編輯:關於Android編程
Activities提供了一種方便管理的創建、保存、回復的對話框機制,例如 onCreateDialog(int), onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog), showDialog(int), dismissDialog(int)等方法,如果使用這些方法的話,Activity將通過getOwnerActivity()方法返回該Activity管理的對話框(dialog).
onCreateDialog(int):當你使用這個回調函數時,Android系統會有效的設置這個Activity為每個對話框的所有者,從而自動管理每個對話框的狀態並掛靠到Activity上。這樣,每個對話框繼承這個Activity的特定屬性。比如,當一個對話框打開時,菜單鍵顯示為這個Activity定義的選項菜單,音量鍵修改Activity使用的音頻流。
showDialog(int): 當你想要顯示一個對話框時,調用showDialog(int id) 方法並傳遞一個唯一標識這個對話框的整數。當對話框第一次被請求時,Android從你的Activity中調用onCreateDialog(int id),你應該在這裡初始化這個對話框Dialog。這個回調方法被傳以和showDialog(int id)相同的ID。當你創建這個對話框後,在Activity的最後返回這個對象。
onPrepareDialog(int, Dialog):在對話框被顯示之前,Android還調用了可選的回調函數onPrepareDialog(int id, Dialog). 如果你想在每一次對話框被打開時改變它的任何屬性,你可以定義這個方法。這個方法在每次打開對話框時被調用,而onCreateDialog(int) 僅在對話框第一次打開時被調用。如果你不定義onPrepareDialog(),那麼這個對話框將保持和上次打開時一樣。這個方法也被傳遞以對話框的ID,和在onCreateDialog()中創建的對話框對象。
dismissDialog(int):當你准備關閉對話框時,你可以通過對這個對話框調用dismiss()來消除它。如果需要,你還可以從這個Activity中調用dismissDialog(int id) 方法,這實際上將為你對這個對話框調用dismiss() 方法。 如果你想使用onCreateDialog(int id) 方法來管理你對話框的狀態(就如同在前面的章節討論的那樣),然後每次你的對話框消除的時候,這個對話框對象的狀態將由該Activity保留。如果你決定不再需要這個對象或者清除該狀態是重要的,那麼你應該調用removeDialog(int id)。這將刪除任何內部對象引用而且如果這個對話框正在顯示,它將被消除。
下面是幾種對話框的效果
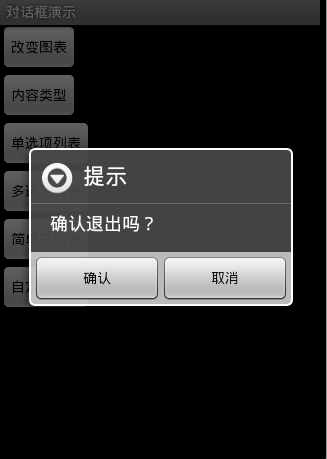
圖1
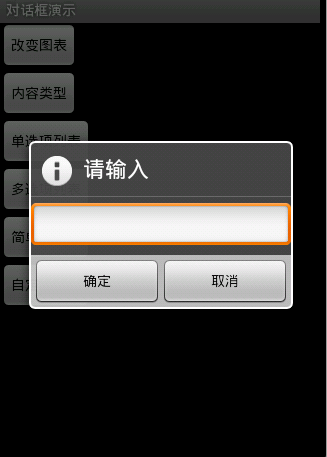
圖2

圖3
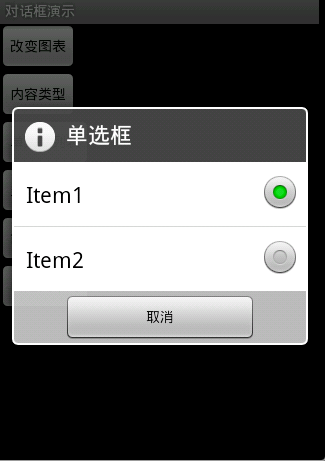
圖4
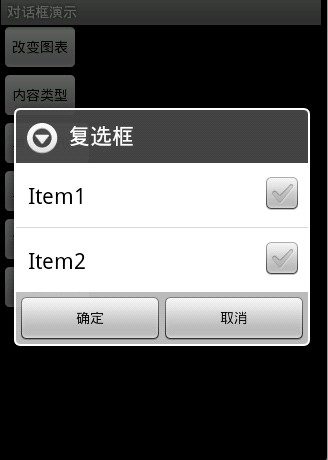
圖5
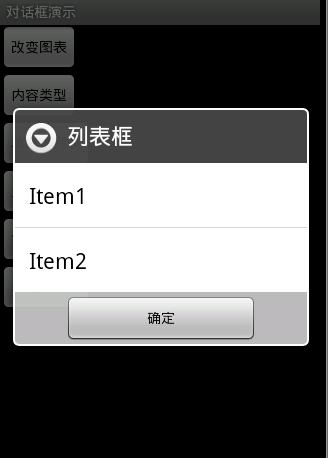
圖6
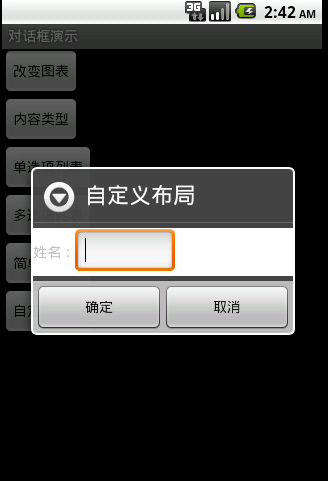
圖7
圖1效果:該效果是當按返回按鈕時彈出一個提示,來確保無誤操作,采用常見的對話框樣式。
代碼:創建對話框方法dialog()
protected void dialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new Builder(Main.this);
builder.setMessage("確認退出嗎?");
builder.setTitle("提示");
builder.setPositiveButton("確認", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
Main.this.finish();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
builder.create().show();
}
在onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)方法中調用此方法
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK && event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
dialog();
}
return false;
}
圖2效果:改變了對話框的圖表,添加了三個按鈕
Dialog dialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setIcon(
android.R.drawable.btn_star).setTitle("喜好調查").setMessage(
"你喜歡李連傑的電影嗎?").setPositiveButton("很喜歡",
new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(Main.this, "我很喜歡他的電影。",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}).setNegativeButton("不喜歡", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(Main.this, "我不喜歡他的電影。", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
}).setNeutralButton("一般", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(Main.this, "談不上喜歡不喜歡。", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
}).create();
dialog.show();
圖3效果:信息內容是一個簡單的View類型
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("請輸入").setIcon(
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_info).setView(
new EditText(this)).setPositiveButton("確定", null)
.setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
圖4效果:信息內容是一組單選框
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("復選框").setMultiChoiceItems(
new String[] { "Item1", "Item2" }, null, null)
.setPositiveButton("確定", null)
.setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
圖5效果:信息內容是一組多選框
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("單選框").setIcon(
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_info).setSingleChoiceItems(
new String[] { "Item1", "Item2" }, 0,
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
}).setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
圖6效果:信息內容是一組簡單列表項
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("列表框").setItems(
new String[] { "Item1", "Item2" }, null).setNegativeButton(
"確定", null).show();
圖7效果:信息內容是一個自定義的布局
1.布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:background="#ffffffff" android:orientation="horizontal" android:id="@+id/dialog"> <TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/tvname" android:text="姓名:" /> <EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/etname" android:minWidth="100dip"/> </LinearLayout>
2.調用代碼
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog,
(ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.dialog));
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("自定義布局").setView(layout)
.setPositiveButton("確定", null)
.setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
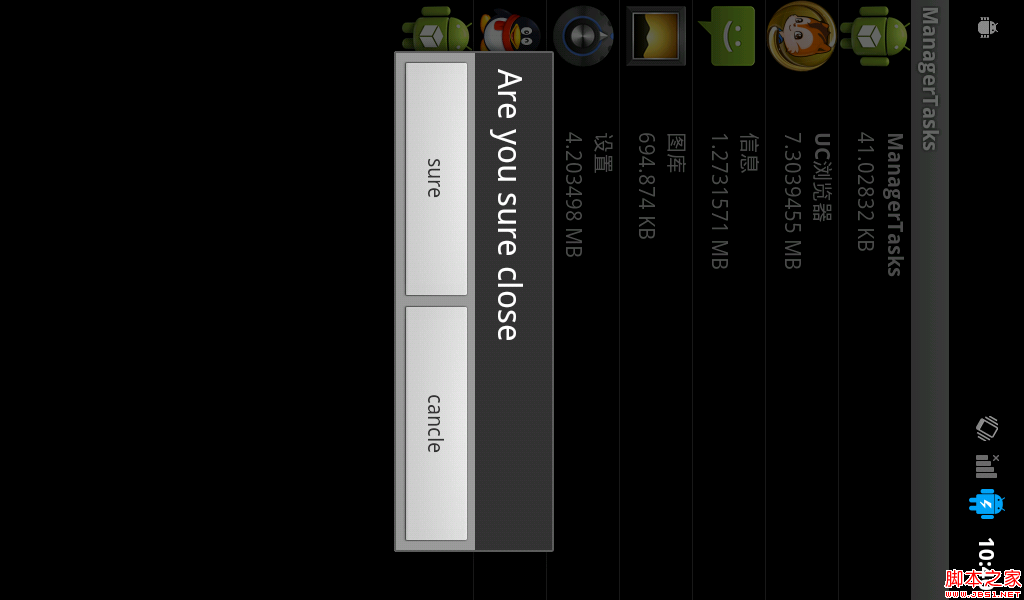 android實現獲取正在運行的應用程序
android實現獲取正在運行的應用程序
因為在framework中想添加這個功能,所以寫了個appliction來實現一下獲取正在運行的應用程序: 還是先看圖吧: 這個app主要是簡單的實現了獲取非系統的應用程
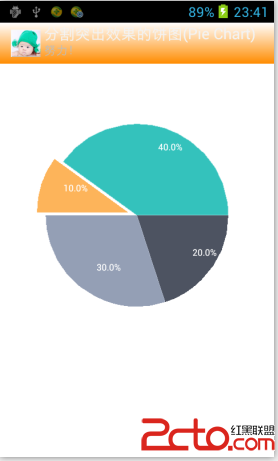 Android Canvas練習(9)自已繪分割突出效果的餅圖(Pie Chart)
Android Canvas練習(9)自已繪分割突出效果的餅圖(Pie Chart)
這裡畫了個餅圖的變種,具有分割突出效果的餅圖(Pie Chart),就是個切蛋糕效果的餅圖,畫這種圖,其技巧就在於圓心的偏移。 在圓心偏移,半徑不變的基礎上,效果就出來了
 Android控件架構與自定義控件詳解(二)——自定義View
Android控件架構與自定義控件詳解(二)——自定義View
在自定義View時,我們通常會去重寫onDraw()方法來繪制View的顯示內容。如果該View還需要使用wrap_content屬性,那麼還必須重寫onMeasure(
 ANDROID L——Material Design詳解(UI控件)
ANDROID L——Material Design詳解(UI控件)
Android L: Google已經確認Android L就是Android Lollipop(5.0)。 前幾