編輯:Android開發實例
xml代碼:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
- <TextView
- android:text="@string/hello"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- />
- <EditText
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_weight="1"
- android:id="@+id/edittext"
- />
- <LinearLayout
- android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal">
- <TextView
- android:text="text1"
- android:id="@+id/TextView01"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- />
- <Button android:text="Button01"
- android:id="@+id/Button01"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_weight="1"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="text2"
- android:id="@+id/TextView02"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="buttom"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
Java代碼(動態添加組件):
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <RelativeLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:id="@+id/relativelayout">
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/image"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/icon"
- />
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/text1"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/hello"
- android:layout_toRightOf="@id/image"
- />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/button1"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="button1"
- android:layout_toRightOf="@id/image"
- android:layout_below="@id/text1"
- />
- </RelativeLayout>
效果圖: 先添加參照物(ImageView),然後就可以依次添加其他組件,定義位置規則rule!位置規則是不分先後的!另外ADT插件提供的預覽圖,有時候是不准的,未能及時更新,所以最好還是要到模擬器上測試! RelativeLayout的xml屬性很多,總的來說分為2類: 1) 要指定參照物的,layout_alignBottom,layout_toLeftOf,layout_above,layout_alignBaseline系列的; layout_above = ”@id/text1“ 2) 以parent為參照物,設置true/false,layout_centerVertical,layout_alignParentLeft系列的。 layout_alignParentLeft = ”true“ 其中layout_alignWithParentIfMissing是比較有用且要注意的屬性,當設置為true,在指定的參照物找不到的情況下,會使用parent作為新的參照物! RelativeLayout.LayoutParams是用於設置位置規則的。上述的xml屬性均來自此靜態類。但它的AddRule(int verb, int anchor),參數的verb動作卻是引用RelativeLayout的常量,而這些常量和部分xml屬性相對應。參數anchor的值可能是參照物的id,RelativeLayout.TRUE,-1(當不需要指定anchor的verb)。可以這樣理解verb和anchor: xml屬性 (verb) = "value" (anchor) 其中它的構造函數之一: RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(int w, int h),參數指定所要設置子View的寬度和高度。
- public class RelativeDemo extends Activity {
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.relative);
- RelativeLayout.LayoutParams lp = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, //width
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT //height
- );
- //設置editText layout_below="@id/button1"
- lp.addRule(RelativeLayout.BELOW, R.id.button1);
- //設置editText layout_alignLeft="@id/image"
- lp.addRule(RelativeLayout.ALIGN_LEFT, R.id.image);
- ((RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.relativelayout)).addView(
- new EditText(this), lp);
- }
- }
本文出自 “學習Android” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://android.blog.51cto.com/268543/298345
 Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android MediaPlayer(多媒體播放)
Android提供了許多方法來控制播放的音頻/視頻文件和流。其中該方法是通過一類稱為MediaPlayer。Android是提供MediaPlayer類訪問內置的媒體播放
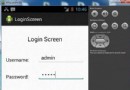 Android登錄實例
Android登錄實例
登錄應用程序的屏幕,詢問憑據登錄到一些特定的應用。可能需要登錄到Facebook,微博等本章介紹了,如何創建一個登錄界面,以及如何管理安全問題和錯誤嘗試。首先,必須定義兩
 Android中庫項目的使用方法圖文介紹
Android中庫項目的使用方法圖文介紹
在軟件開發過程中,程序代碼的復用,是非常重要的概念。我們總是需要使用一些現有的模塊、包、框架,或開發自己的模塊、包、框架,來實現對程序代碼的復用。比如在JavaW
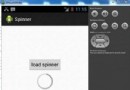 Android加載Spinner
Android加載Spinner
可以顯示在的Android任務,通過加載進度條的進展。進度條有兩種形狀。加載欄和加載微調(spinner)。在本章中,我們將討論微調(spinner)。Spinner 用