編輯:Android開發實例
在開發Android應用時必須遵守單線程模型的原則: Android UI操作並不是線程安全的並且這些操作必須在UI線程中執行。在單線程模型中始終要記住兩條法則:
1. 不要阻塞UI線程
2. 確保只在UI線程中訪問Android UI工具包
當一個程序第一次啟動時,Android會同時啟動一個對應的主線程(Main Thread),主線程主要負責處理與UI相關的事件,如:用戶的按鍵事件,用戶接觸屏幕的事件以及屏幕繪圖事件,並把相關的事件分發到對應的組件進行處理。所以主線程通常又被叫做UI線程。
比如說從網上獲取一個網頁,在一個TextView中將其源代碼顯示出來,這種涉及到網絡操作的程序一般都是需要開一個線程完成網絡訪問,但是在獲得頁面源碼後,是不能直接在網絡操作線程中調用TextView.setText()的.因為其他線程中是不能直接訪問主UI線程成員 。
android提供了幾種在其他線程中訪問UI線程的方法。
Activity.runOnUiThread( Runnable )
View.post( Runnable )
View.postDelayed( Runnable, long )
Hanlder
這些類或方法同樣會使你的代碼很復雜很難理解。然而當你需要實現一些很復雜的操作並需要頻繁地更新UI時這會變得更糟糕。
為了解決這個問題,Android 1.5提供了一個工具類:AsyncTask,它使創建需要與用戶界面交互的長時間運行的任務變得更簡單。相對來說AsyncTask更輕量級一些,適用於簡單的異步處理,不需要借助線程和Handler即可實現。
AsyncTask是抽象類.AsyncTask定義了三種泛型類型 Params,Progress和Result。
Params 啟動任務執行的輸入參數,比如HTTP請求的URL。
Progress 後台任務執行的百分比。
Result 後台執行任務最終返回的結果,比如String。
AsyncTask的執行分為四個步驟,每一步都對應一個回調方法,這些方法不應該由應用程序調用,開發者需要做的就是實現這些方法。
1) 子類化AsyncTask
2) 實現AsyncTask中定義的下面一個或幾個方法
onPreExecute(), 該方法將在執行實際的後台操作前被UI thread調用。可以在該方法中做一些准備工作,如在界面上顯示一個進度條。
doInBackground(Params...), 將在onPreExecute 方法執行後馬上執行,該方法運行在後台線程中。這裡將主要負責執行那些很耗時的後台計算工作。可以調用 publishProgress方法來更新實時的任務進度。該方法是抽象方法,子類必須實現。
onProgressUpdate(Progress...),在publishProgress方法被調用後,UI thread將調用這個方法從而在界面上展示任務的進展情況,例如通過一個進度條進行展示。
onPostExecute(Result), 在doInBackground 執行完成後,onPostExecute 方法將被UI thread調用,後台的計算結果將通過該方法傳遞到UI thread.
為了正確的使用AsyncTask類,以下是幾條必須遵守的准則:
1) Task的實例必須在UI thread中創建
2) execute方法必須在UI thread中調用
3) 不要手動的調用onPreExecute(), onPostExecute(Result),doInBackground(Params...), onProgressUpdate(Progress...)這幾個方法
4) 該task只能被執行一次,否則多次調用時將會出現異常
doInBackground方法和onPostExecute的參數必須對應,這兩個參數在AsyncTask聲明的泛型參數列表中指定,第一個為doInBackground接受的參數,第二個為顯示進度的參數,第第三個為doInBackground返回和onPostExecute傳入的參數。
從網上獲取一個網頁,在一個TextView中將其源代碼顯示出來
代碼如下:
package test.list;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class NetworkActivity extends Activity{
private TextView message;
private Button open;
private EditText url;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.network);
message= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.message);
url= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.url);
open= (Button) findViewById(R.id.open);
open.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View arg0) {
connect();
}
});
}
private void connect() {
PageTask task = new PageTask(this);
task.execute(url.getText().toString());
}
class PageTask extends AsyncTask<String, Integer, String> {
// 可變長的輸入參數,與AsyncTask.exucute()對應
ProgressDialog pdialog;
public PageTask(Context context){
pdialog = new ProgressDialog(context, 0);
pdialog.setButton("cancel", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int i) {
dialog.cancel();
}
});
pdialog.setOnCancelListener(new DialogInterface.OnCancelListener() {
public void onCancel(DialogInterface dialog) {
finish();
}
});
pdialog.setCancelable(true);
pdialog.setMax(100);
pdialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
pdialog.show();
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
try{
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
// params[0]代表連接的url
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(params[0]);
HttpResponse response = client.execute(get);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
long length = entity.getContentLength();
InputStream is = entity.getContent();
String s = null;
if(is != null) {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[128];
int ch = -1;
int count = 0;
while((ch = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
baos.write(buf, 0, ch);
count += ch;
if(length > 0) {
// 如果知道響應的長度,調用publishProgress()更新進度
publishProgress((int) ((count / (float) length) * 100));
}
// 讓線程休眠100ms
Thread.sleep(100);
}
s = new String(baos.toByteArray()); }
// 返回結果
return s;
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled() {
super.onCancelled();
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
// 返回HTML頁面的內容
message.setText(result);
pdialog.dismiss();
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
// 任務啟動,可以在這裡顯示一個對話框,這裡簡單處理
message.setText(R.string.task_started);
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
// 更新進度
System.out.println(""+values[0]);
message.setText(""+values[0]);
pdialog.setProgress(values[0]);
}
}
}
最後需要說明AsyncTask不能完全取代線程,在一些邏輯較為復雜或者需要在後台反復執行的邏輯就可能需要線程來實現了。
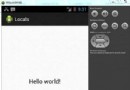 Android本地化
Android本地化
Android應用程序可以在許多不同地區的許多設備上運行。為了使應用程序更具交互性,應用程序應該處理以適合應用程序將要使用的語言環境方面的文字,數字,文件等。在本章中,我
 Andorid TextView字幕效果實例
Andorid TextView字幕效果實例
一、效果圖 二、代碼 代碼如下: public class TextSubView extends TextView { private TextPaint mP
 Android Touch事件分發過程詳解
Android Touch事件分發過程詳解
本文以實例形式講述了Android Touch事件分發過程,對於深入理解與掌握Android程序設計有很大的幫助作用。具體分析如下: 首先,從一個簡單示例入手:
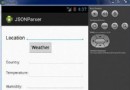 Android JSON解析器
Android JSON解析器
JSON代表JavaScript對象符號。它是一個獨立的數據交換格式,是XML的最佳替代品。本章介紹了如何解析JSON文件,並從中提取所需的信息。Android提供了四個