編輯:關於Android編程
Android平台有三種網絡接口可以使用,他們分別是:java.net.*(標准Java接口)、Org.apache接口和Android.net.*(Android網絡接口)。下面分別介紹這些接口的功能和作用。
1.標准Java接口
java.net.*提供與聯網有關的類,包括流、數據包套接字(socket)、Internet協議、常見Http處理等。比如:創建URL,以及URLConnection/HttpURLConnection對象、設置鏈接參數、鏈接到服務器、向服務器寫數據、從服務器讀取數據等通信。這些在Java網絡編程中均有涉及,我們看一個簡單的socket編程,實現服務器回發客戶端信息。
服務端:
public class Server implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
Socket socket = null;
try {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(18888);
//循環監聽客戶端鏈接請求
while(true){
System.out.println("start...");
//接收請求
socket = server.accept();
System.out.println("accept...");
//接收客戶端消息
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String message = in.readLine();
//發送消息,向客戶端
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())),true);
out.println("Server:" + message);
//關閉流
in.close();
out.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if (null != socket){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//啟動服務器
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread server = new Thread(new Server());
server.start();
}
}
客戶端,MainActivity
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private EditText editText;
private Button button;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
editText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1);
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Socket socket = null;
String message = editText.getText().toString()+ "\r\n" ;
try {
//創建客戶端socket,注意:不能用localhost或127.0.0.1,Android模擬器把自己作為localhost
socket = new Socket("<span >10.0.2.2</span>",18888);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter
(socket.getOutputStream())),true);
//發送數據
out.println(message);
//接收數據
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String msg = in.readLine();
if (null != msg){
editText.setText(msg);
System.out.println(msg);
}
else{
editText.setText("data error");
}
out.close();
in.close();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
if (null != socket){
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
}
}
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" />
<EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="input the message and click the send button"
></EditText>
<Button android:text="send" android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
</LinearLayout>
啟動服務器:
javac com/test/socket/Server.java java com.test.socket.Server
運行客戶端程序:
結果如圖:
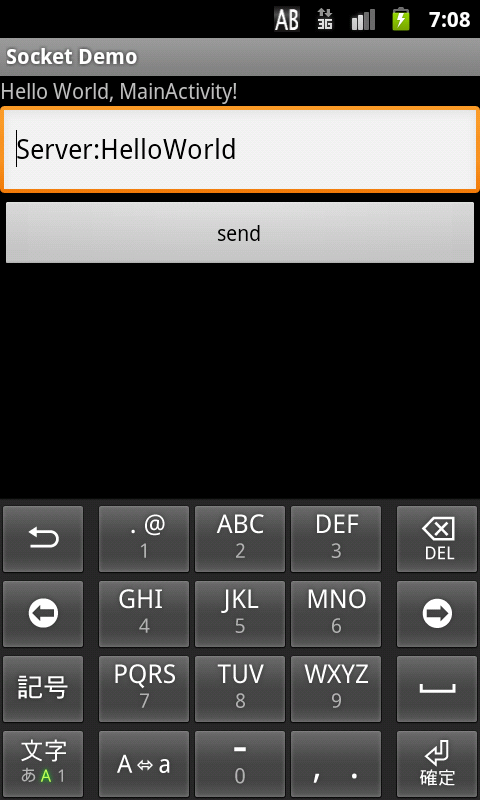

注意:服務器與客戶端無法鏈接的可能原因有:
沒有加訪問網絡的權限:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"></uses-permission>
IP地址要使用:10.0.2.2
模擬器不能配置代理。
2。Apache接口
對於大部分應用程序而言JDK本身提供的網絡功能已遠遠不夠,這時就需要Android提供的Apache HttpClient了。它是一個開源項目,功能更加完善,為客戶端的Http編程提供高效、最新、功能豐富的工具包支持。
下面我們以一個簡單例子來看看如何使用HttpClient在Android客戶端訪問Web。
首先,要在你的機器上搭建一個web應用myapp,只有很簡單的一個http.jsp
內容如下:
<%@page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Http Test
</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
String type = request.getParameter("parameter");
String result = new String(type.getBytes("iso-8859-1"),"utf-8");
out.println("<h1>" + result + "</h1>");
%>
</body>
</html>
然後實現Android客戶端,分別以post、get方式去訪問myapp,代碼如下:
布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <TextView android:gravity="center" android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" /> <Button android:text="get" android:id="@+id/get" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button> <Button android:text="post" android:id="@+id/post" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button> </LinearLayout>
資源文件:
strings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">通過按鈕選擇不同方式訪問網頁</string> <string name="app_name">Http Get</string> </resources>
主Activity:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView textView;
private Button get,post;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView);
get = (Button)findViewById(R.id.get);
post = (Button)findViewById(R.id.post);
//綁定按鈕監聽器
get.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//注意:此處ip不能用127.0.0.1或localhost,Android模擬器已將它自己作為了localhost
String uri = "http://192.168.22.28:8080/myapp/http.jsp?parameter=以Get方式發送請求";
textView.setText(get(uri));
}
});
//綁定按鈕監聽器
post.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String uri = "http://192.168.22.28:8080/myapp/http.jsp";
textView.setText(post(uri));
}
});
}
/**
* 以get方式發送請求,訪問web
* @param uri web地址
* @return 響應數據
*/
private static String get(String uri){
BufferedReader reader = null;
StringBuffer sb = null;
String result = "";
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet request = new HttpGet(uri);
try {
//發送請求,得到響應
HttpResponse response = client.execute(request);
//請求成功
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK){
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(response.getEntity().getContent()));
sb = new StringBuffer();
String line = "";
String NL = System.getProperty("line.separator");
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null){
sb.append(line);
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
if (null != reader){
reader.close();
reader = null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (null != sb){
result = sb.toString();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 以post方式發送請求,訪問web
* @param uri web地址
* @return 響應數據
*/
private static String post(String uri){
BufferedReader reader = null;
StringBuffer sb = null;
String result = "";
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpPost request = new HttpPost(uri);
//保存要傳遞的參數
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
//添加參數
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("parameter","以Post方式發送請求"));
try {
//設置字符集
HttpEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params,"utf-8");
//請求對象
request.setEntity(entity);
//發送請求
HttpResponse response = client.execute(request);
//請求成功
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK){
System.out.println("post success");
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(response.getEntity().getContent()));
sb = new StringBuffer();
String line = "";
String NL = System.getProperty("line.separator");
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null){
sb.append(line);
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
try {
//關閉流
if (null != reader){
reader.close();
reader = null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (null != sb){
result = sb.toString();
}
return result;
}
}
運行結果如下:
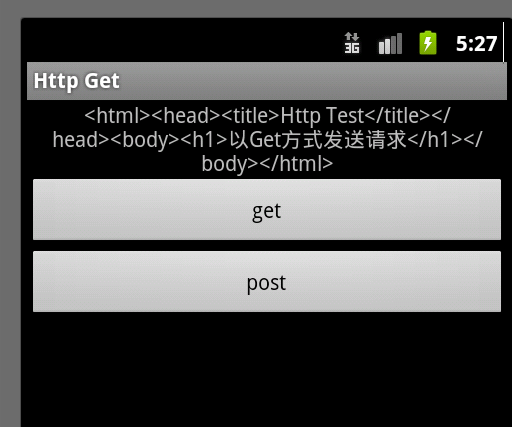
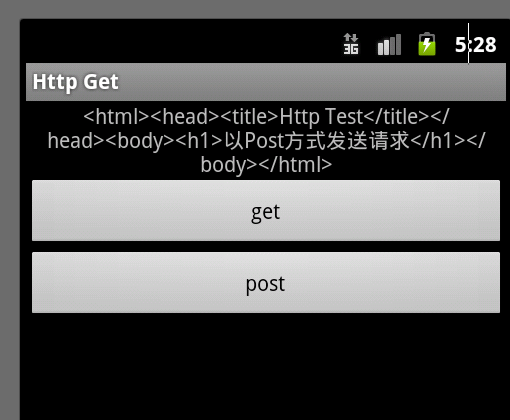
3.android.net編程:
常常使用此包下的類進行Android特有的網絡編程,如:訪問WiFi,訪問Android聯網信息,郵件等功能。這裡不詳細講。
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 自定義AvatarImageView滿足你所有頭像顯示需求
自定義AvatarImageView滿足你所有頭像顯示需求
1.PorterDuffXfermode這是由Tomas Proter和 Tom Duff命名的圖像轉換模式,它有16個枚舉值來控制Canvas上 上下兩個圖層的交互(先
 Android View如何測量
Android View如何測量
對於Android View的測量,我們一句話總結為:給我位置和大小,我就知道您長到
 Android的事件機制
Android的事件機制
一、理論概述最基本的操作類型:down 手指按下 move 手指在屏幕上移動 up 手指從屏幕上離開觸屏操作的順序:down->move->move->
 15、Android數據存儲——SharedPreferences及SDCard
15、Android數據存儲——SharedPreferences及SDCard
一、數據存儲選項:Data Storage ——Storage Options【重點】 1、Shared Preferences Stor