編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述了Android實現為Notification加上一個進度條的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
package com.notification;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class nofificationActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private static final int NOTIFICATION_ID = 0x12;
private Notification notification = null;
private NotificationManager manager = null;
public Handler handler;
private int _progress = 0;
private Thread thread = null;
private boolean isStop = false;
// 當界面處理停止的狀態 時,設置讓進度條取消
@Override
protected void onPause() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
isStop = false;
manager.cancel(NOTIFICATION_ID);
super.onPause();
}
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.Button01);
btn.setOnClickListener(this);
notification = new Notification(R.drawable.icon, "帶進條的提醒", System
.currentTimeMillis());
notification.icon = R.drawable.icon;
// 通過RemoteViews 設置notification中View 的屬性
notification.contentView = new RemoteViews(getApplication()
.getPackageName(), R.layout.custom_dialog);
notification.contentView.setProgressBar(R.id.pb, 100, 0, false);
notification.contentView.setTextViewText(R.id.tv, "進度" + _progress
+ "%");
// 通過PendingIntetn
// 設置要跳往的Activity,這裡也可以設置發送一個服務或者廣播,
// 不過在這裡的操作都必須是用戶點擊notification之後才觸發的
notification.contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0,
new Intent(this, remoteView.class), 0);
// 獲得一個NotificationManger 對象,此對象可以對notification做統一管理,只需要知道ID
manager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
isStop = true;
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification);
thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread();
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while (isStop) {
_progress += 10;
Message msg = handler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = _progress;
msg.sendToTarget();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
thread.start();
handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
notification.contentView.setProgressBar(R.id.pb, 100, msg.arg1,
false);
notification.contentView.setTextViewText(R.id.tv, "進度"
+ msg.arg1 + "%");
manager.notify(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification);
if (msg.arg1 == 100) {
_progress = 0;
manager.cancel(NOTIFICATION_ID);
isStop = false;
Toast.makeText(nofificationActivity.this, "下載完畢", 1000)
.show();
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
}
}
更多關於Android相關內容感興趣的讀者可查看本站專題:《Android基本組件用法總結》、《Android視圖View技巧總結》、《Android資源操作技巧匯總》、《Android文件操作技巧匯總》、《Android操作SQLite數據庫技巧總結》、《Android操作json格式數據技巧總結》、《Android數據庫操作技巧總結》、《Android編程開發之SD卡操作方法匯總》、《Android開發入門與進階教程》、《Android編程之activity操作技巧總結》及《Android控件用法總結》
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
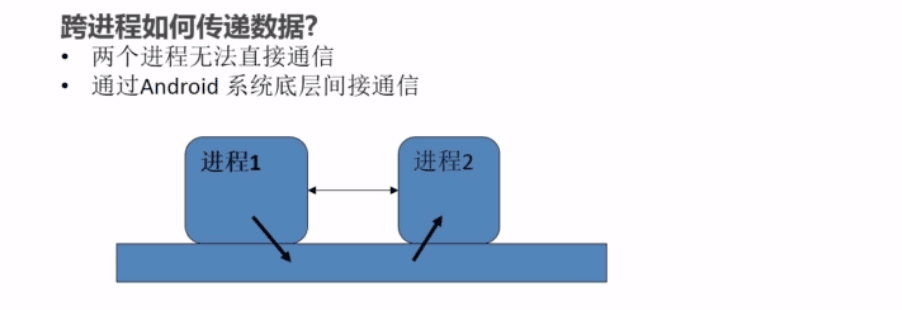 AIDL
AIDL
官網地址詳解分析:http://developer.android.com/guide/components/aidl.html一)什麼是AIDL –》 應用
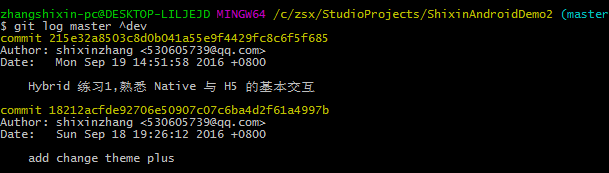 git 對比兩個分支差異
git 對比兩個分支差異
比如我們有 2 個分支:master, dev,現在想查看這兩個 branch 的區別,有以下幾種方式:1.查看 dev 有,而 master 中沒有的:git log
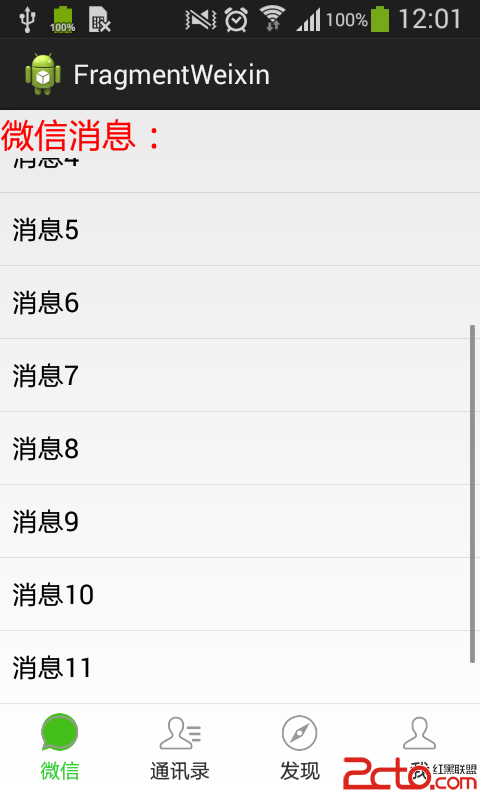 Android組件:Fragment切換後保存狀態
Android組件:Fragment切換後保存狀態
之前寫的第一篇Fragment實例,和大多數人一開始學的一樣,都是通過FragmentTransaction的replace方法來實現,replace方法相
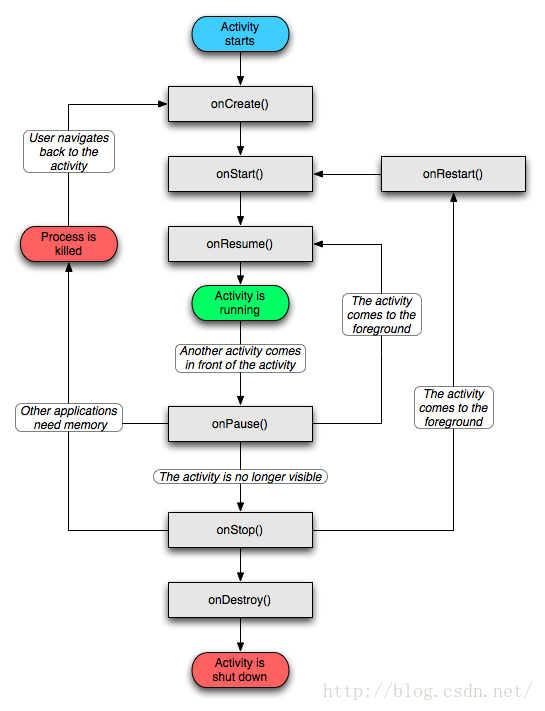 Android中Activity生命周期和啟動模式詳解
Android中Activity生命周期和啟動模式詳解
Activity生命周期經典圖解:按鍵對生命周期的影響:BACK鍵: 當我們按BACK鍵時,我們這個應用程序將結束,這時候我們將先後調用onPause()->on