()</code>).
*
* @throws IllegalThreadStateException - if this thread has already started.
* @see Thread#run
*/
public synchronized void start() {
checkNotStarted();
hasBeenStarted = true;
nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
}
這兩個形成了兩個方法的區別:
用start方法來啟動線程,真正實現了多線程運行,這時無需等待run方法體代碼執行完畢而直接繼續執行下面的代碼。通過調用Thread類的start()方法來啟動一個線程,這時此線程處於就緒(可運行)狀態,並沒有運行,一旦得到cpu時間片,就開始執行run()方法,這裡方法 run()稱為線程體,它包含了要執行的這個線程的內容,Run方法運行結束,此線程隨即終止。
這樣也就很清晰可見,那麼如何開啟線程,
其中之一,和上文類比。
Thread t = new Thread(runnable);
t.start();
Log.d("hello","ok");
}
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
textview.settext(“runable”);
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) {
Log.d("hello", "runable");
}
}
};
根據執行結果也看到真正的開啟了線程,“OK”的輸出並不按代碼執行順序。
06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21369/? D/hello: ok 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable 06-13 19:32:26.252 21369-21429/? D/hello: runable
但是可以修改Ui(textview.settext)?!!!!!!執行的是runable.run()。(不應該在子線程執行這句話嗎?子線程不是不能修改UI嗎?)
為其添加按鈕監聽,打印線程 t 的名字,為Thread-76777
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
t.start();
}
});
得到我想要的結果:: FATAL EXCEPTION: Thread-76777 ,android.view.ViewRootImpl$CalledFromWrongThreadException:
那麼,問題在於。為什麼上述情況可以修改,而添加按鈕點擊後執行t.start()無法修改UI。
希望有人看到幫我解答一下這個疑問,如果本文有錯誤也希望指出。
原因:
onCreate中極短的時間內, viewRootImpl還沒有創建完成, new Thread()是可以修改ui的.
因為那個時候viewRootImpl還沒有創建.
當使用按鈕之後, 就不行了. 因為這個時候的view樹肯定是已經創建完畢了. 只有創建該View的線程才能修改和更新改view.
END!
 詳解實現Android中實現View滑動的幾種方式
詳解實現Android中實現View滑動的幾種方式
注: 本文提到的所有三種滑動方式的完整demo:ScrollDemo1. 關於View我們需要知道的(1)什麼是View? Android中的V
 Android 服務(Service)
Android 服務(Service)
Android 服務(Service)服務是一個後台運行的組件,執行長時間運行且不需要用戶交互的任務。即使應用被銷毀也依然可以工作。服務基本上包含兩種狀態
 Android課程---關於GridView網格視圖的學習
Android課程---關於GridView網格視圖的學習
activity_ui6.xml<?xml version=1.0 encoding=utf-8?><GridView xmlns:android=ht
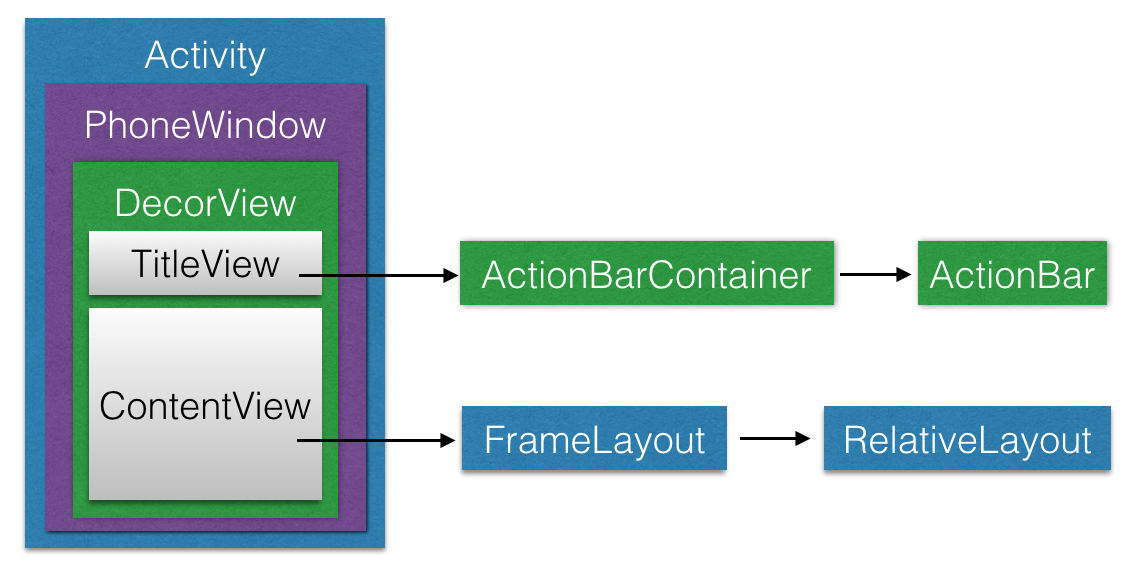 深入了解View的繪制流程
深入了解View的繪制流程
1. ViewRoot ViewRoot是連接WindowManager與DecorView的紐帶,View的整個繪制流程的三大步(