編輯:關於Android編程
QQ音樂中圓形旋轉碟子
思路分析:
1、在onMeasure中測量整個View的寬和高後,設置寬高
2、獲取我們res的圖片資源後,在ondraw方法中進行繪制圓形圖片
3、通過Handler發送Runnable來啟動旋轉線程(如果只想做圓形頭像的話,這步可以去掉)
4、在布局中使用我們的View
效果圖:
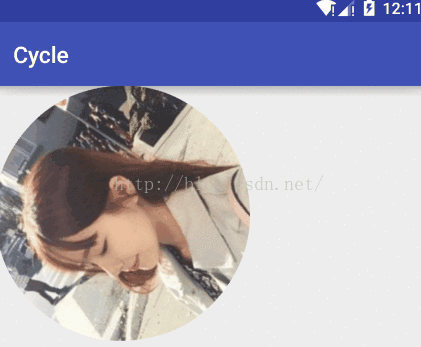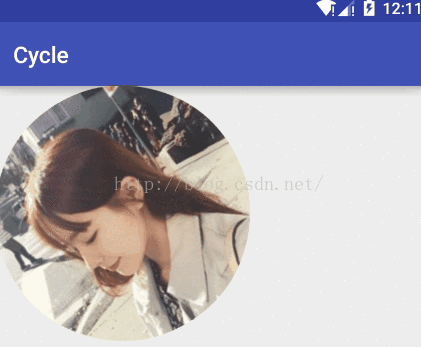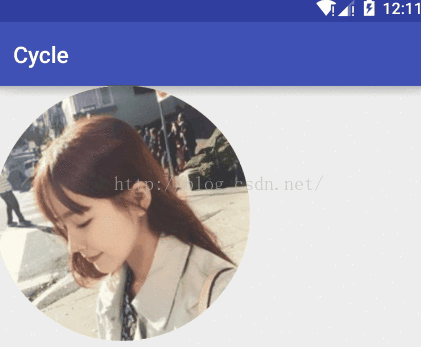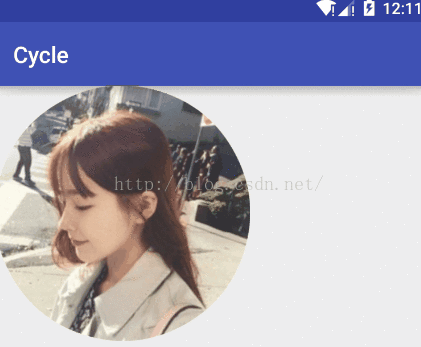
貼出我們的變量信息:
//view的寬和高 int mHeight = 0; int mWidth = 0; //圓形圖片 Bitmap bitmap = null; //圓形圖片的真實半徑 int radius = 0; //旋轉動畫的矩形 Matrix matrix = new Matrix(); //旋轉動畫的角度 int degrees = 0;
步驟一:測量整個View的寬和高後,設置寬高
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//測量整個View的寬和高
mWidth = measuredWidth(widthMeasureSpec);
mHeight= measuredHeight(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}
private int measuredWidth(int widthMeasureSpec) {
int Mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int Size = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
mWidth = Size;
} else {
//由圖片決定寬度
int value = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + bitmap.getWidth();
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//由圖片和Padding決定寬度,但是不能超過View的寬
mWidth = Math.min(value, Size);
}
}
return mWidth;
}
private int measuredHeight(int heightMeasureSpec) {
int Mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int Size = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
mHeight = Size;
} else {
//由圖片決定高度
int value = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + bitmap.getHeight();
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//由圖片和Padding決定高度,但是不能超過View的高
mHeight = Math.min(value, Size);
}
}
return mHeight;
}
步驟二:獲取我們res的圖片資源後,在ondraw方法中進行繪制圓形圖片
//獲取res的圖片資源
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.concat(matrix);
//真實的半徑必須是View的寬高最小值
radius = Math.min(mWidth, mHeight);
//如果圖片本身寬高太大,進行相應的縮放
bitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(bitmap, radius, radius, false);
//畫圓形圖片
canvas.drawBitmap(createCircleImage(bitmap, radius), 0, 0, null);
matrix.reset();
}
private Bitmap createCircleImage(Bitmap source, int radius) {
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
Bitmap target = Bitmap.createBitmap(radius, radius, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
//產生一個同樣大小的畫布
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(target);
//首先繪制圓形
canvas.drawCircle(radius / 2, radius / 2, radius / 2, paint);
//使用SRC_IN模式顯示後畫圖的交集處
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
//繪制圖片,從(0,0)畫
canvas.drawBitmap(source, 0, 0, paint);
return target;
}
步驟三:通過Handler發送Runnable來啟動旋轉線程
//開始旋轉
mHandler.post(runnable);
[java] view plain copy 在CODE上查看代碼片派生到我的代碼片
//-----------旋轉動畫-----------
Handler mHandler = new Handler();
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
matrix.postRotate(degrees++, radius / 2, radius / 2);
//重繪
invalidate();
mHandler.postDelayed(runnable, 50);
}
};
步驟四:在布局中使用我們的View
<com.handsome.cycle.MyCycleView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
下面是整個類的源碼
public class MyCycleView extends View {
//view的寬和高
int mHeight = 0;
int mWidth = 0;
//圓形圖片
Bitmap bitmap = null;
//圓形圖片的真實半徑
int radius = 0;
//旋轉動畫的矩形
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
//旋轉動畫的角度
int degrees = 0;
//-----------旋轉動畫-----------
Handler mHandler = new Handler();
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
matrix.postRotate(degrees++, radius / 2, radius / 2);
//重繪
invalidate();
mHandler.postDelayed(runnable, 50);
}
};
public MyCycleView(Context context) {
super(context);
initView();
}
public MyCycleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView();
}
public MyCycleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
initView();
}
public void initView() {
//獲取res的圖片資源
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.icon);
//開始旋轉
mHandler.post(runnable);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//測量整個View的寬和高
mWidth = measuredWidth(widthMeasureSpec);
mHeight = measuredHeight(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}
private int measuredWidth(int widthMeasureSpec) {
int Mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int Size = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
mWidth = Size;
} else {
//由圖片決定寬度
int value = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + bitmap.getWidth();
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//由圖片和Padding決定寬度,但是不能超過View的寬
mWidth = Math.min(value, Size);
}
}
return mWidth;
}
private int measuredHeight(int heightMeasureSpec) {
int Mode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int Size = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
mHeight = Size;
} else {
//由圖片決定高度
int value = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + bitmap.getHeight();
if (Mode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//由圖片和Padding決定高度,但是不能超過View的高
mHeight = Math.min(value, Size);
}
}
return mHeight;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.concat(matrix);
//真實的半徑必須是View的寬高最小值
radius = Math.min(mWidth, mHeight);
//如果圖片本身寬高太大,進行相應的縮放
bitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(bitmap, radius, radius, false);
//畫圓形圖片
canvas.drawBitmap(createCircleImage(bitmap, radius), 0, 0, null);
matrix.reset();
}
private Bitmap createCircleImage(Bitmap source, int radius) {
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
Bitmap target = Bitmap.createBitmap(radius, radius, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
//產生一個同樣大小的畫布
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(target);
//首先繪制圓形
canvas.drawCircle(radius / 2, radius / 2, radius / 2, paint);
//使用SRC_IN模式顯示後畫圖的交集處
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
//繪制圖片,從(0,0)畫
canvas.drawBitmap(source, 0, 0, paint);
return target;
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android 自定義控件之第三講:obtainStyledAttributes 系列函數詳解
Android 自定義控件之第三講:obtainStyledAttributes 系列函數詳解
在項目中開發自定義控件時,或多或少都會用到 obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet, int[], int, int) 或者 obtain
 數據在不同手機操作系統轉移辦法
數據在不同手機操作系統轉移辦法
目前,手機的更新換代實在太快,安卓和蘋果占據了手機市場的絕大部分份額。作為手機發燒友,第一次使用蘋果的用戶怎樣才能將數據遷移到蘋果呢。或許你知道怎麼轉移通訊
 android自定義控件自動換行效果實現
android自定義控件自動換行效果實現
第一篇博客裡面有介紹一篇關於自動換行實現諸多自定義控件跟各種效果的博文,但是礙於當初技術能力有限,寫的jar包裡的代碼亂七八糟,在最近忙完了手頭的工作,不經意間翻看了之前
 微信電腦版視頻文件夾位置 微信電腦版視頻存在哪裡
微信電腦版視頻文件夾位置 微信電腦版視頻存在哪裡
微信出了電腦版,在收到視頻後,視頻是保存在哪呢?微信電腦版視頻存在哪裡? 微信電腦版視頻文件夾位置就讓下載吧小編來告訴你吧 1、首先我們打開手機上的微信,