編輯:關於Android編程
Gituhb項目
Volley源碼中文注釋項目我已經上傳到github,歡迎大家fork和start.
為什麼寫這篇博客
本來文章是維護在github上的,但是我在分析ImageLoader源碼過程中與到了一個問題,希望大家能幫助解答.
Volley獲取網絡圖片
本來想分析Universal Image Loader的源碼,但是發現Volley已經實現了網絡圖片的加載功能.其實,網絡圖片的加載也是分幾個步驟:
1. 獲取網絡圖片的url.
2. 判斷該url對應的圖片是否有本地緩存.
3. 有本地緩存,直接使用本地緩存圖片,通過異步回調給ImageView進行設置.
4. 無本地緩存,就先從網絡拉取,保存在本地後,再通過異步回調給ImageView進行設置.
我們通過Volley源碼,看一下Volley是否是按照這個步驟實現網絡圖片加載的.
ImageRequest.java
按照Volley的架構,我們首先需要構造一個網絡圖片請求,Volley幫我們封裝了ImageRequest類,我們來看一下它的具體實現:
/** 網絡圖片請求類. */
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class ImageRequest extends Request<Bitmap> {
/** 默認圖片獲取的超時時間(單位:毫秒) */
public static final int DEFAULT_IMAGE_REQUEST_MS = 1000;
/** 默認圖片獲取的重試次數. */
public static final int DEFAULT_IMAGE_MAX_RETRIES = 2;
private final Response.Listener<Bitmap> mListener;
private final Bitmap.Config mDecodeConfig;
private final int mMaxWidth;
private final int mMaxHeight;
private ImageView.ScaleType mScaleType;
/** Bitmap解析同步鎖,保證同一時間只有一個Bitmap被load到內存進行解析,防止OOM. */
private static final Object sDecodeLock = new Object();
/**
* 構造一個網絡圖片請求.
* @param url 圖片的url地址.
* @param listener 請求成功用戶設置的回調接口.
* @param maxWidth 圖片的最大寬度.
* @param maxHeight 圖片的最大高度.
* @param scaleType 圖片縮放類型.
* @param decodeConfig 解析bitmap的配置.
* @param errorListener 請求失敗用戶設置的回調接口.
*/
public ImageRequest(String url, Response.Listener<Bitmap> listener, int maxWidth, int maxHeight,
ImageView.ScaleType scaleType, Bitmap.Config decodeConfig,
Response.ErrorListener errorListener) {
super(Method.GET, url, errorListener);
mListener = listener;
mDecodeConfig = decodeConfig;
mMaxWidth = maxWidth;
mMaxHeight = maxHeight;
mScaleType = scaleType;
}
/** 設置網絡圖片請求的優先級. */
@Override
public Priority getPriority() {
return Priority.LOW;
}
@Override
protected Response<Bitmap> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response) {
synchronized (sDecodeLock) {
try {
return doParse(response);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
return Response.error(new VolleyError(e));
}
}
}
private Response<Bitmap> doParse(NetworkResponse response) {
byte[] data = response.data;
BitmapFactory.Options decodeOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();
Bitmap bitmap;
if (mMaxWidth == 0 && mMaxHeight == 0) {
decodeOptions.inPreferredConfig = mDecodeConfig;
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);
} else {
// 獲取網絡圖片的真實尺寸.
decodeOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);
int actualWidth = decodeOptions.outWidth;
int actualHeight = decodeOptions.outHeight;
int desiredWidth = getResizedDimension(mMaxWidth, mMaxHeight,
actualWidth, actualHeight, mScaleType);
int desireHeight = getResizedDimension(mMaxWidth, mMaxHeight,
actualWidth, actualHeight, mScaleType);
decodeOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
decodeOptions.inSampleSize =
findBestSampleSize(actualWidth, actualHeight, desiredWidth, desireHeight);
Bitmap tempBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);
if (tempBitmap != null && (tempBitmap.getWidth() > desiredWidth ||
tempBitmap.getHeight() > desireHeight)) {
bitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(tempBitmap, desiredWidth, desireHeight, true);
tempBitmap.recycle();
} else {
bitmap = tempBitmap;
}
}
if (bitmap == null) {
return Response.error(new VolleyError(response));
} else {
return Response.success(bitmap, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));
}
}
static int findBestSampleSize(
int actualWidth, int actualHeight, int desiredWidth, int desireHeight) {
double wr = (double) actualWidth / desiredWidth;
double hr = (double) actualHeight / desireHeight;
double ratio = Math.min(wr, hr);
float n = 1.0f;
while ((n * 2) <= ratio) {
n *= 2;
}
return (int) n;
}
/** 根據ImageView的ScaleType設置圖片的大小. */
private static int getResizedDimension(int maxPrimary, int maxSecondary, int actualPrimary,
int actualSecondary, ImageView.ScaleType scaleType) {
// 如果沒有設置ImageView的最大值,則直接返回網絡圖片的真實大小.
if ((maxPrimary == 0) && (maxSecondary == 0)) {
return actualPrimary;
}
// 如果ImageView的ScaleType為FIX_XY,則將其設置為圖片最值.
if (scaleType == ImageView.ScaleType.FIT_XY) {
if (maxPrimary == 0) {
return actualPrimary;
}
return maxPrimary;
}
if (maxPrimary == 0) {
double ratio = (double)maxSecondary / (double)actualSecondary;
return (int)(actualPrimary * ratio);
}
if (maxSecondary == 0) {
return maxPrimary;
}
double ratio = (double) actualSecondary / (double) actualPrimary;
int resized = maxPrimary;
if (scaleType == ImageView.ScaleType.CENTER_CROP) {
if ((resized * ratio) < maxSecondary) {
resized = (int)(maxSecondary / ratio);
}
return resized;
}
if ((resized * ratio) > maxSecondary) {
resized = (int)(maxSecondary / ratio);
}
return resized;
}
@Override
protected void deliverResponse(Bitmap response) {
mListener.onResponse(response);
}
}
因為Volley本身框架已經實現了對網絡請求的本地緩存,所以ImageRequest做的主要事情就是解析字節流為Bitmap,再解析過程中,通過靜態變量保證每次只解析一個Bitmap防止OOM,使用ScaleType和用戶設置的MaxWidth和MaxHeight來設置圖片大小.
總體來說,ImageRequest的實現非常簡單,這裡不做過多的講解.ImageRequest的缺陷在於:
1.需要用戶進行過多的設置,包括圖片的大小的最大值.
2.沒有圖片的內存緩存,因為Volley的緩存是基於Disk的緩存,有對象反序列化的過程.
ImageLoader.java
鑒於以上兩個缺點,Volley又提供了一個更牛逼的ImageLoader類.其中,最關鍵的就是增加了內存緩存.
再講解ImageLoader的源碼之前,需要先介紹一下ImageLoader的使用方法.和之前的Request請求不同,ImageLoader並不是new出來直接扔給RequestQueue進行調度,它的使用方法大體分為4步:
•創建一個RequestQueue對象.
RequestQueue queue = Volley.newRequestQueue(context);
•創建一個ImageLoader對象.
ImageLoader構造函數接收兩個參數,第一個是RequestQueue對象,第二個是ImageCache對象(也就是內存緩存類,我們先不給出具體實現,講解完ImageLoader源碼之後,我會提供一個利用LRU算法的ImageCache實現類)
ImageLoader imageLoader = new ImageLoader(queue, new ImageCache() {
@Override
public void putBitmap(String url, Bitmap bitmap) {}
@Override
public Bitmap getBitmap(String url) { return null; }
});
•獲取一個ImageListener對象.
ImageListener listener = ImageLoader.getImageListener(imageView, R.drawable.default_imgage, R.drawable.failed_image);
•調用ImageLoader的get方法加載網絡圖片.
imageLoader.get(mImageUrl, listener, maxWidth, maxHeight, scaleType);
有了ImageLoader的使用方法,我們結合使用方法來看一下ImageLoader的源碼:
@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "StringBufferReplaceableByString"})
public class ImageLoader {
/**
* 關聯用來調用ImageLoader的RequestQueue.
*/
private final RequestQueue mRequestQueue;
/** 圖片內存緩存接口實現類. */
private final ImageCache mCache;
/** 存儲同一時間執行的相同CacheKey的BatchedImageRequest集合. */
private final HashMap<String, BatchedImageRequest> mInFlightRequests =
new HashMap<String, BatchedImageRequest>();
private final HashMap<String, BatchedImageRequest> mBatchedResponses =
new HashMap<String, BatchedImageRequest>();
/** 獲取主線程的Handler. */
private final Handler mHandler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
private Runnable mRunnable;
/** 定義圖片K1緩存接口,即將圖片的內存緩存工作交給用戶來實現. */
public interface ImageCache {
Bitmap getBitmap(String url);
void putBitmap(String url, Bitmap bitmap);
}
/** 構造一個ImageLoader. */
public ImageLoader(RequestQueue queue, ImageCache imageCache) {
mRequestQueue = queue;
mCache = imageCache;
}
/** 構造網絡圖片請求成功和失敗的回調接口. */
public static ImageListener getImageListener(final ImageView view, final int defaultImageResId,
final int errorImageResId) {
return new ImageListener() {
@Override
public void onResponse(ImageContainer response, boolean isImmediate) {
if (response.getBitmap() != null) {
view.setImageBitmap(response.getBitmap());
} else if (defaultImageResId != 0) {
view.setImageResource(defaultImageResId);
}
}
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
if (errorImageResId != 0) {
view.setImageResource(errorImageResId);
}
}
};
}
public ImageContainer get(String requestUrl, ImageListener imageListener,
int maxWidth, int maxHeight, ScaleType scaleType) {
// 判斷當前方法是否在UI線程中執行.如果不是,則拋出異常.
throwIfNotOnMainThread();
final String cacheKey = getCacheKey(requestUrl, maxWidth, maxHeight, scaleType);
// 從L1級緩存中根據key獲取對應的Bitmap.
Bitmap cacheBitmap = mCache.getBitmap(cacheKey);
if (cacheBitmap != null) {
// L1緩存命中,通過緩存命中的Bitmap構造ImageContainer,並調用imageListener的響應成功接口.
ImageContainer container = new ImageContainer(cacheBitmap, requestUrl, null, null);
// 注意:因為目前是在UI線程中,因此這裡是調用onResponse方法,並非回調.
imageListener.onResponse(container, true);
return container;
}
ImageContainer imageContainer =
new ImageContainer(null, requestUrl, cacheKey, imageListener);
// L1緩存命中失敗,則先需要對ImageView設置默認圖片.然後通過子線程拉取網絡圖片,進行顯示.
imageListener.onResponse(imageContainer, true);
// 檢查cacheKey對應的ImageRequest請求是否正在運行.
BatchedImageRequest request = mInFlightRequests.get(cacheKey);
if (request != null) {
// 相同的ImageRequest正在運行,不需要同時運行相同的ImageRequest.
// 只需要將其對應的ImageContainer加入到BatchedImageRequest的mContainers集合中.
// 當正在執行的ImageRequest結束後,會查看當前有多少正在阻塞的ImageRequest,
// 然後對其mContainers集合進行回調.
request.addContainer(imageContainer);
return imageContainer;
}
// L1緩存沒命中,還是需要構造ImageRequest,通過RequestQueue的調度來獲取網絡圖片
// 獲取方法可能是:L2緩存(ps:Disk緩存)或者HTTP網絡請求.
Request<Bitmap> newRequest =
makeImageRequest(requestUrl, maxWidth, maxHeight, scaleType, cacheKey);
mRequestQueue.add(newRequest);
mInFlightRequests.put(cacheKey, new BatchedImageRequest(newRequest, imageContainer));
return imageContainer;
}
/** 構造L1緩存的key值. */
private String getCacheKey(String url, int maxWidth, int maxHeight, ScaleType scaleType) {
return new StringBuilder(url.length() + 12).append("#W").append(maxWidth)
.append("#H").append(maxHeight).append("#S").append(scaleType.ordinal()).append(url)
.toString();
}
public boolean isCached(String requestUrl, int maxWidth, int maxHeight) {
return isCached(requestUrl, maxWidth, maxHeight, ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE);
}
private boolean isCached(String requestUrl, int maxWidth, int maxHeight, ScaleType scaleType) {
throwIfNotOnMainThread();
String cacheKey = getCacheKey(requestUrl, maxWidth, maxHeight, scaleType);
return mCache.getBitmap(cacheKey) != null;
}
/** 當L1緩存沒有命中時,構造ImageRequest,通過ImageRequest和RequestQueue獲取圖片. */
protected Request<Bitmap> makeImageRequest(final String requestUrl, int maxWidth, int maxHeight,
ScaleType scaleType, final String cacheKey) {
return new ImageRequest(requestUrl, new Response.Listener<Bitmap>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Bitmap response) {
onGetImageSuccess(cacheKey, response);
}
}, maxWidth, maxHeight, scaleType, Bitmap.Config.RGB_565, new Response.ErrorListener() {
@Override
public void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {
onGetImageError(cacheKey, error);
}
});
}
/** 圖片請求失敗回調.運行在UI線程中. */
private void onGetImageError(String cacheKey, VolleyError error) {
BatchedImageRequest request = mInFlightRequests.remove(cacheKey);
if (request != null) {
request.setError(error);
batchResponse(cacheKey, request);
}
}
/** 圖片請求成功回調.運行在UI線程中. */
protected void onGetImageSuccess(String cacheKey, Bitmap response) {
// 增加L1緩存的鍵值對.
mCache.putBitmap(cacheKey, response);
// 同一時間內最初的ImageRequest執行成功後,回調這段時間阻塞的相同ImageRequest對應的成功回調接口.
BatchedImageRequest request = mInFlightRequests.remove(cacheKey);
if (request != null) {
request.mResponseBitmap = response;
// 將阻塞的ImageRequest進行結果分發.
batchResponse(cacheKey, request);
}
}
private void batchResponse(String cacheKey, BatchedImageRequest request) {
mBatchedResponses.put(cacheKey, request);
if (mRunnable == null) {
mRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (BatchedImageRequest bir : mBatchedResponses.values()) {
for (ImageContainer container : bir.mContainers) {
if (container.mListener == null) {
continue;
}
if (bir.getError() == null) {
container.mBitmap = bir.mResponseBitmap;
container.mListener.onResponse(container, false);
} else {
container.mListener.onErrorResponse(bir.getError());
}
}
}
mBatchedResponses.clear();
mRunnable = null;
}
};
// Post the runnable
mHandler.postDelayed(mRunnable, 100);
}
}
private void throwIfNotOnMainThread() {
if (Looper.myLooper() != Looper.getMainLooper()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ImageLoader must be invoked from the main thread.");
}
}
/** 抽象出請求成功和失敗的回調接口.默認可以使用Volley提供的ImageListener. */
public interface ImageListener extends Response.ErrorListener {
void onResponse(ImageContainer response, boolean isImmediate);
}
/** 網絡圖片請求的承載對象. */
public class ImageContainer {
/** ImageView需要加載的Bitmap. */
private Bitmap mBitmap;
/** L1緩存的key */
private final String mCacheKey;
/** ImageRequest請求的url. */
private final String mRequestUrl;
/** 圖片請求成功或失敗的回調接口類. */
private final ImageListener mListener;
public ImageContainer(Bitmap bitmap, String requestUrl, String cacheKey,
ImageListener listener) {
mBitmap = bitmap;
mRequestUrl = requestUrl;
mCacheKey = cacheKey;
mListener = listener;
}
public void cancelRequest() {
if (mListener == null) {
return;
}
BatchedImageRequest request = mInFlightRequests.get(mCacheKey);
if (request != null) {
boolean canceled = request.removeContainerAndCancelIfNecessary(this);
if (canceled) {
mInFlightRequests.remove(mCacheKey);
}
} else {
request = mBatchedResponses.get(mCacheKey);
if (request != null) {
request.removeContainerAndCancelIfNecessary(this);
if (request.mContainers.size() == 0) {
mBatchedResponses.remove(mCacheKey);
}
}
}
}
public Bitmap getBitmap() {
return mBitmap;
}
public String getRequestUrl() {
return mRequestUrl;
}
}
/**
* CacheKey相同的ImageRequest請求抽象類.
* 判定兩個ImageRequest相同包括:
* 1. url相同.
* 2. maxWidth和maxHeight相同.
* 3. 顯示的scaleType相同.
* 同一時間可能有多個相同CacheKey的ImageRequest請求,由於需要返回的Bitmap都一樣,所以用BatchedImageRequest
* 來實現該功能.同一時間相同CacheKey的ImageRequest只能有一個.
* 為什麼不使用RequestQueue的mWaitingRequestQueue來實現該功能?
* 答:是因為僅靠URL是沒法判斷兩個ImageRequest相等的.
*/
private class BatchedImageRequest {
/** 對應的ImageRequest請求. */
private final Request<?> mRequest;
/** 請求結果的Bitmap對象. */
private Bitmap mResponseBitmap;
/** ImageRequest的錯誤. */
private VolleyError mError;
/** 所有相同ImageRequest請求結果的封裝集合. */
private final LinkedList<ImageContainer> mContainers = new LinkedList<ImageContainer>();
public BatchedImageRequest(Request<?> request, ImageContainer container) {
mRequest = request;
mContainers.add(container);
}
public VolleyError getError() {
return mError;
}
public void setError(VolleyError error) {
mError = error;
}
public void addContainer(ImageContainer container) {
mContainers.add(container);
}
public boolean removeContainerAndCancelIfNecessary(ImageContainer container) {
mContainers.remove(container);
if (mContainers.size() == 0) {
mRequest.cancel();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
重大疑問
個人對Imageloader的源碼有兩個重大疑問?
•batchResponse方法的實現.
我很奇怪,為什麼ImageLoader類裡面要有一個HashMap來保存BatchedImageRequest集合呢?
private final HashMap<String, BatchedImageRequest> mBatchedResponses =
new HashMap<String, BatchedImageRequest>();
畢竟batchResponse是在特定的ImageRequest執行成功的回調中被調用的,調用代碼如下:
protected void onGetImageSuccess(String cacheKey, Bitmap response) {
// 增加L1緩存的鍵值對.
mCache.putBitmap(cacheKey, response);
// 同一時間內最初的ImageRequest執行成功後,回調這段時間阻塞的相同ImageRequest對應的成功回調接口.
BatchedImageRequest request = mInFlightRequests.remove(cacheKey);
if (request != null) {
request.mResponseBitmap = response;
// 將阻塞的ImageRequest進行結果分發.
batchResponse(cacheKey, request);
}
}
從上述代碼可以看出,ImageRequest請求成功後,已經從mInFlightRequests中獲取了對應的BatchedImageRequest對象.而同一時間被阻塞的相同的ImageRequest對應的ImageContainer都在BatchedImageRequest的mContainers集合中.
那我認為,batchResponse方法只需要遍歷對應BatchedImageRequest的mContainers集合即可.
但是,ImageLoader源碼中,我認為多余的構造了一個HashMap對象mBatchedResponses來保存BatchedImageRequest集合,然後在batchResponse方法中又對集合進行兩層for循環各種遍歷,實在是非常詭異,求指導.
詭異代碼如下:
private void batchResponse(String cacheKey, BatchedImageRequest request) {
mBatchedResponses.put(cacheKey, request);
if (mRunnable == null) {
mRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (BatchedImageRequest bir : mBatchedResponses.values()) {
for (ImageContainer container : bir.mContainers) {
if (container.mListener == null) {
continue;
}
if (bir.getError() == null) {
container.mBitmap = bir.mResponseBitmap;
container.mListener.onResponse(container, false);
} else {
container.mListener.onErrorResponse(bir.getError());
}
}
}
mBatchedResponses.clear();
mRunnable = null;
}
};
// Post the runnable
mHandler.postDelayed(mRunnable, 100);
}
}
我認為的代碼實現應該是:
private void batchResponse(String cacheKey, BatchedImageRequest request) {
if (mRunnable == null) {
mRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (ImageContainer container : request.mContainers) {
if (container.mListener == null) {
continue;
}
if (request.getError() == null) {
container.mBitmap = request.mResponseBitmap;
container.mListener.onResponse(container, false);
} else {
container.mListener.onErrorResponse(request.getError());
}
}
mRunnable = null;
}
};
// Post the runnable
mHandler.postDelayed(mRunnable, 100);
}
}
•使用ImageLoader默認提供的ImageListener,我認為存在一個缺陷,即圖片閃現問題.當為ListView的item設置圖片時,需要增加TAG判斷.因為對應的ImageView可能已經被回收利用了.
自定義L1緩存類
首先說明一下,所謂的L1和L2緩存分別指的是內存緩存和硬盤緩存.
實現L1緩存,我們可以使用Android提供的Lru緩存類,示例代碼如下:
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.support.v4.util.LruCache;
/** Lru算法的L1緩存實現類. */
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class ImageLruCache implements ImageLoader.ImageCache {
private LruCache<String, Bitmap> mLruCache;
public ImageLruCache() {
this((int) Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() / 8);
}
public ImageLruCache(final int cacheSize) {
createLruCache(cacheSize);
}
private void createLruCache(final int cacheSize) {
mLruCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(cacheSize) {
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getRowBytes() * value.getHeight();
}
};
}
@Override
public Bitmap getBitmap(String url) {
return mLruCache.get(url);
}
@Override
public void putBitmap(String url, Bitmap bitmap) {
mLruCache.put(url, bitmap);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android Paint類介紹以及浮雕和陰影效果的設置
Android Paint類介紹以及浮雕和陰影效果的設置
Paint類介紹Paint即畫筆,在繪制文本和圖形用它來設置圖形顏色, 樣式等繪制信息。1.圖形繪制setARGB(int a,int r,int g,int b);設置
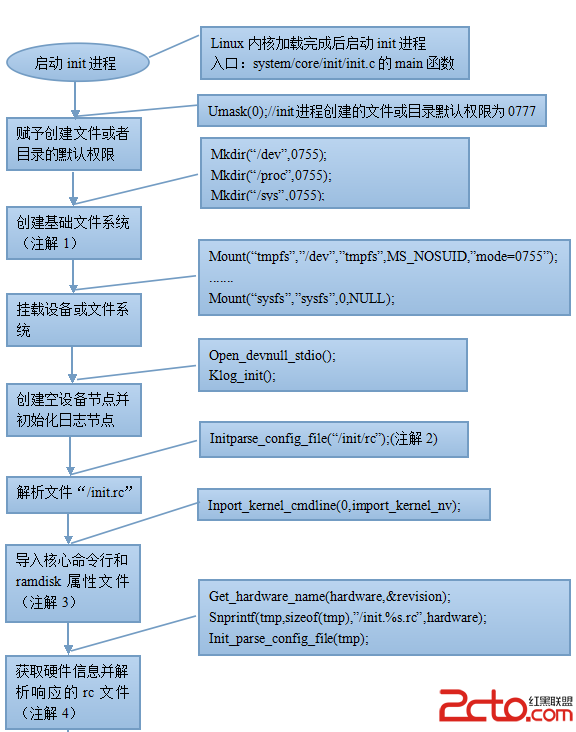 Android核心服務解析篇(一)——Android系統的啟動
Android核心服務解析篇(一)——Android系統的啟動
從大的方面來說,Android系統的啟動可以分為兩個部分:第一部分是Linux核心的啟動,第二部分是Android系統的啟動。第一部分主要包括系統引導,核心和驅動程序等,
 Android中ListView + CheckBox實現單選、多選效果
Android中ListView + CheckBox實現單選、多選效果
還是先來看看是不是你想要的效果:不廢話,直接上代碼,很簡單,代碼裡都有注釋1 單選public class SingleActivity extends AppCompa
 (Android 基礎(十三)) shape
(Android 基礎(十三)) shape
介紹 簡單來說,shape就是用來在xml文件中定義形狀,代碼解析之後就可以當做Drawable一樣使用官方說明關於shape定義的drawable文件位置:res/dr