編輯:關於Android編程
Android實現讀取NFC卡卡號示例,具體如下:
1.權限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.NFC" />
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.nfc"
android:required="true" />
2.注冊(靜態)
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.nfc.action.TAG_DISCOVERED" />
<data android:mimeType="text/plain" />
</intent-filter>
3.Activity
初始化
//初始化NfcAdapter
mNfcAdapter = NfcAdapter.getDefaultAdapter(this);
// 初始化PendingIntent,當有NFC設備連接上的時候,就交給當前Activity處理
pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, new Intent(this, getClass())
.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP), 0);
啟動
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mNfcAdapter.enableForegroundDispatch(this, pi, null, null); //啟動
}
獲取數據
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent);
// 當前app正在前端界面運行,這個時候有intent發送過來,那麼系統就會調用onNewIntent回調方法,將intent傳送過來
// 我們只需要在這裡檢驗這個intent是否是NFC相關的intent,如果是,就調用處理方法
if (NfcAdapter.ACTION_TAG_DISCOVERED.equals(intent.getAction())) {
processIntent(intent);
}
}
解析
/**
* Parses the NDEF Message from the intent and prints to the TextView
*/
private void processIntent(Intent intent) {
//取出封裝在intent中的TAG
Tag tagFromIntent = intent.getParcelableExtra(NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG);
String CardId =ByteArrayToHexString(tagFromIntent.getId());
}
private String ByteArrayToHexString(byte[] inarray) {
int i, j, in;
String[] hex = { "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A",
"B", "C", "D", "E", "F" };
String out = "";
for (j = 0; j < inarray.length; ++j) {
in = (int) inarray[j] & 0xff;
i = (in >> 4) & 0x0f;
out += hex[i];
i = in & 0x0f;
out += hex[i];
}
return out;
}
4.完整參考
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="cn.com.jslh.zjcdprogrect">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.NFC" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.nfc"
android:required="true" />
<application
android:name=".common.MyApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".LoginActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".saoka.WorkActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.nfc.action.TAG_DISCOVERED" />
<data android:mimeType="text/plain" />
</intent-filter>
<!--<meta-data android:name="android.nfc.action.TECH_DISCOVERED" android:resource="@xml/nfc_tech_filter" />-->
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
package cn.com.jslh.zjcdprogrect.saoka;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.nfc.NfcAdapter;
import android.nfc.Tag;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import cn.com.jslh.zjcdprogrect.R;
public class WorkActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private NfcAdapter mNfcAdapter;
private PendingIntent pi;
private IntentFilter tagDetected;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_work);
//初始化NfcAdapter
mNfcAdapter = NfcAdapter.getDefaultAdapter(this);
//初始化PendingIntent
// 初始化PendingIntent,當有NFC設備連接上的時候,就交給當前Activity處理
pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, new Intent(this, getClass())
.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP), 0);
// 新建IntentFilter,使用的是第二種的過濾機制
// tagDetected = new IntentFilter(NfcAdapter.ACTION_TECH_DISCOVERED);
// tagDetected.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_DEFAULT);
}
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent);
// 當前app正在前端界面運行,這個時候有intent發送過來,那麼系統就會調用onNewIntent回調方法,將intent傳送過來
// 我們只需要在這裡檢驗這個intent是否是NFC相關的intent,如果是,就調用處理方法
if (NfcAdapter.ACTION_TAG_DISCOVERED.equals(intent.getAction())) {
processIntent(intent);
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mNfcAdapter.enableForegroundDispatch(this, pi, null, null);
}
/**
* Parses the NDEF Message from the intent and prints to the TextView
*/
private void processIntent(Intent intent) {
//取出封裝在intent中的TAG
Tag tagFromIntent = intent.getParcelableExtra(NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG);
String CardId =ByteArrayToHexString(tagFromIntent.getId());
}
public static void startActivity(Context context){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(context,WorkActivity.class);
context.startActivity(intent);
}
private String ByteArrayToHexString(byte[] inarray) {
int i, j, in;
String[] hex = { "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A",
"B", "C", "D", "E", "F" };
String out = "";
for (j = 0; j < inarray.length; ++j) {
in = (int) inarray[j] & 0xff;
i = (in >> 4) & 0x0f;
out += hex[i];
i = in & 0x0f;
out += hex[i];
}
return out;
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
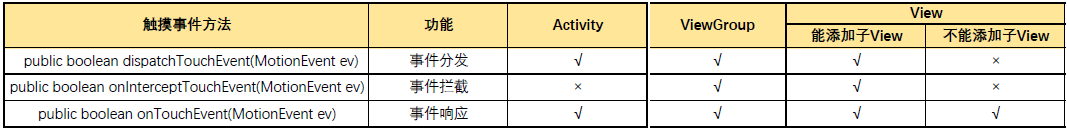 Android的事件分發與消費機制
Android的事件分發與消費機制
一、Touch的三個重要方法在Android中,與觸摸事件也就是 Touch 相關的有三個重要方法,這三個方法共同完成觸摸事件的分發。public boolean dis
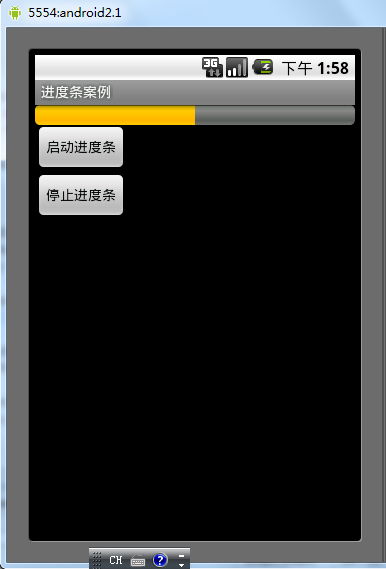 Android控件之ProgressBar用法實例分析
Android控件之ProgressBar用法實例分析
本文實例講述了Android控件之ProgressBar用法。分享給大家供大家參考。具體如下:ProgressBar位於android.widget包下,其繼承於View
 Android屏幕適配方案
Android屏幕適配方案
Android屏幕適配出現的原因在我們學習如何進行屏幕適配之前,我們需要先了解下為什麼Android需要進行屏幕適配。由於Android系統的開放性,任何用戶、開發者、O
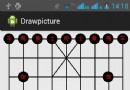 android 用paint,canvas 繪圖
android 用paint,canvas 繪圖
(1)主要用了paint ,canvas 兩個類中的方法 (2)主要用了畫線和畫圓的方法。 (3)drawline(起始點軸坐標,起始點y軸坐標,終點軸坐標,終點y軸坐標