編輯:Android資訊
這幾天一直在思考一個問題,為什麼國內的熱門博客和熱門教程都是很久之前的,例如我向學習EventBus,不論是鴻洋的博文還是其他論壇,幾乎清一色的OnEvent,或者比如我想學習Dagger2,文章數量更是少之又少,關鍵大量還是Dagger1的內容。
基於此,外加上看到CodePath公司整合的Android資源正好符合實際需求,所以特意在sg開辟專欄,希望大家能夠喜歡,在此申明下,因為工作量巨大,我非常有幸能夠同@xixicat一起翻譯這一專題,也懇請大家,如遇到任何翻譯錯誤,請指正,可評論中注明,也可電郵我,同時如果某位志趣相投人士有興趣參與翻譯,也可電郵我,我會進一步聯系你:[email protected]。
廢話不多說,那麼我們就開始吧。
你有多少次在StackOverflow中尋找答案時,發現其答案竟然是2年前的,你又有多少次搜出的博文是幾年前的舊文呢,我相信絕大部分的你都有這樣的經歷,所以我們為什麼不能利用社交讓我們的的Android文檔布滿每個細節呢。
Context對象可以獲取應用狀態的信息,其使得activitys和Fragments以及Services能夠使用資源文件,圖片,主題,以及其他的文件夾內容。其也可以用於使用Android自帶服務,例如inflate,鍵盤,以及content providers。
很多情況下,當你需要用到Context的時候,你肯定只是簡單的利用當前activity的實例this。當你一個被activity創建的內部對象的時候,例如adapters裡或者fragments裡的時候,你需要將activity的實例傳給它們。而當你在activity之外,例如application或者service的時候,我們需要利用application的context對象代替。
Intent intent = new Intent(context, MyActivity.class); startActivity(intent);
TextView textView = new TextView(context);
Contexts包含了以下信息:
我們使用context來獲得LayoutInflater,其可以在內存中inflate xml布局文件
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context); inflater.inflate(R.layout.my_layout, parent);
我們使用context來獲得LocalBroadcastManager,其可以發送或者注冊廣播接收。
Intent broadcastIntent = new Intent("custom-action");
LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(context).sendBroadcast(intent);
例如當你需要發送通知,你需要NotificationManager。
NotificationManager manager =
(NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
int notificationId = 1;
// Context is required to construct RemoteViews
Notification.Builder builder =
new Notification.Builder(context).setContentTitle("custom title");
notificationManager.notify(notificationId, builder.build());
在此就不一一列舉系統服務了, 系統服務列表 參見。
當主題被運用在應用層面,其也可被運用在activity層面,比如當應用層面定義了一些主題,activity可以將其覆蓋。
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/MyCustomTheme">
大部分視圖需要傳入activity級別的Context對象,這樣其才能獲取主題,styles,dimensions等屬性。如果某個控件沒有使用theme,其默認使用了應用的主題。
在大部分情況下,你需要使用activity級別的Context。通常,關鍵字this代表著一個類的實例,其可被用於activity中的Context傳遞。例如:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Toast.makeText(this, "hello", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
當我們使用了匿名內部類的適合,例如實現監聽,this關鍵字的使用:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
TextView tvTest = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.abc);
tvTest.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "hello", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
當你為listview定義適配器的適合,getContext()方法被經常使用,其用來實例化xml布局。
if (convertView == null) {
convertView =
LayoutInflater
.from(getContext())
.inflate(R.layout.item_user, parent, false);
}
注意:當你傳入的是應用級別的context,你會發現themes/styles屬性將不會被應用,所以確保你在這裡傳入的是Activity級別的context。
public class MyRecyclerAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyRecyclerAdapter.ViewHolder> {
@Override
public ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View v =
LayoutInflater
.from(parent.getContext())
.inflate(itemLayout, parent, false);
return new ViewHolder(v);
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(ViewHolder viewHolder, int i) {
// If a context is needed, it can be retrieved
// from the ViewHolder's root view.
Context context = viewHolder.itemView.getContext();
// Dynamically add a view using the context provided.
if(i == 0) {
TextView tvMessage = new TextView(context);
tvMessage.setText("Only displayed for the first item.")
viewHolder.customViewGroup.addView(tvMessage);
}
}
public static class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
public FrameLayout customViewGroup;
public ViewHolder(view imageView) {
super(imageView);
// Perform other view lookups.
customViewGroup = (FrameLayout) imageView.findById(R.id.customViewGroup);
}
}
}
可以看到,ArrayAdapter需要在其構造器裡面傳入context,RecyclerView.Adapter不需要。
RecyclerView通常將其作為父視圖傳給RecyclerView.Adapter.onCreateViewHolder()。
如果在onCreateViewHolder()方法的外面,你需要用到context,你也可以使用ViewHolder,例如viewHolder.itemView.getContext()。itemView是一個公有,非空,final類型的成員變量。
應用級別的context通常在單例中使用,例如一個常用的管理類,其管理Context對象來獲取系統服務,但是其不能同時被多個activity獲取。由於維護一個activity級別的context引用會導致內存洩露,所以你需要使用application級別的context替代。
在下面這個例子中,如果context是activity級別或者service級別,當其被destroy,其實際不會被gc, 因為CustomManager類擁有了其static應用。
pubic class CustomManager {
private static CustomManager sInstance;
public static CustomManager getInstance(Context context) {
if (sInstance == null) {
// This class will hold a reference to the context
// until it's unloaded. The context could be an Activity or Service.
sInstance = new CustomManager(context);
}
return sInstance;
}
private Context mContext;
private CustomManager(Context context) {
mContext = context;
}
}
為了避免內存洩露,不要在其生命周期以外持有該對象。檢查你的非主線程,pending handlers或者內部類是否持有context對象。
存儲應用級別的context的最好的辦法是CustomManager.getInstance(),其為單例,生命周期為整個應用的進程。
public static CustomManager getInstance(Context context) {
if (sInstance == null) {
// When storing a reference to a context, use the application context.
// Never store the context itself, which could be a component.
sInstance = new CustomManager(context.getApplicationContext());
}
return sInstance;
}
 深入理解Android NDK日志符號化
深入理解Android NDK日志符號化
前言 為了進行代碼及產品保護,幾乎所有的非開源App都會進行代碼混淆。這樣,當收集到崩潰信息後,就需要進行符號化來還原代碼信息,以便開發者可以定 位Bug。基於使
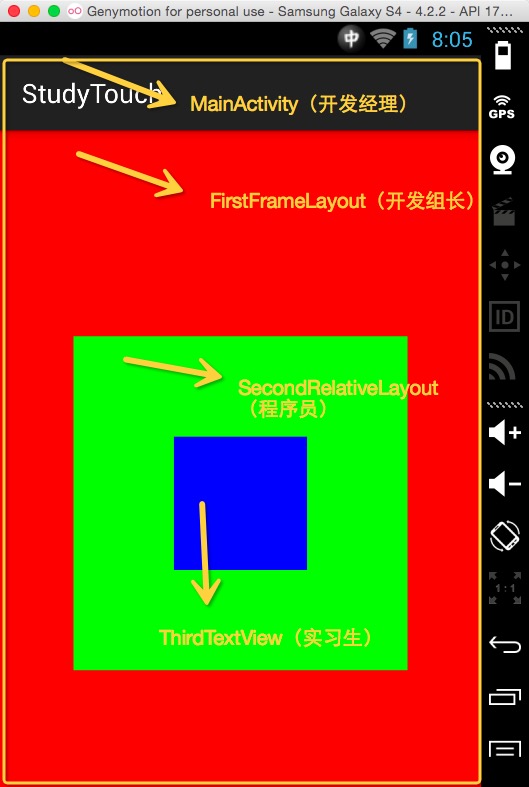 Android Touch事件傳遞機制通俗講解
Android Touch事件傳遞機制通俗講解
在講正題之前我們講一段有關任務傳遞的小故事,拋磚迎玉下: 話說一家軟件公司,來一個任務,分派給了開發經理去完成: 開發經理拿到,看了一下,感覺好簡單,於是 開發
 22 個 Android Studio 優秀插件匯總
22 個 Android Studio 優秀插件匯總
第一部分 插件的介紹 Google 在2013年5月的I/O開發者大會推出了基於IntelliJ IDEA java ide上的Android Studio。An
 Android UI控件系列:Spinner(下拉列表)
Android UI控件系列:Spinner(下拉列表)
當在某個網站注冊賬號的時候,網站會讓我們提供性別,生日,城市等信息,為了方便,就提供了一個下拉列表供我們選擇,在Android也同樣有這樣的功能,這就是Spinn