編輯:Android編程入門
現在,當我們打開任意的一個app時,其中的大部分都會顯示一個啟動界面,展示本公司的logo和當前的版本,有的則直接把廣告放到了上面。啟動畫面的可以分為兩種設置方式:一種是兩個Activity實現,和一個Ativity實現。下面介紹兩種設置啟動畫面的方式:
一:兩個Activity源代碼:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.view.Window;
public class SplashActivity extends Activity{
private static int SPLASH_DISPLAY_LENGHT= 6000; //延遲6秒
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
getWindow().requestFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);//去掉標題
setContentView(R.layout.activity_splash);
new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
Intent intent = new Intent(SplashActivity.this, MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
SplashActivity.this.finish(); //關閉splashActivity,將其回收,否則按返回鍵會返回此界面
}
}, SPLASH_DISPLAY_LENGHT);
}
}
別忘設置AndroidManifest.xml
<activity
android:name="com.example.andorid_splash_0.SplashActivity"
android:label="splash">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
</activity>
容易看出:SplashActivity是先於MainActivity之前啟動,當過了6秒後,才啟動MainActivity。
補充一點知識:
// 立即執行Runnable對象 public final boolean post(Runnable r); // 在指定的時間(uptimeMillis)執行Runnable對象 public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, long uptimeMillis); // 在指定的時間間隔(delayMillis)執行Runnable對象 public final boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis);
二:一個Activity啟動
先看布局文件:裡面放了兩個充滿屏幕的ImageView和TextView
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/splashScreen"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/iv_image"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/new00"/>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:textSize="100dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="主界面"/>
</LinearLayout>
activity的代碼:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private LinearLayout splash;
private ImageView iv_image;
private static final int STOPSPLASH = 0;
private static final long SPLASHTIME = 1000;
private Handler splashHandler = new Handler(){
public void handleMessage(Message msg){
switch (msg.what){
case STOPSPLASH:
SystemClock.sleep(4000); //休眠4s
splash.setVisibility(View.GONE);
break;
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
splash = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.splashScreen);
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = STOPSPLASH;
splashHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, SPLASHTIME);//設置在SPLASHTIME時間後,發送消息
}
}
三、總結:
上面兩種方法都可以實現應用啟動前的開機畫面,但在實際開發中還是建議使用第一種較好,因為主界面的代碼不宜過多,應當簡潔。
 Android Studio 單元測試
Android Studio 單元測試
單元測試(unit testing),是指對軟件中的最小可測試單元進行檢查和驗證。 針對Android開發,目前網上有很多在Eclipse環境下進行單元測試的教程,然而
 Android—自定義控件實現ListView下拉刷新
Android—自定義控件實現ListView下拉刷新
這篇博客為大家介紹一個android常見的功能——ListView下拉刷新(參考自他人博客,網址忘記了,閱讀他的代碼自己理解注釋的,希望能幫助到大
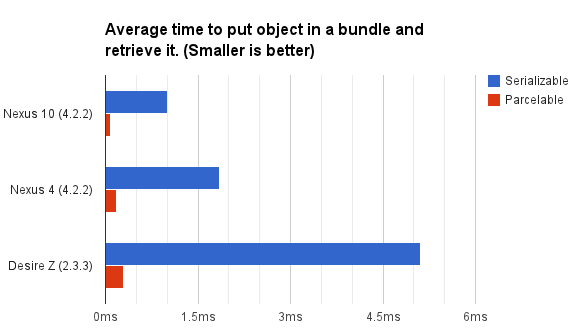 Android序列化之Serializable和Parcelable
Android序列化之Serializable和Parcelable
PS:還有幾天就開學了.先來一發. 學習內容:1.序列化的目的2.Android中序列化的兩種方式3.Parcelable與Serializable的性能比較4
 Android 碎片(Fragment)
Android 碎片(Fragment)
Android 碎片(Fragment)碎片是活動的一部分,是的活動更加的模塊化設計。我們可以任務碎片是一種子活動。下面是關於碎片的重要知識點 -碎片擁有