編輯:Android編程入門
上一章講述了Android界面開發中的Widget,Service,BroadcastReceiver基本知識點,本章以一個實際案例-後台音樂播放器解析各個知識點之間的關系。
做一個Android音樂播放器
圖1
圖2
圖3
簡易說明
長按手機界面出現如圖2所示信息,彈出小部件選項,點擊進入小部件如圖1。選擇極客班-作業四,根據提示拖放界面到桌面,出現如圖3所示音樂播放界面。點擊按鈕可實現音樂切換播放歌曲功能。
後台音樂播放器主要是通過Widget的特性,用廣播為通道,完成Widget與Service之間的交互。
Widget:更新桌面信息,發送廣播信息,接收用戶操作事件。
Service:注冊服務,接收廣播信息,發送廣播信息。
音樂播放器在界面布局和配置文件中主要包括以下方面:
在用戶添加Widget時,會調用OnUpdate()函數,在OnUpdate()中要實現綁定RemoteView和更新Widget的操作。在綁定控件時,主要應用了PendingIntent的方式。
PendingIntent 是Intent的封裝,在構造PendingIntent前,也要先構造一個Intent,並可以利用Intent 的屬性傳進去action,Extra等,同樣,在接收時,對方依然是接收Intent的,而不是接收PaddingIntent。
PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0,intent, 0);指從系統中獲取一個用於可以發送BroadcastReceiver廣播的PendingIntent對象。PendingIntent這個類用於 處理即將發生的事情。比如在通知Notification中用於跳轉頁面,但不是馬上跳轉。所以可以將它理解成
一個封裝成消息的intent的。即這個intent並不是立即start,而是像消息一樣被發送出去,等接收方接到以後,再分析裡面的內容。項目相關代 碼摘抄如下:
private PendingIntent getPendingIntent(Context context, int buttonId) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(context, ExampleAppWidgetProvider.class);
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_ALTERNATIVE);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("harvic:" + buttonId));
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(context, 0, intent, 0);
return pi;
}
// 更新所有的 widget
private void pushUpdate(Context context,AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,String songName,Boolean play_pause) {
RemoteViews remoteView = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),R.layout.music_app_widget);
//將按鈕與點擊事件綁定
remoteView.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.play_pause,getPendingIntent(context, R.id.play_pause));
remoteView.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.prev_song, getPendingIntent(context, R.id.prev_song));
remoteView.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.next_song, getPendingIntent(context, R.id.next_song));
//設置內容
if (!songName.equals("")) {
remoteView.setTextViewText(R.id.song_name, songName);
}
//設定按鈕圖片
if (play_pause) {
remoteView.setImageViewResource(R.id.play_pause, R.drawable.button_stop);
}else {
remoteView.setImageViewResource(R.id.play_pause, R.drawable.button_on);
}
// 相當於獲得所有本程序創建的appwidget
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(context,ExampleAppWidgetProvider.class);
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(componentName, remoteView);
}
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int[] appWidgetIds) {
pushUpdate(context,appWidgetManager,"",false);
}
Widget-onUpdate()
接收用戶操作,在接收時,首先根據當前用戶點擊的哪個按鈕,然後給MusicManageService發送不同的廣播(發送按鈕id),讓MusicManageService做出不同的響應,接收代碼如下 :
// 接收廣播的回調函數
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
Log.d("harvic", "action:"+action);
if (intent.hasCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_ALTERNATIVE)) {
Uri data = intent.getData();
int buttonId = Integer.parseInt(data.getSchemeSpecificPart());
switch (buttonId) {
case R.id.play_pause:
pushAction(context,MusicManageService.ACTION_PLAY_PAUSE);
if(mStop){
Intent startIntent = new Intent(context,MusicManageService.class);
context.startService(startIntent);
mStop = false;
}
break;
case R.id.prev_song:
pushAction(context, MusicManageService.ACTION_PRE);
break;
case R.id.next_song:
pushAction(context, MusicManageService.ACTION_NEXT);
break;
}
}else if (MAIN_UPDATE_UI.equals(action)){
int play_pause = intent.getIntExtra(KEY_MAIN_ACTIVITY_UI_BTN, -1);
String songid = intent.getStringExtra(KEY_MAIN_ACTIVITY_UI_TEXT);
if(songid==null) songid="歌曲";
switch (play_pause) {
case VAL_UPDATE_UI_PLAY:
pushUpdate(context, AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context), songid,true);
break;
case VAL_UPDATE_UI_PAUSE:
pushUpdate(context, AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context), songid,false);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
super.onReceive(context, intent);
}
Widget-onReceive()
//發送按鍵廣播
private void pushAction(Context context, int ACTION) {
//發送目的服務
Intent actionIntent = new Intent(MusicManageService.ACTION);
//發送參數
actionIntent.putExtra(MusicManageService.KEY_USR_ACTION, ACTION);
context.sendBroadcast(actionIntent);
}
服 務要與按鈕相交互,在Service中一般是通過BroadcastReceiver來實現,所以在 MusicManageService的OnCreate函數中(Service起來的時候調用OnCreate)應該包括下面幾個步驟:注冊 Receiver。對應的項目代碼如下:
private BroadcastReceiver receiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (ACTION.equals(action)) {
int widget_action = intent.getIntExtra(KEY_USR_ACTION, -1);
switch (widget_action){
case ACTION_PRE:
playPrev(context);Log.d("harvic","action_prev");break;
case ACTION_PLAY_PAUSE:
if (mPlayState) {
pause(context);Log.d("harvic","action_pause");
}else{
play(context);Log.d("harvic","action_play");
}
break;
case ACTION_NEXT:playNext(context);Log.d("harvic","action_next");break;
default:break;
}}
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction(ACTION);
//注冊服務
registerReceiver(receiver, intentFilter);
//加載歌曲
initList();
//播放默認歌曲
mediaPlayerStart();
}
歌曲為本地歌曲文件,放在項目的raw目錄下:
//歌曲播放
private void mediaPlayerStart(){
mPlayer = new MediaPlayer();
mPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(getApplicationContext(), mArrayList[mIndex]);
mPlayer.start();
mPlayState = true;
//通過廣播發送當前播放狀態到Widget
postState(getApplicationContext(), ExampleAppWidgetProvider.VAL_UPDATE_UI_PLAY,mIndex);
}
//歌曲初始化
private void initList() {
//歌曲路徑
mArrayList[0] = R.raw.night_two;
mArrayList[1] = R.raw.night_four;
mArrayList[2] = R.raw.night_five;
mArrayList[3] = R.raw.night_six;
//歌曲名稱
mArrayListName[0] ="石進-夜的鋼琴曲二";
mArrayListName[1] = "石進-夜的鋼琴曲四";
mArrayListName[2] ="石進-夜的鋼琴曲五";
mArrayListName[3] = "石進-夜的鋼琴曲六";
}
歌曲通過Widget不同按鈕切換發送廣播到Service,Service通過播放功能函數(參考項目源代碼)做出相應的播放功能切換處理以後,就又一次發送一個廣播信息回饋給Widget,Widget接收到廣播信息後進行更新處理,項目代碼如下:
//回饋廣播信息給Widget
private void postState(Context context, int state,int songid) {
//定義發送廣播接收者
Intent actionIntent = new Intent(ExampleAppWidgetProvider.MAIN_UPDATE_UI);
//定義歌曲播放狀態(播放/暫停)
actionIntent.putExtra(ExampleAppWidgetProvider.KEY_MAIN_ACTIVITY_UI_BTN,state);
//定義發送信息(歌曲名稱)
actionIntent.putExtra(ExampleAppWidgetProvider.KEY_MAIN_ACTIVITY_UI_TEXT, mArrayListName[songid]);
context.sendBroadcast(actionIntent);
}
本項目源代碼在360雲盤上,開發環境為 Android Studio 2.0 beta 7。
https://yunpan.cn/cYamkZG3sq9jf 訪問密碼 f3d5
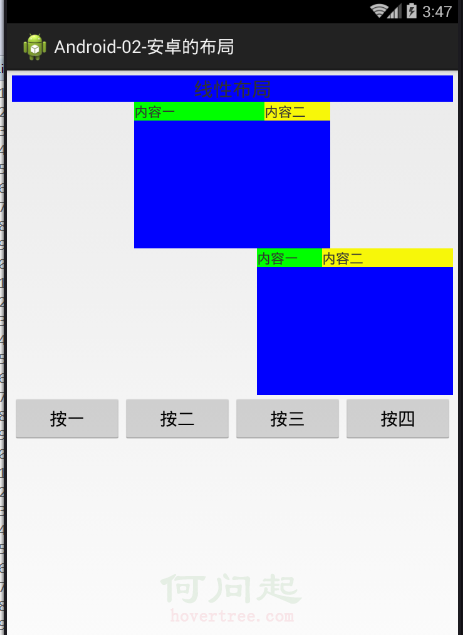 安卓的主要幾大布局
安卓的主要幾大布局
今天我們的主要內容就是安卓的主要幾個基礎的布局方式。(主要布局如下:)1.線性布局(LinerLayout)2.相對布局(RelativeLayout)3.表格布局(Ta
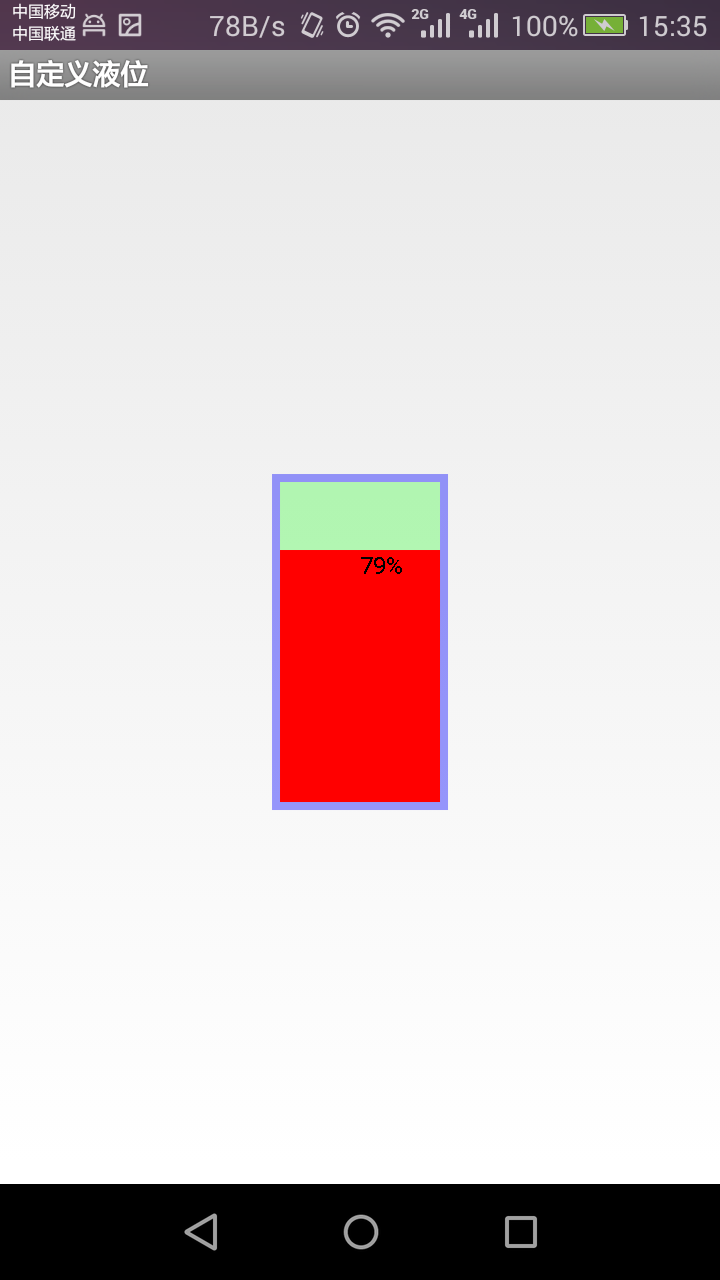 android-自定義控件之液位指示器
android-自定義控件之液位指示器
由於安卓應用很廣泛,在工業中也常有一些應用,比如可以用安卓來去工業中的一些數據進行實現的監測,顯示,同時可以做一些自動化控制,當然在這裡,我不是做這些自動化控制方面的研究
 Android中的Semaphore
Android中的Semaphore
信號量,了解過操作系統的人都知道,信號量是用來做什麼的···在Android中,已經提供了Semaphore來幫助我們使用~那麼
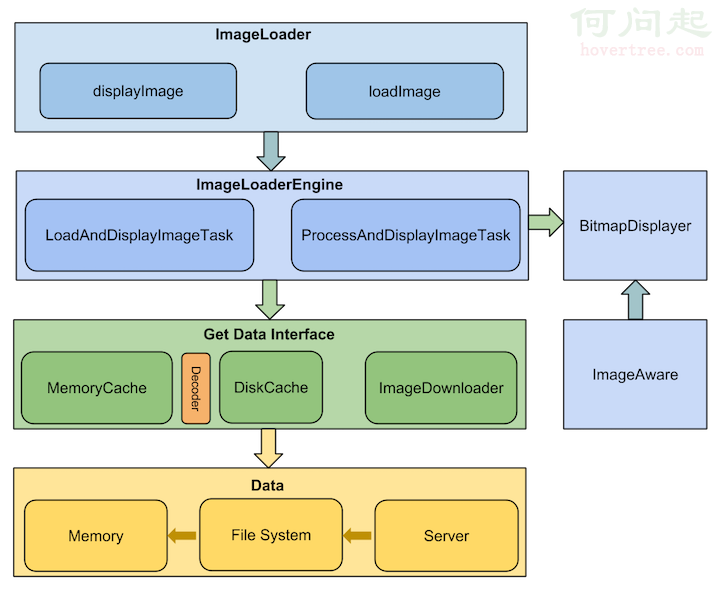 Android圖片加載庫的理解
Android圖片加載庫的理解
前言 這是“基礎自測”系列的第三篇文章,以Android開發需要熟悉的20個技術點為切入點,本