編輯:Android開發實例
ListFragment繼承於Fragment。因此它具有Fragment的特性,能夠作為activity中的一部分,目的也是為了使頁面設計更加靈活。
相比Fragment,ListFragment的內容是以列表(list)的形式顯示的。ListFragment的布局默認包含一個ListView。因此,在ListFragment對應的布局文件中,必須指定一個 android:id 為 “@android:id/list” 的ListView控件!
ListFragment基礎使用
下面介紹在Activity中顯示ListFragment的步驟。
1. Activity對應的代碼
public class FragmentTest extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
}
2. Activity對應的布局
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <fragment android:name="com.skw.fragmenttest.MyListFragment" android:id="@+id/myfragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </LinearLayout>
說明:該Activity的布局中只包行了一個Fragment。下面看看MyListFragment的內容。
3. MyListFragment的內容
public class MyListFragment extends ListFragment {
private static final String TAG = "##MyListFragment##";
private ListView selfList;
String[] cities = {
"Shenzhen",
"Beijing",
"Shanghai",
"Guangzhou",
"Wuhan",
"Tianjing",
"Changsha",
"Xi'an",
"Chongqing",
"Guilin",
};
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreateView");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_fragment, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 設置ListFragment默認的ListView,即@id/android:list
this.setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cities));
}
public void onListItemClick(ListView parent, View v,
int position, long id) {
Log.d(TAG, "onListItemClick");
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "You have selected " + cities[position],
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
說明:MyListFragment是自定義的ListFragment。它使用了list_fragment.xml作為布局,並通過android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1顯示ListView中的每一項。
4. list_fragment.xml的內容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <!-- ListFragment對應的android:id值固定為"@id/android:list" --> <ListView android:id="@id/android:list" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" /> </LinearLayout>
"Activity的布局以及代碼"和前面一樣,這裡就不再重復說明。
5. MyListFragment的內容
public class MyListFragment extends ListFragment {
private static final String TAG = "##MyListFragment##";
private ListView selfList;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreateView");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_fragment, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final String[] from = new String[] {"title", "info"};
final int[] to = new int[] {R.id.text1, R.id.text2};
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 建立SimpleAdapter,將from和to對應起來
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(
this.getActivity(), getSimpleData(),
R.layout.item, from, to);
this.setListAdapter(adapter);
}
public void onListItemClick(ListView parent, View v,
int position, long id) {
Log.d(TAG, "onListItemClick");
Toast.makeText(getActivity(),
"You have selected " + position,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
private List<Map<String, Object>> getSimpleData() {
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("title", "Ferris wheel");
map.put("info", "Suzhou Ferris wheel");
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("title", "Flower");
map.put("info", "Roser");
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("title", "Disk");
map.put("info", "Song Disk");
list.add(map);
return list;
}
}
說明:MyListFragment使用了R.layout.list_fragment作為布局,並且對於ListView中的每一項都使用了R.layout.item作為布局。
6. list_fragment.xml的內容
<!-- ListFragment對應的android:id值固定為"@id/android:list" -->
<ListView
android:id="@id/android:list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:drawSelectorOnTop="false"
/>
7. item.xml的內容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" android:textSize="12sp" android:text android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/text2" android:textSize="24sp" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout>
ListFragment實例
應用實例說明:建立一個activity,包括2個ListFragment。第1個ListFragment采用中ListView每一行的內容通過android自帶的android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1布局來顯示;第2個ListFragment每一行的內容通過自定義的layout文件來顯示,每一行顯示兩個文本。
activity對應的layout文件代碼:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <fragment android:name="com.skywang.app.ListFragmentImpl" android:id="@+id/fragment1" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> <fragment android:name="com.skywang.app.ListFragmentSelf" android:id="@+id/fragment2" android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </LinearLayout>
說明:
(01) 該layout布局包含兩個fragment。
activity的代碼:
package com.skywang.app;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.view.Menu;
public class ListFragmentTest extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.list_fragment_test);
}
}
說明:
(01) 在 onCreateView()中,調用list_fragment_impl作為該ListFragment的布局文件。
(02) 在 onCreate()中,通過setListAdapter() 設置android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1為ListView每一行的布局文件,設置cities為其中數據的每一項內容。
ListFragmentImpl.java的代碼:
package com.skywang.app;
import android.app.ListFragment;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ListFragmentImpl extends ListFragment{
private static final String TAG = "ListFragmentImpl";
private ListView selfList;
String[] cities = {
"Shenzhen",
"Beijing",
"Shanghai",
"Guangzhou",
"Wuhan",
"Tianjing",
"Changsha",
"Xi'an",
"Chongqing",
"Guilin",
};
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreateView");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_fragment_impl, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 設置ListFragment默認的ListView,即@id/android:list
this.setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(getActivity(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, cities));
}
public void onListItemClick(ListView parent, View v,
int position, long id) {
Log.d(TAG, "onListItemClick");
Toast.makeText(getActivity(),
"You have selected " + cities[position],
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
list_fragment_impl.xml的內容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <!-- ListFragment對應的android:id值固定為"@id/android:list" --> <ListView android:id="@id/android:list" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" /> </LinearLayout>
ListFragmentSelf.java的代碼:
package com.skywang.app;
import android.app.ListFragment;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ListFragmentSelf extends ListFragment{
private static final String TAG = "ListFragmentImpl";
private ListView selfList;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreateView");
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_fragment_self, container, false);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
final String[] from = new String[] {"title", "info"};
final int[] to = new int[] {R.id.text1, R.id.text2};
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate");
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 建立SimpleAdapter,將from和to對應起來
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(
this.getActivity(), getSimpleData(),
R.layout.two_textview, from, to);
this.setListAdapter(adapter);
}
public void onListItemClick(ListView parent, View v,
int position, long id) {
Log.d(TAG, "onListItemClick");
Toast.makeText(getActivity(),
"You have selected " + position,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
private List<Map<String, Object>> getSimpleData() {
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("title", "Ferris wheel");
map.put("info", "Suzhou Ferris wheel");
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("title", "Flower");
map.put("info", "Roser");
list.add(map);
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("title", "Disk");
map.put("info", "Song Disk");
list.add(map);
return list;
}
}
說明:
(01) 在 onCreateView()中,調用list_fragment_self作為該ListFragment的布局文件。
(02) 在 onCreate()中,通過setListAdapter() 設置R.layout.two_textview為ListView每一行的布局文件。
list_fragment_self.xml的內容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <!-- ListFragment對應的android:id值固定為"@id/android:list" --> <ListView android:id="@id/android:list" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:drawSelectorOnTop="false" /> </LinearLayout>
two_textview.xml的內容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" android:textSize="12sp" android:text android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/text2" android:textSize="24sp" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout>
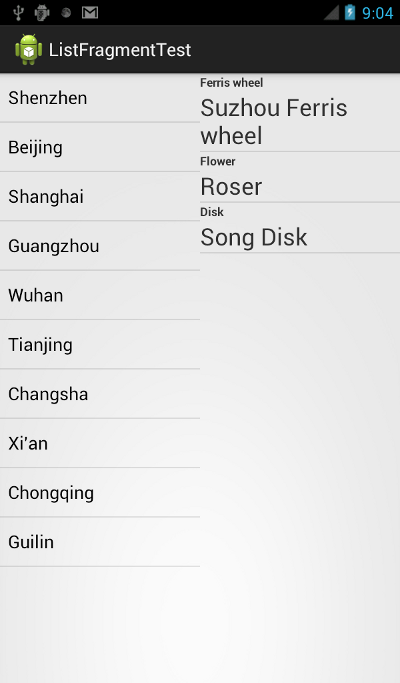
效果圖:
 Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android提供了許多方法來控制播放的音頻/視頻文件和流。其中該方法是通過一類稱為MediaPlayer。Android是提供MediaPlayer類訪問內置的媒體播放
 Android控件系列之CheckBox使用介紹
Android控件系列之CheckBox使用介紹
學習目的: 1、掌握在Android中如何建立CheckBox 2、掌握CheckBox的常用屬性 3、掌握CheckBox選中狀態變換的事件(監聽器) Chec
 Android入門之Gallery用法實例解析
Android入門之Gallery用法實例解析
本文實例介紹的Android的Gallery控件是個很不錯的看圖控件,可以大大減輕開發者對於看圖功能的開發,並且效果也很美觀。本文實例中的Gallery的用法,主
 Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android提供了許多方法來控制播放的音頻/視頻文件和流。其中該方法是通過一類稱為MediaPlayer。Android是提供MediaPlayer類訪問內置的媒體播放