編輯:Android開發實例
View
Android所有的控件都是View或者View的子類,它其實表示的就是屏幕上的一塊矩形區域,用一個Rect來表示,left,top表示View相對於它的parent View的起點,width,height表示View自己的寬高,通過這4個字段就能確定View在屏幕上的位置,確定位置後就可以開始繪制View的內容了。
View繪制過程
View的繪制可以分為下面三個過程:
Measure
View會先做一次測量,算出自己需要占用多大的面積。View的Measure過程給我們暴露了一個接口onMeasure,方法的定義是這樣的,
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {}
View類已經提供了一個基本的onMeasure實現,
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
其中invoke了setMeasuredDimension()方法,設置了measure過程中View的寬高,getSuggestedMinimumWidth()返回View的最小Width,Height也有對應的方法。插幾句,MeasureSpec類是View類的一個內部靜態類,它定義了三個常量UNSPECIFIED、AT_MOST、EXACTLY,其實我們可以這樣理解它,它們分別對應LayoutParams中match_parent、wrap_content、xxxdp。我們可以重寫onMeasure來重新定義View的寬高。
Layout
Layout過程對於View類非常簡單,同樣View給我們暴露了onLayout方法
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
因為我們現在討論的是View,沒有子View需要排列,所以這一步其實我們不需要做額外的工作。插一句,對ViewGroup類,onLayout方法中,我們需要將所有子View的大小寬高設置好,這個我們下一篇會詳細說。
Draw
Draw過程,就是在canvas上畫出我們需要的View樣式。同樣View給我們暴露了onDraw方法
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
}
默認View類的onDraw沒有一行代碼,但是提供給我們了一張空白的畫布,舉個例子,就像一張畫卷一樣,我們就是畫家,能畫出什麼樣的效果,完全取決我們。
View中還有三個比較重要的方法
requestLayout
View重新調用一次layout過程。
invalidate
View重新調用一次draw過程
forceLayout
標識View在下一次重繪,需要重新調用layout過程。
自定義屬性
整個View的繪制流程我們已經介紹完了,還有一個很重要的知識,自定義控件屬性,我們都知道View已經有一些基本的屬性,比如layout_width,layout_height,background等,我們往往需要定義自己的屬性,那麼具體可以這麼做。
1.在values文件夾下,打開attrs.xml,其實這個文件名稱可以是任意的,寫在這裡更規范一點,表示裡面放的全是view的屬性。
2.因為我們下面的實例會用到2個長度,一個顏色值的屬性,所以我們這裡先創建3個屬性。
<declare-styleable name="rainbowbar"> <attr name="rainbowbar_hspace" format="dimension"></attr> <attr name="rainbowbar_vspace" format="dimension"></attr> <attr name="rainbowbar_color" format="color"></attr> </declare-styleable>
那麼到底怎麼用呢,我們會看一個實例。
實現一個比較簡單的Google彩虹進度條。
為了簡單起見,這裡我只用一種顏色,多種顏色就留給大家了,我們直接上代碼。
public class RainbowBar extends View {
//progress bar color
int barColor = Color.parseColor("#1E88E5");
//every bar segment width
int hSpace = Utils.dpToPx(80, getResources());
//every bar segment height
int vSpace = Utils.dpToPx(4, getResources());
//space among bars
int space = Utils.dpToPx(10, getResources());
float startX = 0;
float delta = 10f;
Paint mPaint;
public RainbowBar(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public RainbowBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public RainbowBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//read custom attrs
TypedArray t = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.rainbowbar, 0, 0);
hSpace = t.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.rainbowbar_rainbowbar_hspace, hSpace);
vSpace = t.getDimensionPixelOffset(R.styleable.rainbowbar_rainbowbar_vspace, vSpace);
barColor = t.getColor(R.styleable.rainbowbar_rainbowbar_color, barColor);
t.recycle(); // we should always recycle after used
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setColor(barColor);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(vSpace);
}
.......
}
View有了三個構造方法需要我們重寫,這裡介紹下三個方法會被調用的場景,
第一個方法,一般我們這樣使用時會被調用,View view = new View(context);
第二個方法,當我們在xml布局文件中使用View時,會在inflate布局時被調用,
<View layout_width="match_parent" layout_height="match_parent"/>。
第三個方法,跟第二種類似,但是增加style屬性設置,這時inflater布局時會調用第三個構造方法。
<View layout_width="match_parent" layout_height="match_parent"/>。
上面大家可能會感覺到有點困惑的是,我把初始化讀取自定義屬性hspace,vspace,和barcolor的代碼寫在第三個構造方法裡面,但是我RainbowBar在線性布局中沒有加style屬性(),那按照我們上面的解釋,inflate布局時應該會invoke第二個構造方法啊,但是我們在第二個構造方法裡面調用了第三個構造方法,this(context, attrs, 0); 所以在第三個構造方法中讀取自定義屬性,沒有問題,這是一點小細節,避免代碼冗余-,-
Draw
因為我們這裡不用關注measrue和layout過程,直接重寫onDraw方法即可。
//draw be invoke numbers.
int index = 0;
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
//get screen width
float sw = this.getMeasuredWidth();
if (startX >= sw + (hSpace + space) - (sw % (hSpace + space))) {
startX = 0;
} else {
startX += delta;
}
float start = startX;
// draw latter parse
while (start < sw) {
canvas.drawLine(start, 5, start + hSpace, 5, mPaint);
start += (hSpace + space);
}
start = startX - space - hSpace;
// draw front parse
while (start >= -hSpace) {
canvas.drawLine(start, 5, start + hSpace, 5, mPaint);
start -= (hSpace + space);
}
if (index >= 700000) {
index = 0;
}
invalidate();
}
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="40dp"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<com.sw.demo.widget.RainbowBar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:rainbowbar_color="@android:color/holo_blue_bright"
app:rainbowbar_hspace="80dp"
app:rainbowbar_vspace="10dp"
></com.sw.demo.widget.RainbowBar>
</LinearLayout>
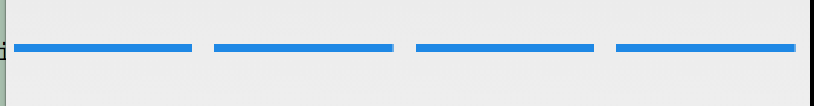
其實就是調用canvas的drawLine方法,然後每次將draw的起點向前推進,在方法的結尾,我們調用了invalidate方法,上面我們已經說明了,這個方法會讓View重新調用onDraw方法,所以就達到我們的進度條一直在向前繪制的效果。下面是最後的顯示效果,制作成gif時好像有色差,但是真實效果是藍色的。我們只寫了短短的幾十行代碼,自定義View並不是我們想象中那麼難,下一篇我們會繼續ViewGroup的繪制流程學習。

自定義ViewGroup
ViewGroup
我們知道ViewGroup就是View的容器類,我們經常用的LinearLayout,RelativeLayout等都是ViewGroup的子類,因為ViewGroup有很多子View,所以它的整個繪制過程相對於View會復雜一點,但是還是三個步驟measure,layout,draw,我們一次說明。
Measure
Measure過程還是測量ViewGroup的大小,如果layout_widht和layout_height是match_parent或具體的xxxdp,就很簡答了,直接調用setMeasuredDimension()方法,設置ViewGroup的寬高即可,如果是wrap_content,就比較麻煩了,我們需要遍歷所有的子View,然後對每個子View進行測量,然後根據子View的排列規則,計算出最終ViewGroup的大小。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = this.getChildAt(i);
this.measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int cw = child.getMeasuredWidth();
// int ch = child.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
你可能需要類似上面的代碼,其中getChildCount()方法,返回子View的數量,measureChild()方法,調用子View的測量方法。
Layout
上面View的自定義中,我們稍微提到了,layout過程其實就是對子View的位置進行排列,onLayout方法給我一個機會,來按照我們想要的規則自定義子View排列。
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4) {
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = this.getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams lParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(lParams.left, lParams.top, lParams.left + childWidth,
lParams.top + childHeight);
}
}
你同樣可能需要類似上面的代碼,其中child.layout(left,top,right,bottom)方法可以對子View的位置進行設置,四個參數的意思大家通過變量名都應該清楚了。
Draw
ViewGroup在draw階段,其實就是按照子類的排列順序,調用子類的onDraw方法,因為我們只是View的容器, 本身一般不需要draw額外的修飾,所以往往在onDraw方法裡面,只需要調用ViewGroup的onDraw默認實現方法即可。
LayoutParams
ViewGroup還有一個很重要的知識LayoutParams,LayoutParams存儲了子View在加入ViewGroup中時的一些參數信息,在繼承ViewGroup類時,一般也需要新建一個新的LayoutParams類,就像SDK中我們熟悉的LinearLayout.LayoutParams,RelativeLayout.LayoutParams類等一樣,那麼可以這樣做,在你定義的ViewGroup子類中,新建一個LayoutParams類繼承與ViewGroup.LayoutParams。
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
public int left = 0;
public int top = 0;
public LayoutParams(Context arg0, AttributeSet arg1) {
super(arg0, arg1);
}
public LayoutParams(int arg0, int arg1) {
super(arg0, arg1);
}
public LayoutParams(android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams arg0) {
super(arg0);
}
}
那麼現在新的LayoutParams類已經有了,如何讓我們自定義的ViewGroup使用我們自定義的LayoutParams類來添加子View呢,ViewGroup同樣提供了下面這幾個方法供我們重寫,我們重寫返回我們自定義的LayoutParams對象即可。
@Override
public android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(
AttributeSet attrs) {
return new NinePhotoView.LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(
android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new LayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof NinePhotoView.LayoutParams;
}
實例
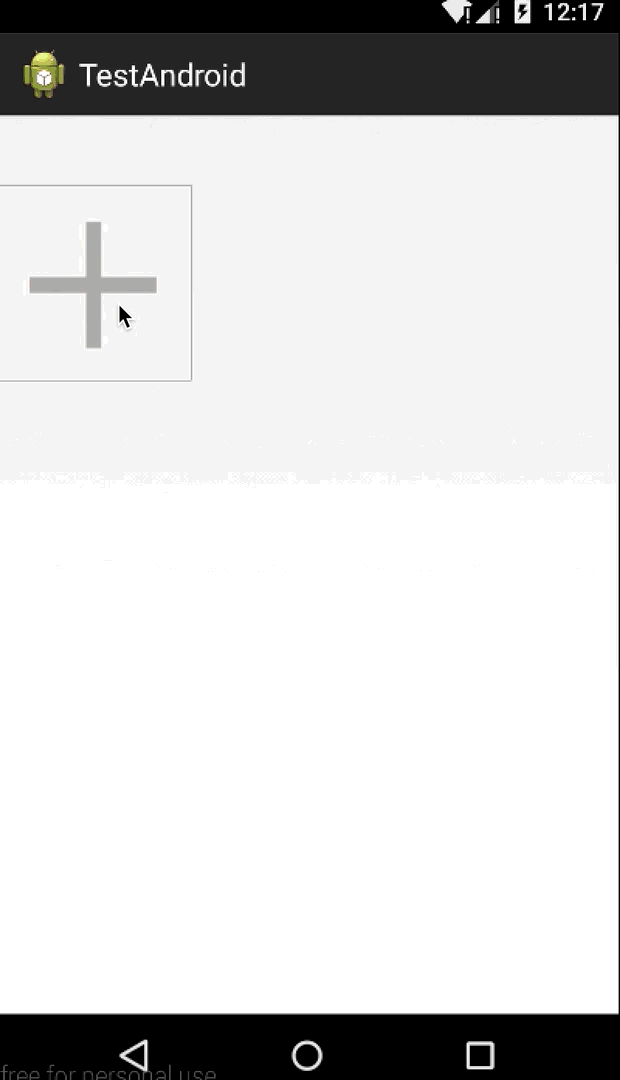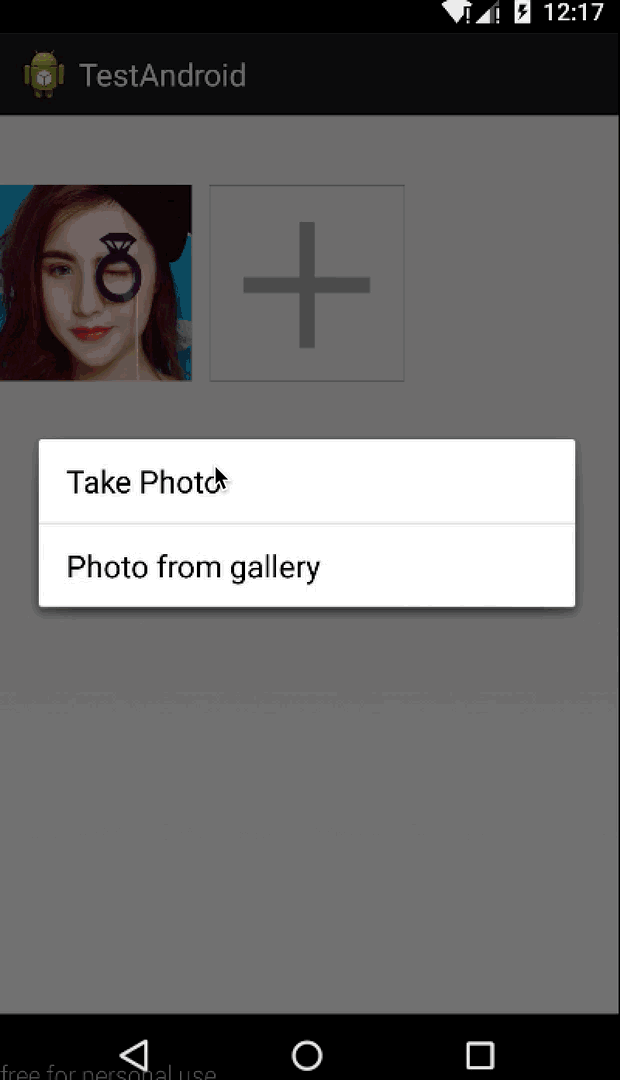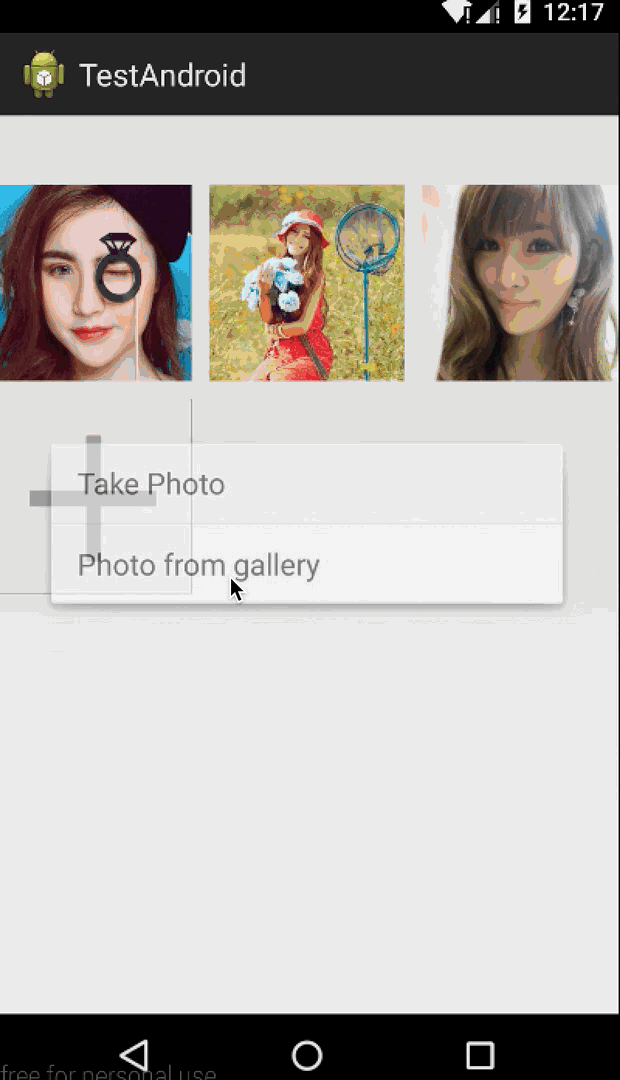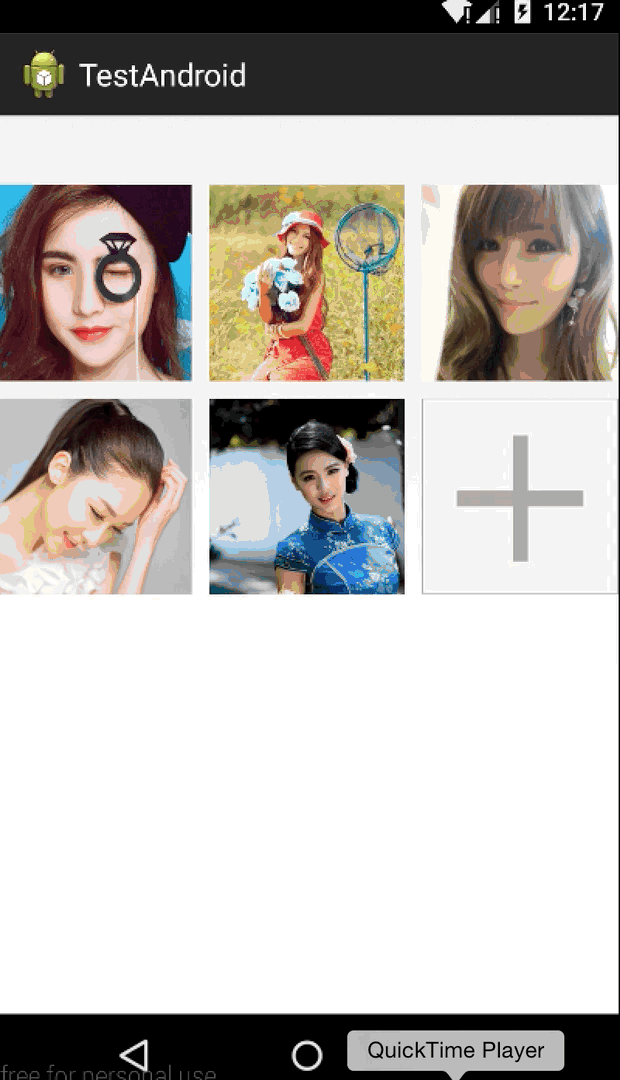
我們還是做一個實例來說明,我們今天做一個類似微信朋友圈 存儲要發送圖片的控件,點擊+號圖片,可以一直加圖片,最多9張。那麼微信是4個一排,我們這裡是3個一排,因為一般常規都是三個一排,這些都是細節不要在意(另外偷偷告訴大家,微信的實現是用TableLayout,-.-)。
public class NinePhotoView extends ViewGroup {
public static final int MAX_PHOTO_NUMBER = 9;
private int[] constImageIds = { R.drawable.girl_0, R.drawable.girl_1,
R.drawable.girl_2, R.drawable.girl_3, R.drawable.girl_4,
R.drawable.girl_5, R.drawable.girl_6, R.drawable.girl_7,
R.drawable.girl_8 };
// horizontal space among children views
int hSpace = Utils.dpToPx(10, getResources());
// vertical space among children views
int vSpace = Utils.dpToPx(10, getResources());
// every child view width and height.
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
// store images res id
ArrayList<integer> mImageResArrayList = new ArrayList<integer>(9);
private View addPhotoView;
public NinePhotoView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public NinePhotoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public NinePhotoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray t = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.NinePhotoView, 0, 0);
hSpace = t.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.NinePhotoView_ninephoto_hspace, hSpace);
vSpace = t.getDimensionPixelSize(
R.styleable.NinePhotoView_ninephoto_vspace, vSpace);
t.recycle();
addPhotoView = new View(context);
addView(addPhotoView);
mImageResArrayList.add(new integer());
}
目前為止,都跟上一篇說的大致差不多,另外拍照和從相冊選擇圖片不是我們這一篇的重點,所以我們把圖片硬編碼到代碼中(全是美女...),ViewGroup初始化時我們添加了一個+號按鈕,給用戶點擊添加新的圖片。
Measure
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int rw = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int rh = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
childWidth = (rw - 2 * hSpace) / 3;
childHeight = childWidth;
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = this.getChildAt(i);
//this.measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
LayoutParams lParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
lParams.left = (i % 3) * (childWidth + hSpace);
lParams.top = (i / 3) * (childWidth + vSpace);
}
int vw = rw;
int vh = rh;
if (childCount < 3) {
vw = childCount * (childWidth + hSpace);
}
vh = ((childCount + 3) / 3) * (childWidth + vSpace);
setMeasuredDimension(vw, vh);
}
我們的子View三個一排,而且都是正方形,所以我們上面通過循環很好去得到所有子View的位置,注意我們上面把子View的左上角坐標存儲到我們自定義的LayoutParams 的left和top二個字段中,Layout階段會使用,最後我們算得整個ViewGroup的寬高,調用setMeasuredDimension設置。
Layout
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4) {
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = this.getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams lParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(lParams.left, lParams.top, lParams.left + childWidth,
lParams.top + childHeight);
if (i == mImageResArrayList.size() - 1 && mImageResArrayList.size() != MAX_PHOTO_NUMBER) {
child.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.add_photo);
child.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
addPhotoBtnClick();
}
});
}else {
child.setBackgroundResource(constImageIds[i]);
child.setOnClickListener(null);
}
}
}
public void addPhoto() {
if (mImageResArrayList.size() < MAX_PHOTO_NUMBER) {
View newChild = new View(getContext());
addView(newChild);
mImageResArrayList.add(new integer());
requestLayout();
invalidate();
}
}
public void addPhotoBtnClick() {
final CharSequence[] items = { "Take Photo", "Photo from gallery" };
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getContext());
builder.setItems(items, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface arg0, int arg1) {
addPhoto();
}
});
builder.show();
}
最核心的就是調用layout方法,根據我們measure階段獲得的LayoutParams中的left和top字段,也很好對每個子View進行位置排列。然後判斷在圖片未達到最大值9張時,默認最後一張是+號圖片,然後設置點擊事件,彈出對話框供用戶選擇操作。
Draw
不需要重寫,使用ViewGroup默認實現即可。
附上布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_marginTop="40dp" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.sw.demo.widget.NinePhotoView android:id="@+id/photoview" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:ninephoto_hspace="10dp" app:ninephoto_vspace="10dp" app:rainbowbar_color="@android:color/holo_blue_bright" > </com.sw.demo.widget.NinePhotoView> </LinearLayout>
最後還是加上程序運行的效果圖,今天自定義ViewGroup的講解就這麼多了,祝大家每天都有新收獲,每天都有好心情~~~
 Android最佳實踐
Android最佳實踐
有一些做法可以遵循,在開發Android應用程序。這些建議由Android自身和保持在對於時間裡可改善。這些最佳實踐包括交互設計功能,性能,安全性和私隱,兼容性,測試,分
 Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android提供了許多方法來控制播放的音頻/視頻文件和流。其中該方法是通過一類稱為MediaPlayer。Android是提供MediaPlayer類訪問內置的媒體播放
 Android加載Spinner
Android加載Spinner
可以顯示在的Android任務,通過加載進度條的進展。進度條有兩種形狀。加載欄和加載微調(spinner)。在本章中,我們將討論微調(spinner)。Spinner 用
 Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android提供了許多方法來控制播放的音頻/視頻文件和流。其中該方法是通過一類稱為MediaPlayer。Android是提供MediaPlayer類訪問內置的媒體播放