編輯:關於Android編程
一、概述
EventBus是一款針對Android優化的發布/訂閱事件總線。主要功能是替代Intent,Handler,BroadCast在Fragment,Activity,Service,線程之間傳遞消息.優點是開銷小,代碼更優雅。以及將發送者和接收者解耦。
1、下載EventBus的類庫
源碼:EventBus_jb51.rar
2、基本使用
(1)自定義一個類,可以是空類,比如:
public class AnyEventType {
public AnyEventType(){}
}
(2)在要接收消息的頁面注冊:
eventBus.register(this);
(3)發送消息
eventBus.post(new AnyEventType event);
(4)接受消息的頁面實現(共有四個函數,各功能不同,這是其中之一,可以選擇性的實現,這裡先實現一個):
public void onEvent(AnyEventType event) {}
(5)解除注冊
eventBus.unregister(this);
順序就是這麼個順序,可真正讓自己寫,估計還是雲裡霧裡的,下面舉個例子來說明下。
首先,在EventBus中,獲取實例的方法一般是采用EventBus.getInstance()來獲取默認的EventBus實例,當然你也可以new一個又一個,個人感覺還是用默認的比較好,以防出錯。
二、實戰
先給大家看個例子:
當擊btn_try按鈕的時候,跳到第二個Activity,當點擊第二個activity上面的First Event按鈕的時候向第一個Activity發送消息,當第一個Activity收到消息後,一方面將消息Toast顯示,一方面放入textView中顯示。
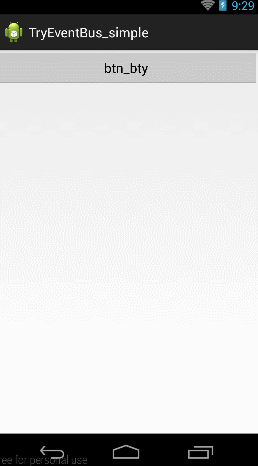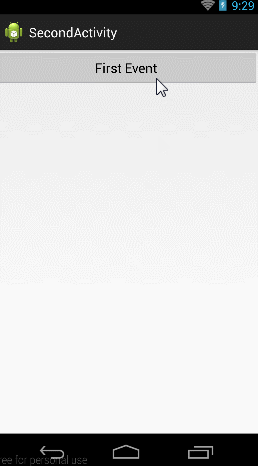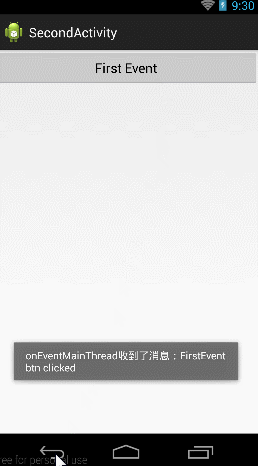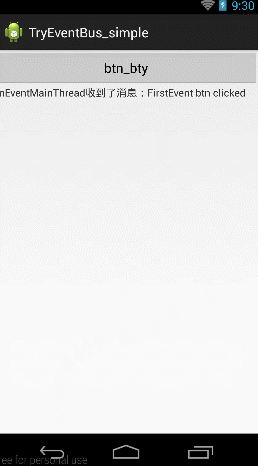
按照下面的步驟,下面來建這個工程:
1、基本框架搭建
想必大家從一個Activity跳轉到第二個Activity的程序應該都會寫,這裡先稍稍把兩個Activity跳轉的代碼建起來。後面再添加EventBus相關的玩意。
MainActivity布局(activity_main.xml)
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_try" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="btn_bty"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> </LinearLayout>
新建一個Activity,SecondActivity布局(activity_second.xml)
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.harvic.try_eventbus_1.SecondActivity" > <Button android:id="@+id/btn_first_event" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="First Event"/> </LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java (點擊btn跳轉到第二個Activity)
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button btn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_try);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),
SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
到這,基本框架就搭完了,下面開始按步驟使用EventBus了。
2、新建一個類FirstEvent
package com.harvic.other;
public class FirstEvent {
private String mMsg;
public FirstEvent(String msg) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
mMsg = msg;
}
public String getMsg(){
return mMsg;
}
}
這個類很簡單,構造時傳進去一個字符串,然後可以通過getMsg()獲取出來。
3、在要接收消息的頁面注冊EventBus:
在上面的GIF圖片的演示中,大家也可以看到,我們是要在MainActivity中接收發過來的消息的,所以我們在MainActivity中注冊消息。
通過我們會在OnCreate()函數中注冊EventBus,在OnDestroy()函數中反注冊。所以整體的注冊與反注冊的代碼如下:
package com.example.tryeventbus_simple;
import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent;
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button btn;
TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//注冊EventBus
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_try);
tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),
SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy(){
super.onDestroy();
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);//反注冊EventBus
}
}
4、發送消息
發送消息是使用EventBus中的Post方法來實現發送的,發送過去的是我們新建的類的實例!
EventBus.getDefault().post(new FirstEvent("FirstEvent btn clicked"));
完整的SecondActivity.Java的代碼如下:
package com.example.tryeventbus_simple;
import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent;
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
private Button btn_FirstEvent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_second);
btn_FirstEvent = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_first_event);
btn_FirstEvent.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
EventBus.getDefault().post(
new FirstEvent("FirstEvent btn clicked"));
}
});
}
}
5、接收消息
接收消息時,我們使用EventBus中最常用的onEventMainThread()函數來接收消息,具體為什麼用這個,我們下篇再講,這裡先給大家一個初步認識,要先能把EventBus用起來先。
在MainActivity中重寫onEventMainThread(FirstEvent event),參數就是我們自己定義的類:
在收到Event實例後,我們將其中攜帶的消息取出,一方面Toast出去,一方面傳到TextView中;
public void onEventMainThread(FirstEvent event) {
String msg = "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg();
Log.d("harvic", msg);
tv.setText(msg);
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
完整的MainActiviy代碼如下:
package com.example.tryeventbus_simple;
import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent;
import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button btn;
TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_try);
tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),
SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
public void onEventMainThread(FirstEvent event) {
String msg = "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg();
Log.d("harvic", msg);
tv.setText(msg);
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy(){
super.onDestroy();
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
}
}
好了,到這,基本上算初步把EventBus用起來了,下篇再講講EventBus的幾個函數,及各個函數間是如何識別當前如何調用哪個函數的。
源碼地址:EventBus_jb51.rar
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 android高分段進階攻略(5)android指南針
android高分段進階攻略(5)android指南針
前段時間,有一位網友發私信給我(@伍歌),問我做過磁場傳感器可以做過指南針嗎?其實我第一節裡面已經說過了,磁場傳感器可以做,只是算法比較麻煩,最簡單的指南針使用方向傳感器
 最常用和最難用的Android控件ListView
最常用和最難用的Android控件ListView
ListView允許用戶通過手指上下滑動的方式將屏幕外的數據滾動到屏幕內,同時屏幕上原有的數據則會滾動出屏幕.1. ListView的簡單用法首先新建一個ListView
 Android7.0 PackageManagerService (2) PKMS構造函數的主要工作
Android7.0 PackageManagerService (2) PKMS構造函數的主要工作
從本篇博客開始,我們開始分析PKMS的構造函數,看看PKMS到底是如何解析和管理手機中APK的信息的。由於PKMS的構造函數較長,我們會分段進行研究。public Pac
 Android Socket IQ聊天軟件 之 聊天氣泡編碼步驟講解
Android Socket IQ聊天軟件 之 聊天氣泡編碼步驟講解
之前我們說到了關於IQ聊天軟件的局域網聊天測試,今天給大伙說說氣泡的生成和編碼,這不是第三方的東西,是自己 開發的,需要整合布局和容器來實現,其實當你看到源碼後,就會覺得