編輯:Android開發實例
本文實例講述了Android編程實現圖標拖動效果的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
最近優化圖標拖動時的速率,稍微有一點點效果,直接把代碼貼出來,有興趣一起討論的朋友可以給我留言。
代碼如下:
DragView.java
package com.android.dragtest;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
public class DragView extends FrameLayout {
private static final String TAG = "DragView";
private float X;
private float Y;
private View mDragView;
public DragView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public DragView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public DragView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
mDragView = new View(context);
mDragView.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(60, 60));
mDragView.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.gamecenter));
mDragView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
addView(mDragView);
}
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.d(TAG, "===============>onInterceptTouchEvent ACTION_DOWN");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.d(TAG, "===============>onInterceptTouchEvent ACTION_MOVE");
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.d(TAG, "===============>onInterceptTouchEvent ACTION_UP");
break;
}
return true;
}
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
X = ev.getX();
Y = ev.getY();
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent ACTION_DOWN");
mDragView.layout((int)X - 30, (int)Y - 30, (int)X + 30, (int)Y + 30);
mDragView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent ACTION_MOVE x:" + X + " Y:" + Y);
mDragView.layout((int)X - 30, (int)Y - 30, (int)X + 30, (int)Y + 30);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent ACTION_UP");
mDragView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
break;
}
return true;
}
}
DragTestActivity.java
package com.android.dragtest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class DragTestActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
}
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.android.dragtest.DragView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> </com.android.dragtest.DragView> </LinearLayout>
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
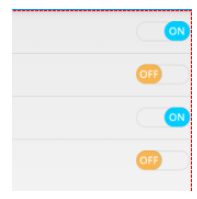 Android自定義實現開關按鈕代碼
Android自定義實現開關按鈕代碼
我們在應用中經常看到一些選擇開關狀態的配置文件,做項目的時候用的是android的Switch控件,但是感覺好丑的樣子子 個人認為還是自定義的比較好,先上個效果
 Android本地化
Android本地化
Android應用程序可以在許多不同地區的許多設備上運行。為了使應用程序更具交互性,應用程序應該處理以適合應用程序將要使用的語言環境方面的文字,數字,文件等。在本章中,我
 Android仿QQ聊天撒花特效 很真實
Android仿QQ聊天撒花特效 很真實
先看看效果圖吧 實現這樣的效果,你要知道貝塞爾曲線,何謂貝塞爾曲線?先在這裡打個問號 下面就直接寫了 1.activity_main.xml <Rel
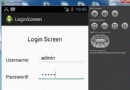 Android登錄實例
Android登錄實例
登錄應用程序的屏幕,詢問憑據登錄到一些特定的應用。可能需要登錄到Facebook,微博等本章介紹了,如何創建一個登錄界面,以及如何管理安全問題和錯誤嘗試。首先,必須定義兩