編輯:關於Android編程
Rsa加密
RSA是目前最有影響力的公鑰加密算法,RSA也是第一個既能用於數據加密也能用於數字簽名的算法。該算法基於一個十分簡單的數論事實:將兩個大素數相乘十分容易,但那時想要對其乘積進行因式分解卻極其困 難,因此可以將乘積公開作為加密密鑰,即公鑰,而兩個大素數組合成私鑰。公鑰是可發布的供任何人使用,私鑰則為自己所有,供解密之用。
RSA算法原理
1.隨機選擇兩個大質數p和q,p不等於q,計算N=pq;
2.選擇一個大於1小於N的自然數e,e必須與(p-1)(q-1)互素。
3.用公式計算出d:d×e = 1 (mod (p-1)(q-1)) 。
4.銷毀p和q。
最終得到的N和e就是“公鑰”,d就是“私鑰”,發送方使用N去加密數據,接收方只有使用d才能解開數據內容。
RSA的安全性依賴於大數分解,小於1024位的N已經被證明是不安全的,而且由於RSA算法進行的都是大數計算,使得RSA最快的情況也比DES慢上倍,這是RSA最大的缺陷,因此通常只能用於加密少量數據或者加密密鑰,但RSA仍然不失為一種高強度的算法。
Rsa使用
首先生成秘鑰對
/**
* 隨機生成RSA密鑰對
*
* @param keyLength 密鑰長度,范圍:512~2048
* 一般1024
* @return
*/
public static KeyPair generateRSAKeyPair(int keyLength) {
try {
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(RSA);
kpg.initialize(keyLength);
return kpg.genKeyPair();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
具體加密實現:
公鑰加密
/**
* 用公鑰對字符串進行加密
*
* @param data 原文
*/
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
// 得到公鑰
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PublicKey keyPublic = kf.generatePublic(keySpec);
// 加密數據
Cipher cp = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cp.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keyPublic);
return cp.doFinal(data);
}
私鑰加密
/**
* 私鑰加密
*
* @param data 待加密數據
* @param privateKey 密鑰
* @return byte[] 加密數據
*/
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKey(byte[] data, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
// 得到私鑰
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PrivateKey keyPrivate = kf.generatePrivate(keySpec);
// 數據加密
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, keyPrivate);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
公鑰解密
/**
* 公鑰解密
*
* @param data 待解密數據
* @param publicKey 密鑰
* @return byte[] 解密數據
*/
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKey(byte[] data, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
// 得到公鑰
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PublicKey keyPublic = kf.generatePublic(keySpec);
// 數據解密
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keyPublic);
return cipher.doFinal(data);
}
私鑰解密
/**
* 使用私鑰進行解密
*/
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKey(byte[] encrypted, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
// 得到私鑰
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKey);
KeyFactory kf = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA);
PrivateKey keyPrivate = kf.generatePrivate(keySpec);
// 解密數據
Cipher cp = Cipher.getInstance(ECB_PKCS1_PADDING);
cp.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, keyPrivate);
byte[] arr = cp.doFinal(encrypted);
return arr;
}
幾個全局變量解說:
public static final String RSA = "RSA";// 非對稱加密密鑰算法 public static final String ECB_PKCS1_PADDING = "RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding";//加密填充方式 public static final int DEFAULT_KEY_SIZE = 2048;//秘鑰默認長度 public static final byte[] DEFAULT_SPLIT = "#PART#".getBytes(); // 當要加密的內容超過bufferSize,則采用partSplit進行分塊加密 public static final int DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE = (DEFAULT_KEY_SIZE / 8) - 11;// 當前秘鑰支持加密的最大字節數
加密填充方式
之前以為上面這些操作就能實現rsa加解密,以為萬事大吉了,呵呵,這事還沒完,悲劇還是發生了,Android這邊加密過的數據,服務器端死活解密不了,原來android系統的RSA實現是"RSA/None/NoPadding",而標准JDK實現是"RSA/None/PKCS1Padding" ,這造成了在android機上加密後無法在服務器上解密的原因,所以在實現的時候這個一定要注意。
實現分段加密
搞定了填充方式之後又自信的認為萬事大吉了,可是意外還是發生了,RSA非對稱加密內容長度有限制,1024位key的最多只能加密127位數據,否則就會報錯(javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException: Data must not be longer than 117 bytes) , RSA 是常用的非對稱加密算法。最近使用時卻出現了“不正確的長度”的異常,研究發現是由於待加密的數據超長所致。RSA 算法規定:待加密的字節數不能超過密鑰的長度值除以 8 再減去 11(即:KeySize / 8 - 11),而加密後得到密文的字節數,正好是密鑰的長度值除以 8(即:KeySize / 8)。
公鑰分段加密
/**
* 用公鑰對字符串進行分段加密
*
*/
public static byte[] encryptByPublicKeyForSpilt(byte[] data, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
int dataLen = data.length;
if (dataLen <= DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE) {
return encryptByPublicKey(data, publicKey);
}
List<Byte> allBytes = new ArrayList<Byte>(2048);
int bufIndex = 0;
int subDataLoop = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
buf[bufIndex] = data[i];
if (++bufIndex == DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE || i == dataLen - 1) {
subDataLoop++;
if (subDataLoop != 1) {
for (byte b : DEFAULT_SPLIT) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
}
byte[] encryptBytes = encryptByPublicKey(buf, publicKey);
for (byte b : encryptBytes) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
bufIndex = 0;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
buf = null;
} else {
buf = new byte[Math.min(DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE, dataLen - i - 1)];
}
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
私鑰分段加密
/**
* 分段加密
*
* @param data 要加密的原始數據
* @param privateKey 秘鑰
*/
public static byte[] encryptByPrivateKeyForSpilt(byte[] data, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
int dataLen = data.length;
if (dataLen <= DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE) {
return encryptByPrivateKey(data, privateKey);
}
List<Byte> allBytes = new ArrayList<Byte>(2048);
int bufIndex = 0;
int subDataLoop = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
buf[bufIndex] = data[i];
if (++bufIndex == DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE || i == dataLen - 1) {
subDataLoop++;
if (subDataLoop != 1) {
for (byte b : DEFAULT_SPLIT) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
}
byte[] encryptBytes = encryptByPrivateKey(buf, privateKey);
for (byte b : encryptBytes) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
bufIndex = 0;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
buf = null;
} else {
buf = new byte[Math.min(DEFAULT_BUFFERSIZE, dataLen - i - 1)];
}
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
公鑰分段解密
/**
* 公鑰分段解密
*
* @param encrypted 待解密數據
* @param publicKey 密鑰
*/
public static byte[] decryptByPublicKeyForSpilt(byte[] encrypted, byte[] publicKey) throws Exception {
int splitLen = DEFAULT_SPLIT.length;
if (splitLen <= 0) {
return decryptByPublicKey(encrypted, publicKey);
}
int dataLen = encrypted.length;
List<Byte> allBytes = new ArrayList<Byte>(1024);
int latestStartIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
byte bt = encrypted[i];
boolean isMatchSplit = false;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
// 到data的最後了
byte[] part = new byte[dataLen - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPublicKey(part, publicKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
} else if (bt == DEFAULT_SPLIT[0]) {
// 這個是以split[0]開頭
if (splitLen > 1) {
if (i + splitLen < dataLen) {
// 沒有超出data的范圍
for (int j = 1; j < splitLen; j++) {
if (DEFAULT_SPLIT[j] != encrypted[i + j]) {
break;
}
if (j == splitLen - 1) {
// 驗證到split的最後一位,都沒有break,則表明已經確認是split段
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
}
} else {
// split只有一位,則已經匹配了
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
if (isMatchSplit) {
byte[] part = new byte[i - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPublicKey(part, publicKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
私鑰分段解密
/**
* 使用私鑰分段解密
*
*/
public static byte[] decryptByPrivateKeyForSpilt(byte[] encrypted, byte[] privateKey) throws Exception {
int splitLen = DEFAULT_SPLIT.length;
if (splitLen <= 0) {
return decryptByPrivateKey(encrypted, privateKey);
}
int dataLen = encrypted.length;
List<Byte> allBytes = new ArrayList<Byte>(1024);
int latestStartIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataLen; i++) {
byte bt = encrypted[i];
boolean isMatchSplit = false;
if (i == dataLen - 1) {
// 到data的最後了
byte[] part = new byte[dataLen - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPrivateKey(part, privateKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
} else if (bt == DEFAULT_SPLIT[0]) {
// 這個是以split[0]開頭
if (splitLen > 1) {
if (i + splitLen < dataLen) {
// 沒有超出data的范圍
for (int j = 1; j < splitLen; j++) {
if (DEFAULT_SPLIT[j] != encrypted[i + j]) {
break;
}
if (j == splitLen - 1) {
// 驗證到split的最後一位,都沒有break,則表明已經確認是split段
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
}
} else {
// split只有一位,則已經匹配了
isMatchSplit = true;
}
}
if (isMatchSplit) {
byte[] part = new byte[i - latestStartIndex];
System.arraycopy(encrypted, latestStartIndex, part, 0, part.length);
byte[] decryptPart = decryptByPrivateKey(part, privateKey);
for (byte b : decryptPart) {
allBytes.add(b);
}
latestStartIndex = i + splitLen;
i = latestStartIndex - 1;
}
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[allBytes.size()];
{
int i = 0;
for (Byte b : allBytes) {
bytes[i++] = b.byteValue();
}
}
return bytes;
}
這樣總算把遇見的問題解決了,項目中使用的方案是客戶端公鑰加密,服務器私鑰解密,服務器開發人員說是出於效率考慮,所以還是自己寫了個程序測試一下真正的效率
第一步:准備100條對象數據
List<Person> personList=new ArrayList<>();
int testMaxCount=100;//測試的最大數據條數
//添加測試數據
for(int i=0;i<testMaxCount;i++){
Person person =new Person();
person.setAge(i);
person.setName(String.valueOf(i));
personList.add(person);
}
//FastJson生成json數據
String jsonData=JsonUtils.objectToJsonForFastJson(personList);
Log.e("MainActivity","加密前json數據 ---->"+jsonData);
Log.e("MainActivity","加密前json數據長度 ---->"+jsonData.length());
第二步生成秘鑰對
KeyPair keyPair=RSAUtils.generateRSAKeyPair(RSAUtils.DEFAULT_KEY_SIZE);
// 公鑰
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
// 私鑰
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
接下來分別使用公鑰加密 私鑰解密 私鑰加密 公鑰解密
//公鑰加密
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] encryptBytes= RSAUtils.encryptByPublicKeyForSpilt(jsonData.getBytes(),publicKey.getEncoded());
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.e("MainActivity","公鑰加密耗時 cost time---->"+(end-start));
String encryStr=Base64Encoder.encode(encryptBytes);
Log.e("MainActivity","加密後json數據 --1-->"+encryStr);
Log.e("MainActivity","加密後json數據長度 --1-->"+encryStr.length());
//私鑰解密
start=System.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] decryptBytes= RSAUtils.decryptByPrivateKeyForSpilt(Base64Decoder.decodeToBytes(encryStr),privateKey.getEncoded());
String decryStr=new String(decryptBytes);
end=System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.e("MainActivity","私鑰解密耗時 cost time---->"+(end-start));
Log.e("MainActivity","解密後json數據 --1-->"+decryStr);
//私鑰加密
start=System.currentTimeMillis();
encryptBytes= RSAUtils.encryptByPrivateKeyForSpilt(jsonData.getBytes(),privateKey.getEncoded());
end=System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.e("MainActivity","私鑰加密密耗時 cost time---->"+(end-start));
encryStr=Base64Encoder.encode(encryptBytes);
Log.e("MainActivity","加密後json數據 --2-->"+encryStr);
Log.e("MainActivity","加密後json數據長度 --2-->"+encryStr.length());
//公鑰解密
start=System.currentTimeMillis();
decryptBytes= RSAUtils.decryptByPublicKeyForSpilt(Base64Decoder.decodeToBytes(encryStr),publicKey.getEncoded());
decryStr=new String(decryptBytes);
end=System.currentTimeMillis();
Log.e("MainActivity","公鑰解密耗時 cost time---->"+(end-start));
Log.e("MainActivity","解密後json數據 --2-->"+decryStr);
運行結果:
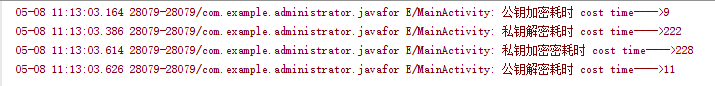
對比發現:私鑰的加解密都很耗時,所以可以根據不同的需求采用不能方案來進行加解密。個人覺得服務器要求解密效率高,客戶端私鑰加密,服務器公鑰解密比較好一點
加密後數據大小的變化:數據量差不多是加密前的1.5倍

總結
以上就是關於Android Rsa數據加解密的全部內容,希望這篇文章的內容對大家的學習或者工作能帶來一定的幫助,如果有疑問大家可以留言交流。
 Android開發本地及網絡Mp3音樂播放器(二十)歌曲下載完成後通知主界面更新本地音樂
Android開發本地及網絡Mp3音樂播放器(二十)歌曲下載完成後通知主界面更新本地音樂
實現功能:歌曲下載完成後通知主界面更新本地音樂除了下面說明的一個問題,還有一些BUG有待修復,後續博文將會繼續更新//DownloadDialogFragment回傳的是
 修改android應用包名
修改android應用包名
由於項目需要,要修改已經開發好的應用包名,這本身很簡單,但是如果你沒找到門道,可能會白白浪費許多時間。修改包名有三個地方要改,這三個地方的修改一定要按順序來,否則你可能會
 Android TV開發總結(五)TV上屏幕適配總結
Android TV開發總結(五)TV上屏幕適配總結
前言:前面幾篇總結一些TV上的小Sample,開源到GitHub:https://github.com/hejunlin2013/TVSample, 點擊鏈接,可以持續關
 Android RecyclerView滾動定位
Android RecyclerView滾動定位
概述 RecyclerView在安卓開發中非常實用,而且簡單易用,但是在實際開發中一直有一個問題困擾著我,就是定位問題,實際的項目中總是會遇到這樣的需求:檢索Recycl