編輯:Android開發實例
本文實例講述了Android中數據庫常見操作。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
android中數據庫操作是非常常見了,我們會經常用到,操作的方法也有很多種形式,這裡我就把最常見的兩種形式記錄下來了,以備以後用到方便查看。我就不寫注釋和解釋了,因為android數據庫的操作和其它數據庫操作本質上都是一樣的,大同小異。需要的一些基本解釋都在代碼中,直接上代碼了。
簡單的代碼文件目錄:
首先這個類是數據庫幫助類,DBHelper.java,代碼如下:
package net.loonggg.db;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
/**
* 數據庫幫助類,繼承android自帶的SQLiteOpenHelper 主要用於數據庫的創建與更新
*
* @author loonggg
*
*/
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
public DBHelper(Context context) {
super(context, DBInfo.DB.DB_NAME, null, DBInfo.DB.DB_VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
db.execSQL(DBInfo.Table.USER_INFO_CREATE);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
db.execSQL(DBInfo.Table.USER_INFO_DROP);
onCreate(db);
}
}
其次是數據庫信息類,DBInfo.java,代碼如下:
package net.loonggg.db;
/**
* 數據庫信息類,主要是保存一些數據庫的版本,名字,及數據庫表的創建語句和表的信息等,通過這個類記錄,方便操作
*
* @author loonggg
*
*/
public class DBInfo {
/**
* 數據庫信息
*
* @author loonggg
*
*/
public static class DB {
// 數據庫名稱
public static final String DB_NAME = "test.db";
// 數據庫的版本號
public static final int DB_VERSION = 1;
}
/**
* 數據庫表的信息
*
* @author loonggg
*
*/
public static class Table {
public static final String USER_INFO_TB_NAME = "user_table";
public static final String USER_INFO_CREATE = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "
+ USER_INFO_TB_NAME
+ " ( _id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,userId text,userName text)";
public static final String USER_INFO_DROP = "DROP TABLE"
+ USER_INFO_TB_NAME;
}
}
再次是數據庫操作類,DBService.java,代碼如下:
package net.loonggg.service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import net.loonggg.db.DBHelper;
import net.loonggg.db.DBInfo.Table;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
/**
* 數據庫操作類,這個類主要的功能是:存放數據庫操作的一些方法 這裡有一些例子:包含數據庫的增刪改查,分別有兩種方法的操作,各有優缺點,都在解釋中
*
* @author loonggg
*
*/
public class DBService {
private DBHelper dbHelper = null;
public DBService(Context context) {
dbHelper = new DBHelper(context);
}
/**
* 添加一條記錄到數據庫
*
* @param id
* @param name
*/
public void add(String id, String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
// 不好之處:無返回值,無法判斷是否插入成功
db.execSQL("insert into user_table (userId,userName) values (?,?)",
new Object[] { id, name });
db.close();
}
public long addAndroid(String id, String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("userId", id);
values.put("userName", name);
// 好處:有返回值
long result = db.insert(Table.USER_INFO_TB_NAME, null, values);// 返回值是插入的是第幾行,大於0代表添加成功
db.close();
return result;
}
/**
* 查詢某條記錄是否存在
*
* @param name
* @return
*/
public boolean find(String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery(
"select * from user_table where userName = ?",
new String[] { name });
boolean result = cursor.moveToNext();
db.close();
return result;
}
public boolean findAndroid(String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query(Table.USER_INFO_TB_NAME, null, "userName = ?",
new String[] { name }, null, null, null);
boolean result = cursor.moveToNext();// true代表查找到了
db.close();
return result;
}
/**
* 修改一條記錄
*
* @param id
* @param name
*/
public void update(String id, String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
// 缺點無返回值
db.execSQL("update user_table set userName = ? where userId = ?",
new Object[] { name, id });
db.close();
}
public int updateAndroid(String id, String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("userName", name);
// 返回值大於0代表修改更新成功
int result = db.update(Table.USER_INFO_TB_NAME, values, "userId = ?",
new String[] { id });
db.close();
return result;
}
/**
* 刪除一條記錄
*
* @param name
*/
public void delete(String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
db.execSQL("delete from user_table where userName = ?",
new String[] { name });
db.close();
}
public int deleteAndroid(String name) {
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
int result = db.delete(Table.USER_INFO_TB_NAME, "userName = ?",
new String[] { name });// 返回值為受影響的行數,大於0代表成功
db.close();
return result;
}
/**
* 返回所有的數據庫信息
*
* @return
*/
public List<HashMap<String, String>> findAll() {
List<HashMap<String, String>> list = null;
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from user_table", null);
if (cursor.getCount() > 0) {
list = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String id = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("userId"));
String name = cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("userName"));
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("name", name);
list.add(map);
}
}
cursor.close();
db.close();
return list;
}
public List<HashMap<String, String>> findAllAndroid() {
List<HashMap<String, String>> list = null;
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query(Table.USER_INFO_TB_NAME, new String[] {
"userId", "userName" }, null, null, null, null, null);
if (cursor.getCount() > 0) {
list = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String id = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("userId"));
String name = cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("userName"));
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("id", id);
map.put("name", name);
list.add(map);
}
}
cursor.close();
db.close();
return list;
}
}
最後是MainActivity,簡單的調用了一下,這些操作,代碼如下:
package net.loonggg.test;
import net.loonggg.service.DBService;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button queryOne;
private Button insert;
private Button update;
private Button delete;
private Button findAll;
private DBService service;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
queryOne = (Button) findViewById(R.id.queryOne);
insert = (Button) findViewById(R.id.insert);
update = (Button) findViewById(R.id.update);
delete = (Button) findViewById(R.id.delete);
findAll = (Button) findViewById(R.id.findAll);
queryOne.setOnClickListener(new ButtonListener());
insert.setOnClickListener(new ButtonListener());
update.setOnClickListener(new ButtonListener());
delete.setOnClickListener(new ButtonListener());
findAll.setOnClickListener(new ButtonListener());
service = new DBService(this);
}
class ButtonListener implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.queryOne:
// service.find("loonggg");
service.findAndroid("loonggg");
break;
case R.id.insert:
// service.add("1", "loonggg");
service.addAndroid("2", "heihei");
break;
case R.id.update:
// service.update("1", "timmy");
service.updateAndroid("1", "haha");
break;
case R.id.delete:
// service.delete("timmy");
service.deleteAndroid("heihei");
break;
case R.id.findAll:
// service.findAll();
service.findAllAndroid();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
還有MainActivity對應的布局文件,activity_main.xml:
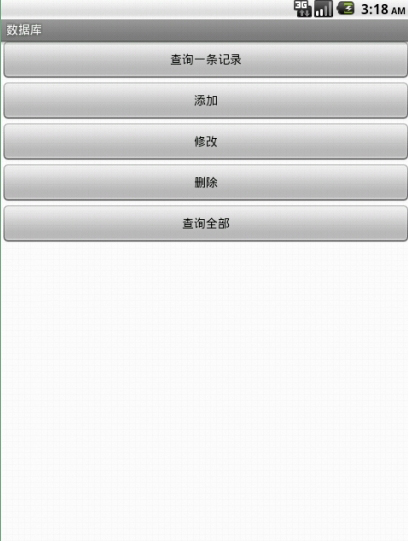
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <Button android:id="@+id/queryOne" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="查詢一條記錄" /> <Button android:id="@+id/insert" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="添加" /> <Button android:id="@+id/update" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="修改" /> <Button android:id="@+id/delete" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="刪除" /> <Button android:id="@+id/findAll" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="查詢全部" /> </LinearLayout>
到這裡就介紹完了,這些代碼並不高深,之所以記錄下來,是留著以後用到的時候方便查看,當然這個代碼對於初學者,還是非常有幫助的。
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
 android編程之XML文件解析方法詳解(附源碼)
android編程之XML文件解析方法詳解(附源碼)
本文實例講述了android編程之XML文件解析方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下: 在android開發中,經常用到去解析xml文件,常見的解析xml的方式有
 Android登錄實例
Android登錄實例
登錄應用程序的屏幕,詢問憑據登錄到一些特定的應用。可能需要登錄到Facebook,微博等本章介紹了,如何創建一個登錄界面,以及如何管理安全問題和錯誤嘗試。首先,必須定義兩
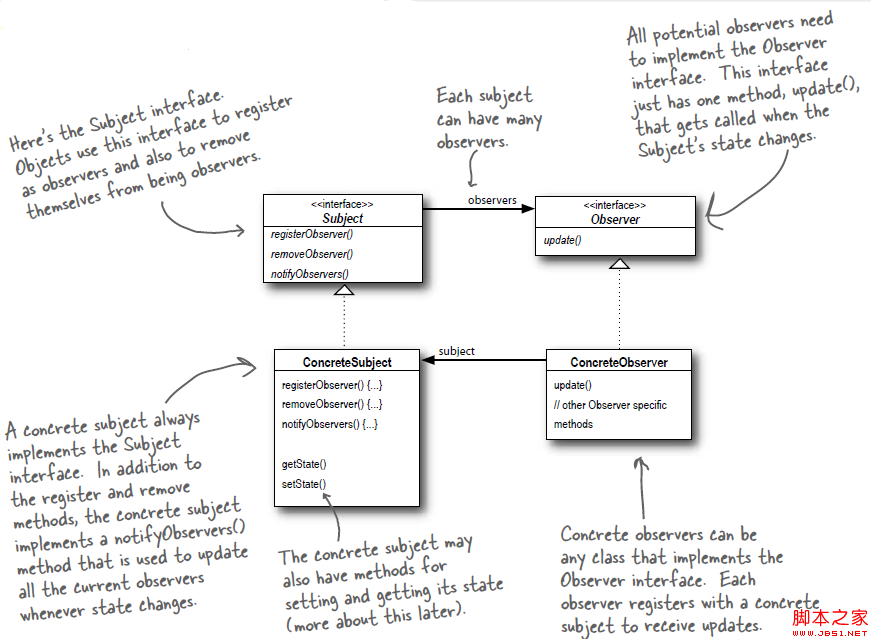 Android源碼學習之觀察者模式應用及優點介紹
Android源碼學習之觀察者模式應用及優點介紹
觀察者模式定義: Define a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object
 基於Android設計模式之
基於Android設計模式之
策略模式其實特別簡單(聽到這句話,大家是不是心裡一下子放松了?)。比如排序,官方告訴大家我這裡有一個排序的接口ISort的sort()方法,然後民間各盡其能,實現