編輯:Android編程入門
LRU是Least Recently Used的縮寫,即“最近最少使用”,說明LRU緩存算法的淘汰策略是把最近最少使用的數據移除,讓出內存給最新讀取的數據。下面看一下Android中的LruCache。
這個LruCache在android.util包下,是API level 12引入的,對於API level 12之前的系統可以使用support library中的LruCache。先來看看android.util.LruCache的源碼。
首先是成員變量:
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements. */
private int size;
private int maxSize;
private int putCount;
private int createCount;
private int evictionCount;
private int hitCount;
private int missCount;LruCache內部使用一個LinkedHashMap作為存儲容器,並對各種操作進行計次。
構造器:
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}構造器的參數maxSize用於指定緩存的最大容量,並初始化一個LinkedHashMap,順便看看這個LinkedHashMap的構造函數:
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
init();
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}initialCapacity即初始容量設為0,裝填因子loadFactor設為0.75,accessOrder設為true,即鏈表中的元素按照最近最少訪問到最多訪問排序。這裡設置的裝填因子為0.75,設置其它值行不行呢?在LinkedHashMap這個構造器中只是將loadFactor作為參數傳給了父類構造器,該父類構造器如下:
public HashMap(int capacity, float loadFactor) {
this(capacity);
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Load factor: " + loadFactor);
}
/*
* Note that this implementation ignores loadFactor; it always uses
* a load factor of 3/4. This simplifies the code and generally
* improves performance.
*/
}調用了HashMap的構造器,可以看到只是對loadFactor進行了合法檢查,除此之外沒有其他調用或賦值操作,Note中解釋了,這個loadFactor沒用,裝填因子永遠使用3/4,也就是0.75。所以在構造LinkedHashMap時,設了裝填因子也沒什麼用。
繼續看LruCache,resize方法更新鏈表容量,調用trimToSize方法。
public void resize(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
synchronized (this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
}先看get方法,key為空會拋異常,取出對應的value,若不為空則命中次數hitCount加1並return這個value,否則missCount加1。該value為空時繼續向下執行,根據key嘗試創建value,如果創建返回的createdValue是null,那就確實沒有該值,若創建操作返回的createdValue不為null,則嘗試把createdValue放回map,若存在舊值則返回舊值,否則返回這個createdValue。
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}put方法將鍵值對放入map,重新計算大小之後調用trimToSize方法,刪除訪問次數最少的元素。
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}trimToSize方法中會一直嘗試刪除隊首元素即訪問次數最少的元素,直到size不超過最大容量。
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}support v4包中的LruCache可以用於API level 12之前的系統,和android.util包的LruCache的區別是在trimToSize中獲取將要刪除元素的方法不一樣:
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();LinkedHashMap的eldest()方法已經被標注為@hide,所以使用android.support.v4.util.LruCache更加保險一點。
 android系統架構
android系統架構
Android其本質就是在標准的Linux系統上增加了Java虛擬機Dalvik,並在Dalvik虛擬機上搭建了一個JAVA的application framework,
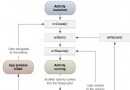 Android 活動(Activity)
Android 活動(Activity)
Android 活動(Activity)活動代表了一個具有用戶界面的單一屏幕,如 Java 的窗口或者幀。Android 的活動是 ContextThem
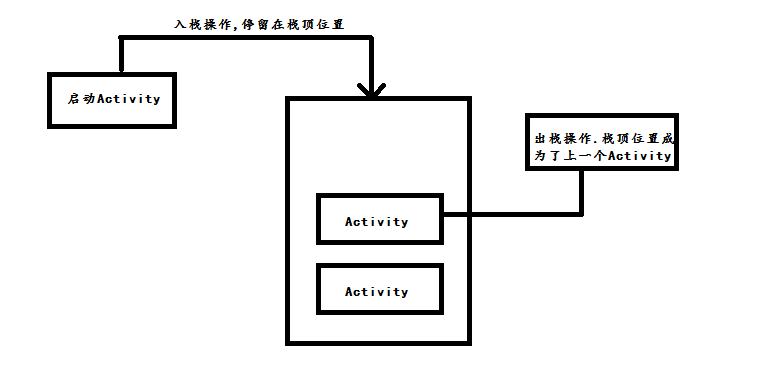 Android之Activity的生命周期
Android之Activity的生命周期
PS:寫一發關於Activity的生命周期,也算是面試的重點內容. 學習內容:1.Activity的生命周期2.面對多種情況的時候Activity的生命周期3.
 在Ubuntu Server14.04上編譯Android6.0源碼
在Ubuntu Server14.04上編譯Android6.0源碼
此前編譯過Android4.4的源碼,但是現在Android都到了7.0的版本,不禁讓我感歎Google的步伐真心難跟上,趁這周周末時間比較充裕,於是在過去的24小時裡,