編輯:Android編程入門
Android UI基礎之五大布局
Android的界面是有布局和組件協同完成的,布局好比是建築裡的框架,而組件則相當於建築裡的磚瓦。組件按照布局的要求依次排列,就組成了用戶所看見的界面。Android的五大布局分別是LinearLayout(線性布局)、FrameLayout(單幀布局)、RelativeLayout(相對布局)、AbsoluteLayout(絕對布局,Android2.0中標注為已過期)和TableLayout(表格布局)。
LinearLayout
線性布局
子元素任意
FrameLayout
幀布局
子元素任意
TableLayout
表格布局
子元素為<TableRow>,其中可放各種控件
RelativeLayout
相對布局
子元素任意
AbsoluteLayout
絕對布局
子元素任意
公共控件屬性:
android:id=
"@+id/***"
控件id
android:layout_width=
android:layout_height=
"wrap_content"
"match_parent"
"fill_parent"
控件的寬度
控件的高度
android:layout_marginLeft=
android:layout_marginRight=
android:layout_marginTop=
android:layout_marginBottom=
“5dip”
控件各邊距離其他控件的距離
android:text=
"***"
控件的文本內容
android:textSize=
控件的文本大小
android:textColor=
“#FFFFFFFF”
控件的文本顏色
android:textStyle =
"normal"/"bold"/"italic"
控件的文本格式
android:background =
“@drawable/background”
“#FFFFFFFF”
控件的背景(圖片或顏色)
android:src =
“@drawable/image”
控件的圖片
android:visibility=
"visible"
"invisible"
"gone"
"visible"表可見,
"invisible"表不可見,但在布局中占用的位置還在,
"gone"表不可見,完全從布局中消失
android:padding=
“5dip”
控件內容距離控件邊界的距離
android:weight=
控件占有的權重
android:ems=
android:maxEms=
android:minEms=
空間的寬度
android:gravity=
“top”,”left”,”start”,”fill”,”center”…
控件元素在控件顯示的位置
一、LinearLayout:
LinearLayout重要屬性
android:orientation=
“horizontal”
“vertaical”
布局中子控件排布方向
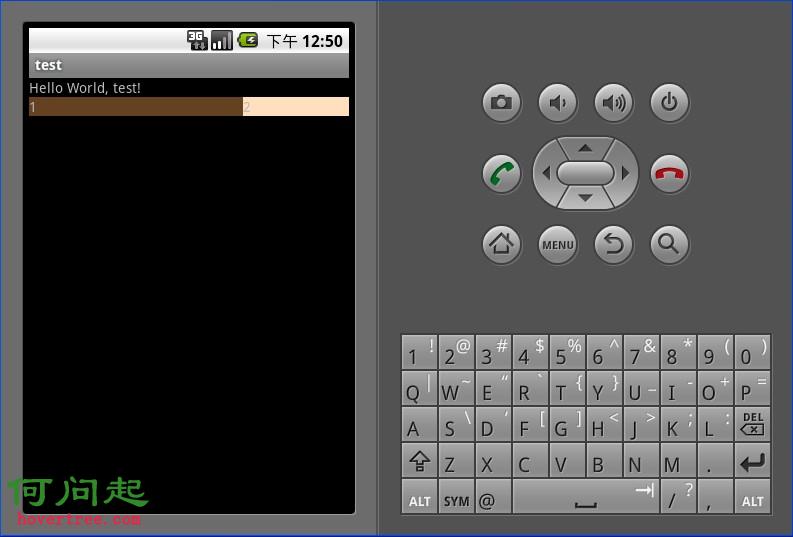
LinearLayout按照垂直或者水平的順序依次排列子元素,每一個子元素都位於前一個元素之後。如果是垂直排列,那麼將是一個N行單列的結構,每一行只會有一個元素,而不論這個元素的寬度為多少;如果是水平排列,那麼將是一個單行N列的結構。如果搭建兩行兩列的結構,通常的方式是先垂直排列兩個元素,每一個元素裡再包含一個LinearLayout進行水平排列。
LinearLayout中的子元素屬性android:layout_weight生效,它用於描述該子元素在剩余空間中占有的大小比例。加入一行只有一個文本框,那麼它的默認值就為0,如果一行中有兩個等長的文本框,那麼他們的android:layout_weight值可以是同為1。如果一行中有兩個不等長的文本框,那麼他們的android:layout_weight值分別為1和2,那麼第一個文本框將占據剩余空間的三分之二,第二個文本框將占據剩余空間中的三分之一。android:layout_weight遵循數值越小,重要度越高的原則。顯示效果如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff000000"
android:text="@string/hello"/>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff654321"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="1"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#fffedcba"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="2"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
二、FrameLayout:
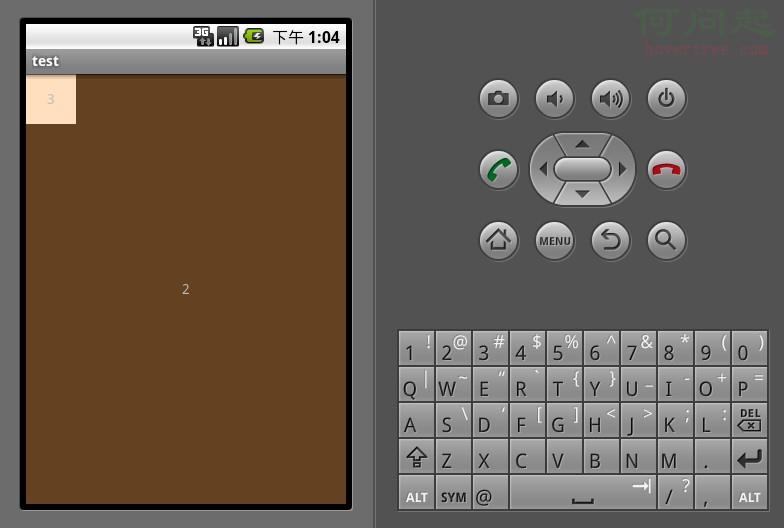
FrameLayout是五大布局中最簡單的一個布局,在這個布局中,整個界面被當成一塊空白備用區域,所有的子元素都不能被指定放置的位置,它們統統放於這塊區域的左上角,並且後面的子元素直接覆蓋在前面的子元素之上,將前面的子元素部分和全部遮擋。顯示效果如下,第一個TextView被第二個TextView完全遮擋,第三個TextView遮擋了第二個TextView的部分位置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#ff000000"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="1"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#ff654321"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="2"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#fffedcba"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="3"/>
</FrameLayout>
三、AbsoluteLayout:(Android2.0中標注為已過期,不推薦使用)
AbsoluteLayout重要屬性
android:layout_X/Y
控件的X,Y坐標
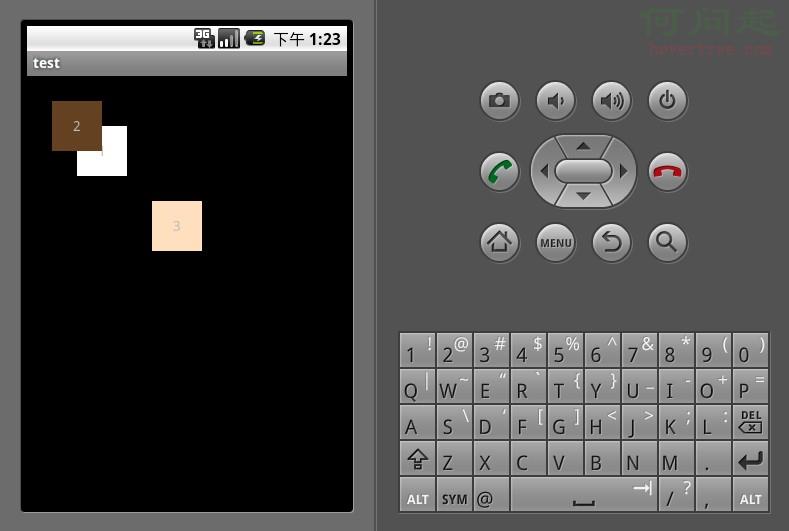
AbsoluteLayout是絕對位置布局。在此布局中的子元素的android:layout_x和android:layout_y屬性將生效,用於描述該子元素的坐標位置。屏幕左上角為坐標原點(0,0),第一個0代表橫坐標,向右移動此值增大,第二個0代表縱坐標,向下移動,此值增大。在此布局中的子元素可以相互重疊。在實際開發中,通常不采用此布局格式,因為它的界面代碼過於剛性,以至於有可能不能很好的適配各種終端。顯示效果如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#ffffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_x="50dp"
android:layout_y="50dp"
android:text="1"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#ff654321"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_x="25dp"
android:layout_y="25dp"
android:text="2"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#fffedcba"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_x="125dp"
android:layout_y="125dp"
android:text="3"/>
</AbsoluteLayout>
四、RelativeLayout:
RelativeLayout重要屬性
android:layout_alignParentLeft
android:layout_alignParentRight
android:layout_alignParentTop
android:layout_alignParentBottom
“true”
“false”
控件在布局中的相對位置
android:orientation
“horizontal”
“vertaical”
布局中子控件排布方向
android:layout_toRightOf
android:layout_toLeftOf
android:layout_below
android:layout_above
“@+id/***”
控件和某個控件的位置關系
android:layout_alignTop
android:layout_alignBottom
android:layout_alignLeft
android:layout_alignRight
android:layout_alignBaseline
“@+id/***”
控件與其他控件對齊
android:layout_centerHorizontal
android:layout_centerVirtical
android:layout_centerInParent
指定控件位於水平/垂直/父控件的中間位置
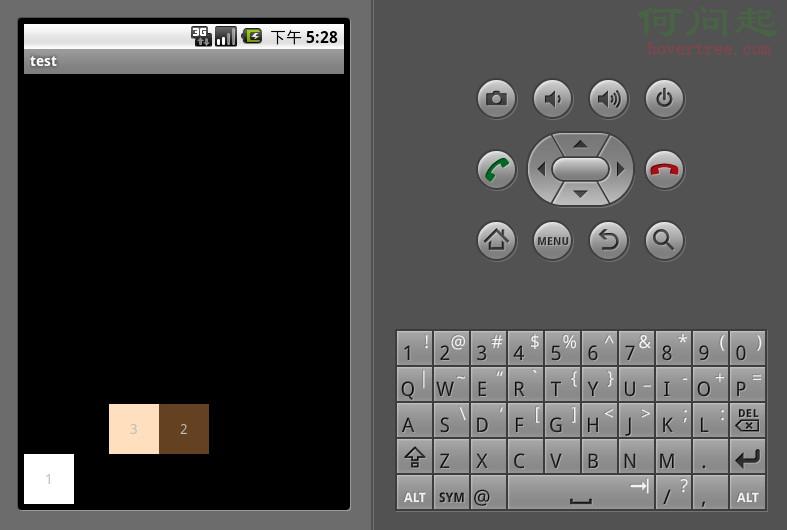
RelativeLayout按照各子元素之間的位置關系完成布局。在此布局中的子元素裡與位置相關的屬性將生效。例如android:layout_below, android:layout_above等。子元素就通過這些屬性和各自的ID配合指定位置關系。注意在指定位置關系時,引用的ID必須在引用之前,先被定義,否則將出現異常。
RelativeLayout是Android五大布局結構中最靈活的一種布局結構,比較適合一些復雜界面的布局。下面示例就展示這麼一個情況,第一個文本框與父組件的底部對齊,第二個文本框位於第一個文本框的上方,並且第三個文本框位於第二個文本框的左方。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_01"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#ffffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="1"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_02"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#ff654321"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_above="@id/text_01"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:text="2"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_03"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#fffedcba"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/text_02"
android:layout_above="@id/text_01"
android:text="3"/>
</RelativeLayout>
五、TableLayout:
TableLayout重要屬性
android:stretchColums
指定當一個TableRow中的控件不夠填充滿整個寬度時,將會被拉伸的條目
TableLayout顧名思義,此布局為表格布局,適用於N行N列的布局格式。一個TableLayout由許多TableRow組成,一個TableRow就代表TableLayout中的一行。
TableRow是LinearLayout的子類,它的android:orientation屬性值恆為horizontal,並且它的android:layout_width和android:layout_height屬性值恆為MATCH_PARENT和WRAP_CONTENT。所以它的子元素都是橫向排列,並且寬高一致的。這樣的設計使得每個TableRow裡的子元素都相當於表格中的單元格一樣。在TableRow中,單元格可以為空,但是不能跨列。
下面示例演示了一個TableLayout的布局結構,其中第二行只有兩個單元格,而其余行都是三個單元格。
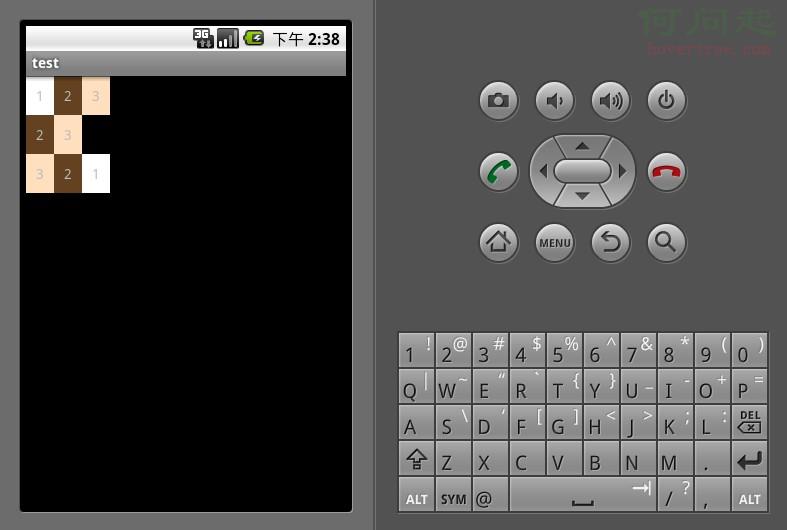
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TableRow
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:background="#ffffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="1"/>
<TextView
android:background="#ff654321"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="2"/>
<TextView
android:background="#fffedcba"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="3"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:background="#ff654321"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="2"/>
<TextView
android:background="#fffedcba"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="3"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView android:background="#fffedcba"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="3"/>
<TextView
android:background="#ff654321"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="2"/>
<TextView
android:background="#ffffffff"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="1"/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
 Android 5.0+刪除Sdcard文件
Android 5.0+刪除Sdcard文件
在Android5.0往後的平台上,你想通過單純的調用File.delete()或著ContentResolver.delete()來刪除Sdcard上的文件會刪除失敗。
 android 基本布局(RelativeLayout、TableLayout等)使用方法及各種屬性
android 基本布局(RelativeLayout、TableLayout等)使用方法及各種屬性
本文介紹 Android 界面開發中最基本的四種布局LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、FrameLayout、TableLayout 的使用方法及這
 java/android線程池詳解
java/android線程池詳解
一,簡述線程池:線程池是如何工作的:一系列任務出現後,根據自己的線程池安排任務進行。如圖: 線程池的好處:重用線程池中的線程,避免因為線程的創建和銷毀所帶來的性能開銷。能
 Android開發學習之路-Android Studio真神器!
Android開發學習之路-Android Studio真神器!
放假之後電腦配置升級就開始用Android Studio(下面簡稱AS)了,那個酸爽真的不是一般的啊,這裡開一篇博客來記錄下AS裡面各種酷炫的功能,有更好玩的,大家不要吝