編輯:Android資訊
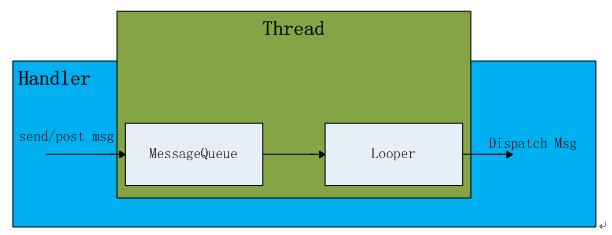
Android的消息機制幾乎是面試必問的話題,當然也並不是因為面試,而去學習,更重要的是它在Android的開發中是必不可少的,占著舉足輕重的地位,所以弄懂它是很有必要的。下面就來說說最基本的東西。
作用:
Looper構造方法是私有的,其中做了兩件事
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
不能,一個線程對應一個Looper對象,通過ThreadLocal保證一個線程只有一個Looper與之對應,如果多次調用Looper.prepare();則會拋出運行時異常。
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { // 查看是否有looper與當前線程對應
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
是,當開啟一個loop後是一個死循環,從MessageQueue中取出消息,處理消息,但是也有可能退出,在沒有消息後退出循環。
public static void loop() {
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
}
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// 略
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) { // 當沒有消息的時候,退出
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
}
// 略
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
}
不可以,Looper.prepareMainLooper最終也是調用prepare(),同2.
public static void prepareMainLooper() {
prepare(false); // 創建一個Looper
synchronized (Looper.class) {
if (sMainLooper != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");
}
sMainLooper = myLooper();
}
}
MainLooper是啟動Activity創建ActivityThread(並不是一個Thread)時候創建,所以不能多次創建。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 略
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// 略
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
// 略
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
// 略
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
}
作用:
我們知道一個Looper對應一個Thread,一個Looper包含一個MessageQueue。當我們創建Handler時就會從當前線程中取出與之對應的Looper,讓後在從Looper中取出MessageQueue。
// 1、自動獲取
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
// 略
mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); // 取出當前線程中的Looper
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; // 取出MessageQueue
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
// 2、傳遞一個Looper進來
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = looper;
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
單項鏈表結構。
作用:
從全局消息池(鏈表結構)中
public static Message obtain() {
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPool != null) {
Message m = sPool;
sPool = m.next;
m.next = null;
m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag
sPoolSize--;
return m;
}
}
return new Message();
}
Android中想要傳遞對象要麼實現Serializable要麼Parcelable,在這裡是實現了Parcelable接口。
public final class Message implements Parcelable {
// 略
}
我們知道在消息傳機制中Handler充當著“快遞員”的角色,那麼他又是如何與“貨物”--Message發生關系呢?實際上Message有一個成員變量target他的類型正是Handler,
/*package*/ Runnable callback; public int arg1; public int arg2; public Object obj; /*package*/ Handler target; // 關鍵點
當我們通過Handler去send一個Message時候最終都會為target賦值為this,即當前的Handler。
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {
msg.target = this; // 賦值語句
if (mAsynchronous) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
另為如果是通過Message.Obtain(),獲取的復用Message也會為其賦值。
多說一句,Handler.obtainMessage()調用的就是Message.Obtain()。
public final Message obtainMessage(){
return Message.obtain(this);
}
通過一系列的包涵關系,最終Looper、Handler、Message、MessageQueue即發生關聯,從而形成一個閉合,開啟消息循環。
最近一直在看這方面的知識,但是能力有限,還是有不少困惑,如果有錯誤,或你理解下面的問題請聯系我[email protected],願與君交流學習,謝謝
1、Message中的sPool,哪裡初始化的?為什麼Message.obtain()中不會拋異常?
2、ActivityThread並不是線程,為什麼可以創建一個Looper,Main Thread什麼時候創建?
3、為什麼序列化了的對象就可以傳遞?與Binder有關?
4、MessageQueue對應的是NativeMessageQueue,具體實現需要學習?
5、Loop.loop(),會退出嗎?退出時機是什麼?如果會退出,那麼主線程同樣會退出嗎?
 Android內存洩漏的8種可能
Android內存洩漏的8種可能
Java是垃圾回收語言的一種,其優點是開發者無需特意管理內存分配,降低了應用由於局部故障(segmentation fault)導致崩潰,同時防止未釋放的內存把堆
 Android自動化測試解決方案
Android自動化測試解決方案
桌面應用程序與浏覽器端的自動化測試都已經歷了十年的發展,無論是從工具上還是項目管理方 法論上都已經趨於成熟。而移動設備端應用程序的自動化測試近兩年才剛起步,似乎一
 Android項目的依賴關系解析
Android項目的依賴關系解析
在Android SDK Tools和Eclipse ADT 插件的第17版本 (revision 17)中,我們對Android項目的依賴關系管理做了很多改變。
 Android 社會化分享項目總結
Android 社會化分享項目總結
隨著現在社交網絡的日益繁多,眾多的社交客戶端已占據了人們的大量時間,所以在我們的應用中具有一鍵分享的功能對提高我們產品的知名度有很大的幫助。新浪微博、騰訊微博、騰