編輯:關於Android編程
數據庫是Android存儲方案的核心,在Andorid中SQLite非常輕量,而且執行sql語句甚至比MySQL還要快。
SQLiteDatabase 是 Android 中操作數據庫的核心類之一,使用SQLiteDatabase可以打開數據庫,也可以對數據庫進行操作,然而,為了數據庫升級以及使用更加方便,我們常用SQLiteOpenHelper的子類來完成創建,打開數據庫的操作。
SQLiteOpenHelper是一個抽象類,在該類中有下面兩個必須實現的方法:
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db);// 該函數在數據庫第一次被建立時調用 public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db,int oldVersion,int newVersion);// 數據庫更新升級操作
我們新建一個類DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper
import java.util.Random;
import android.R.bool;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
// 設置數據庫默認版本
private static final int VERSON = 1;
// 自定義數據庫名,可以隨便取名字
private static final String DBNAME = "mydb";
// 繼承SQLiteOpenHelper類的類必須有自己的構造函數
// 該構造函數4個參數,直接調用父類的構造函數。其中第一個參數為該類本身;第二個參數為數據庫的名字;
public DBHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory,
int version) {
super(context, name, factory, version);
}
// 該構造函數有3個參數,因為它把上面函數的第3個參數固定為null了
public DBHelper(Context context, String name, int verson) {
this(context, name, null, verson);
}
// 該構造函數只有2個參數,在上面函數 的基礎上將版本號固定了
public DBHelper(Context context, String name) {
this(context, name, VERSON);
}
// 該構造函數只有1個參數,固定默認數據庫,在這裡我們實現增刪改查為了方便,就用它了
public DBHelper(Context context) {
this(context, DBNAME, null, VERSON);
}
// 該函數在數據庫第一次被建立時調用
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
System.out.println("create a sqlite database");
//建表語句(注意:因為在綁定數據時,Cursor對象返回的記錄集中必須包含一個"_id"字段,否則無法完成數據綁定
String sql = "CREATE TABLE [test]("+
"[_id] AUTOINC,"+
"[name] varchar(20),"+
"[age] varchar(20),"+
"PRIMARY KEY ([_id]))";
db.execSQL(sql);
//向test表中插入10條數據
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
String name = "Jepson";
name+=i;
String age = "age";
age+=i;
db.execSQL("insert into test(name,age) values(?,?)",new Object[]{name,age});
}
}
// 數據庫更新操作
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase arg0, int arg1, int arg2) {
System.out.println("update a sqlite database");
}
//自定義query方法,用以執行查詢語句,返回Cursor對象
public Cursor query(String sql,String[] args){
//調用 getReadableDatabase方法時,如果數據庫文件不存在,會調用 onCreate方法
SQLiteDatabase db = this.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery(sql, args);
return cursor;
}
}
這樣,我們的DBHelper 類寫好了,我們來實現一個查詢操作。
第一步,activity_main.xml添加 listview 展示控件
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#FFFFFF" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <ListView android:id="@android:id/list" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:divider="#6b6f74" android:dividerHeight="1px" > </ListView> </LinearLayout>
第二步,新建一個xml布局文件,用來作為列表項使用的布局資源
user_list_cell.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:background="#FFFFFF"> <!-- 大字體TextView,用以展示 name姓名 --> <TextView android:id="@+id/tvName" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Large" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="20dp" /> <!-- 小字體TextView,用以展示 age年齡 --> <TextView android:id="@+id/tvAge" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Small" android:textColor="#000000" android:textSize="14dp" /> </LinearLayout>
第三步,主Activity
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.support.v4.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends ListActivity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
public void initView(){
//調用只有1個參數的構造函數,實例化dbHelper
DBHelper dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
//新建Cursor對象來保存query查詢方法返回的結果,查詢test表中所有記錄
Cursor cursor = dbHelper.query("select * from test", null);
//創建SimpleCursorAdapter對象,5個參數,
//第一個是context,就寫當前this就行
//第二個是布局文件,我這裡是自定義的布局文件user_list_cell.xml
//第三個就是Cursor對象
//第四個對應就是,cursor查詢後,需要顯示出來的字段名,比如我要顯示姓名name和年齡age
//第五個就是對應列表項布局中的控件ID了
SimpleCursorAdapter simpleCursorAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
R.layout.user_list_cell, cursor,
new String[] { "name", "age" }, new int[] { R.id.tvName,
R.id.tvAge });
setListAdapter(simpleCursorAdapter);
Toast.makeText(this, "查詢成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
執行一下看看,我們是不是查詢成功了?
操作SQLite數據庫應了解,對數據庫的增刪改查都有兩種方法,一種是前面的使用 rawQuery方法直接執行SQL語句,另一種就是使用SQLiteDatabase類的相應方法來操作,下面舉一個第二種的例子,比如我們要插入數據 name=11 age=22
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.support.v4.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends ListActivity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
public void initView(){
//執行添加操作
DBHelper dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
//獲得寫入權限getWritableDatabase
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
//新建contentvalues保存insert數據
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("name", "11");
cv.put("age", "22");
db.insert("test", null, cv);
Toast.makeText(this, "添加成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
////查詢操作
////調用只有1個參數的構造函數,實例化dbHelper
//DBHelper dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
////新建Cursor對象來保存query查詢方法返回的結果,查詢test表中所有記錄
//Cursor cursor = dbHelper.query("select * from test", null);
////創建SimpleCursorAdapter對象,5個參數,
////第一個是context,就寫當前this就行
////第二個是布局文件,我這裡是自定義的布局文件user_list_cell.xml
////第三個就是Cursor對象
////第四個對應就是,cursor查詢後,需要顯示出來的字段名,比如我要顯示姓名name和年齡age
////第五個就是對應列表項布局中的控件ID了
//SimpleCursorAdapter simpleCursorAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
// R.layout.user_list_cell, cursor,
// new String[] { "name", "age" }, new int[] { R.id.tvName,
// R.id.tvAge });
//setListAdapter(simpleCursorAdapter);
//Toast.makeText(this, "查詢成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
執行插入成功以後,再將插入語句注釋,將查詢語句去掉注釋,重新啟動,會發現最後一多了一個item,添加成功。
另外查詢記錄獲得的Cursor對象,需要使用movetoFirst,moveToNext,movToPosition(position)等方法將指針移動相應的位置,來進行查詢結果的讀取。
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.support.v4.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends ListActivity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
}
public void initView(){
//解析Cursor對象的查詢操作
DBHelper dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query("test", null, null, null, null, null, null,
null);
//定義結果字符串
String result = "";
// 判斷cursor不為空 這個很重要
if (cursor != null) {
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("name"));// 獲取name列的值
String age = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex("age"));// 獲取age列的值
result += "姓名:" + name + ",年齡:" + age + "\n";
}
}
cursor.close();
db.close();
System.out.println(result);
Toast.makeText(this, result, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// //執行添加操作
// DBHelper dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
// //獲得寫入權限getWritableDatabase
// SQLiteDatabase db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase();
// //新建contentvalues保存insert數據
// ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
// cv.put("name", "11");
// cv.put("age", "22");
// db.insert("test", null, cv);
// Toast.makeText(this, "添加成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
////查詢操作
////調用只有1個參數的構造函數,實例化dbHelper
//DBHelper dbHelper = new DBHelper(this);
////新建Cursor對象來保存query查詢方法返回的結果,查詢test表中所有記錄
//Cursor cursor = dbHelper.query("select * from test", null);
////創建SimpleCursorAdapter對象,5個參數,
////第一個是context,就寫當前this就行
////第二個是布局文件,我這裡是自定義的布局文件user_list_cell.xml
////第三個就是Cursor對象
////第四個對應就是,cursor查詢後,需要顯示出來的字段名,比如我要顯示姓名name和年齡age
////第五個就是對應列表項布局中的控件ID了
//SimpleCursorAdapter simpleCursorAdapter = new SimpleCursorAdapter(this,
// R.layout.user_list_cell, cursor,
// new String[] { "name", "age" }, new int[] { R.id.tvName,
// R.id.tvAge });
//setListAdapter(simpleCursorAdapter);
//Toast.makeText(this, "查詢成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
執行以後,可以發現,name和age全都獲取到了,並顯示在了Toast和system.out中。是不是很有意思呢?
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
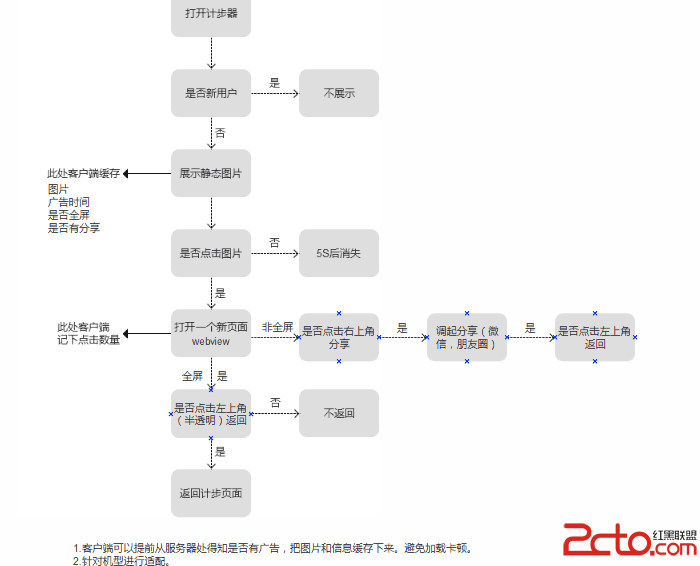 開發首屏廣告(Android)簡述
開發首屏廣告(Android)簡述
作為一個成熟的應用, 必須要有廣告. 那麼, 如何優雅地開發廣告呢? 需要注意一些細節.本文提供一個簡單的示例, 代碼僅供參考.需求:1. 下載廣告在歡迎頁面中, 啟動一
 UIPickerView的使用
UIPickerView的使用
UIPickerView功能與UIDatePicker類似初始化實例時,通常只需要設置原點坐標,不需要設置寬高(默認寬高為:frame = (0 0; 320 216))
 Android App中使用Pull解析XML格式數據的使用示例
Android App中使用Pull解析XML格式數據的使用示例
Pull解析XML文件的方式與SAX解析XML文件的方式大致相同,他們都是基於事件驅動的。所以,利用pull解析XML文件需要下面幾個步驟: &nb
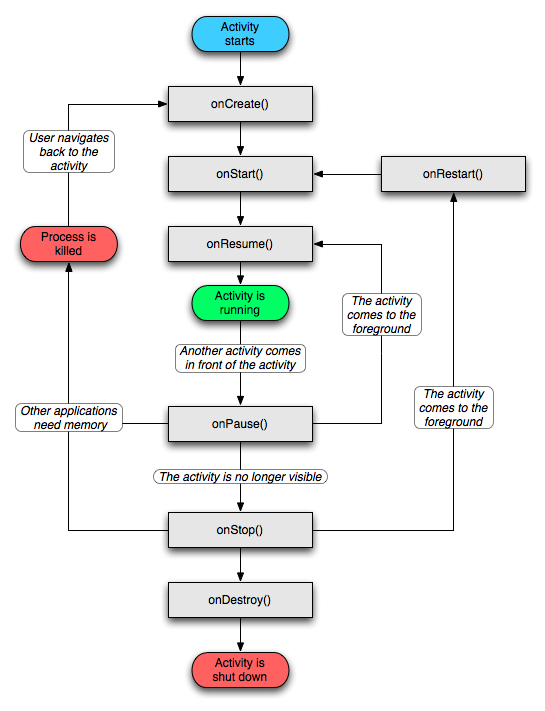 Android的activity學習筆記
Android的activity學習筆記
一、什麼是activity Activity 是用戶接口程序,原則上它會提供給用戶一個交互式的接口功能。它是 android 應用程