編輯:關於Android編程
Android中實現圓角矩形和圓形有很多種方式,其中最常見的方法有ImageLoader設置Option和自定義View。
1.ImageLoader加載圖片
public static DisplayImageOptions getRoundOptions() {
DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
// 是否設置為圓角,弧度為多少,當弧度為90時顯示的是一個圓
.displayer(new RoundedBitmapDisplayer(30))
.build();
return options;
}
ImageLoader.getInstance().displayImage(imageURL, imageView, Options.getRoundOptions());
2.自定義View實現
自定義View實現圓角矩形和圓形也有很多方法,其中最常見的就是利用Xfermode,Shader。本文就是使用BitmapShader實現圓角的繪制。
自定義CircleImageView
•淺談BitmapShader
BitmapShader是Shader的子類,可以通過Paint.setShader(Shader shader)進行設置,這裡我們只關注BitmapShader,構造方法:
mBitmapShader = new BitmapShader(bitmap,TileMode.CLAMP, TileMode.CLAMP);
參數1:bitmap
參數2,參數3:TileMode;
TileMode的取值有三種:
CLAMP 拉伸
REPEAT 重復
MIRROR 鏡像
重復:就是橫向、縱向不斷重復這個bitmap
鏡像:橫向不斷翻轉重復,縱向不斷翻轉重復;
拉伸:重復圖片最後的那一個像素;橫向的最後一個橫行像素,不斷的重復,縱項的那一列像素,不斷的重復;
現在大概明白了,BitmapShader通過設置給mPaint,然後用這個mPaint繪圖時,就會根據你設置的TileMode,對繪制區域進行著色。
對於我們的圓角,以及圓形,我們設置的模式都是CLAMP,但是你會不會會有一個疑問:
view的寬或者高大於我們的bitmap寬或者高豈不是會拉伸?
嗯,我們會為BitmapShader設置一個matrix,去適當的放大或者縮小圖片,不會讓“ view的寬或者高大於我們的bitmap寬或者高 ”此條件成立的。
•自定義屬性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="CircleImageView"> <attr name="type" format="enum"> <enum name="circle" value="0"/> <enum name="round" value="1"/> </attr> <attr name="round_Radius" format="dimension" /> <attr name="border_width" format="dimension" /> <attr name="border_color" format="color" /> </declare-styleable> </resources>
•獲取自定義屬性
public CircleImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleImageView, defStyle, 0);
// 獲取類型
type = a.getInt(R.styleable.CircleImageView_type, TYPE_CIRCLE);
// 獲取圓角半徑
mRoundRadius = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CircleImageView_round_Radius, DEFAULT_ROUND_RADIUS);
// 獲取邊界的寬度
mBorderWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CircleImageView_border_width, DEFAULT_BORDER_WIDTH);
// 獲取邊緣的顏色
mBorderColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.CircleImageView_border_color,DEFAULT_BORDER_COLOR);
//調用 recycle() 回收TypedArray,以便後面重用
a.recycle();
init();
}
•onMeasure
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
/**
* 如果類型是圓形,則強制改變view的寬高一致,以小值為准
*/
if (type == TYPE_CIRCLE) {
mWidth = Math.min(getMeasuredWidth(), getMeasuredHeight());
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mWidth);
}
}
•設置初始化參數
/**
* 作用就是保證第一次執行setup函數裡下面代碼要在構造函數執行完畢時調用
*/
private void init() {
//在這裡ScaleType被強制設定為CENTER_CROP,就是將圖片水平垂直居中,進行縮放
super.setScaleType(SCALE_TYPE);
mReady = true;
if (mSetupPending) {
setup();
mSetupPending = false;
}
}
/**
* 這個函數很關鍵,進行圖片畫筆和邊界畫筆(Paint)一些重繪參數初始化:
* 構建渲染器BitmapShader用Bitmap來填充繪制區域,設置樣式以及內外圓半徑計算等,以及調用updateShaderMatrix()函數和 invalidate()函數;
*/
private void setup() {
//因為mReady默認值為false,所以第一次進這個函數的時候if語句為真進入括號體內
//設置mSetupPending為true然後直接返回,後面的代碼並沒有執行。
if (!mReady) {
mSetupPending = true;
return;
}
//防止空指針異常
if (mBitmap == null) {
return;
}
// 構建渲染器,用mBitmap來填充繪制區域 ,參數值代表如果圖片太小的話 就直接拉伸
mBitmapShader = new BitmapShader(mBitmap, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
// 設置圖片畫筆反鋸齒
mBitmapPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
// 設置圖片畫筆渲染器
mBitmapPaint.setShader(mBitmapShader);
// 設置邊界畫筆樣式
mBorderPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mBorderPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mBorderPaint.setColor(mBorderColor);
mBorderPaint.setStrokeWidth(mBorderWidth);
//這個地方是取的原圖片的寬高
mBitmapHeight = mBitmap.getHeight();
mBitmapWidth = mBitmap.getWidth();
//設置含邊界顯示區域,取的是CircleImageView的布局實際大小
mBorderRect.set(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
//初始圖片顯示區域為mBorderRect減去邊緣部分
mDrawableRect.set(mBorderWidth, mBorderWidth, mBorderRect.width() - mBorderWidth, mBorderRect.height() - mBorderWidth);
//下面計算的值都是為onDraw中畫圖做准備
if (type == TYPE_CIRCLE) {
//計算 圓形帶邊界部分(外圓)的半徑,取mBorderRect的寬高減去一個邊緣大小的一半的較小值
mBorderRadius = (mBorderRect.width() - mBorderWidth)/2;
//這裡計算的是內圓的半徑,也即去除邊界寬度的半徑
mDrawableRadius = mDrawableRect.width()/2;
} else if (type == TYPE_ROUND) {
//如果是圓角矩形,重新計算邊緣區域,使處於邊緣正中央
mBorderRect.set(mBorderWidth/2, mBorderWidth/2, getWidth() - mBorderWidth/2, getHeight() - mBorderWidth/2);
}
//設置渲染器的變換矩陣也即是mBitmap用何種縮放形式填充
updateShaderMatrix();
//手動觸發ondraw()函數 完成最終的繪制
invalidate();
}
•設置渲染器的變換矩陣
/**
* 這個函數為設置BitmapShader的Matrix參數,設置最小縮放比例,平移參數。
* 作用:保證圖片損失度最小和始終繪制圖片正中央的那部分
*/
private void updateShaderMatrix() {
float scaleX = 1.0f;
float scaleY = 1.0f;
float scale = 1.0f;
float dx = 0;
float dy = 0;
// 如果圖片的寬或者高與view的寬高不匹配,計算出需要縮放的比例;縮放後的圖片的寬高,一定要大於我們view的寬高;所以我們這裡取大值
if (type == TYPE_CIRCLE) {
scaleX = mWidth * 1.0f / mBitmapWidth;
scaleY = mWidth * 1.0f / mBitmapHeight;
scale = Math.max(scaleX, scaleY);
} else if (type == TYPE_ROUND) {
scaleX = getWidth() * 1.0f / mBitmapWidth;
scaleY = getHeight() * 1.0f / mBitmapHeight;
scale = Math.max(scaleX, scaleY);
}
if (scaleX > scaleY) {
// x軸縮放 y軸平移 使得圖片的x軸方向的邊的尺寸縮放到圖片顯示區域(mDrawableRect)一樣)
dy = (mDrawableRect.height() - mBitmapHeight * scale) * 0.5f;
} else {
// y軸縮放 x軸平移 使得圖片的y軸方向的邊的尺寸縮放到圖片顯示區域(mDrawableRect)一樣)
dx = (mDrawableRect.width() - mBitmapWidth * scale) * 0.5f;
}
mShaderMatrix.set(null);
//縮放
mShaderMatrix.setScale(scale, scale);
// 平移
mShaderMatrix.postTranslate((int) (dx + 0.5f) + mBorderWidth, (int) (dy + 0.5f) + mBorderWidth);
// 設置變換矩陣
mBitmapShader.setLocalMatrix(mShaderMatrix);
}
•onDraw
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//如果圖片不存在就不畫
if (getDrawable() == null)
return;
if (type == TYPE_ROUND) {
//繪制內圓角矩形,參數矩形區域,圓角半徑,圖片畫筆為mBitmapPaint
canvas.drawRoundRect(mDrawableRect, mRoundRadius, mRoundRadius, mBitmapPaint);
if (mBorderWidth != 0) {
//如果圓形邊緣的寬度不為0 我們還要繪制帶邊界的外圓角矩形 參數矩形區域,圓角半徑,邊界畫筆為mBorderPaint
canvas.drawRoundRect(mBorderRect , mRoundRadius + mBorderWidth / 2, mRoundRadius + mBorderWidth / 2, mBorderPaint);
}
} else if (type == TYPE_CIRCLE) {
//繪制內圓形,參數圓心坐標,內圓半徑,圖片畫筆為mBitmapPaint
canvas.drawCircle(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2, mDrawableRadius, mBitmapPaint);
//如果圓形邊緣的寬度不為0 我們還要繪制帶邊界的外圓形 參數圓心坐標,外圓半徑,邊界畫筆為mBorderPaint
if (mBorderWidth != 0) {
canvas.drawCircle(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2, mBorderRadius, mBorderPaint);
}
}
}
而且,我們給自定義View添加了幾個接口,可以用來直接設置類型、邊緣顏色、邊緣寬度和圖片信息等。
使用CircleImageView
布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:attr="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.hx.circleimageview" android:id="@+id/container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#CDCDC1" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.hx.circleimageview.CircleImageView android:id="@+id/image1" android:layout_width="150dp" android:layout_height="150dp" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/crazy_1" attr:type="circle" attr:border_color="#FFffffff" attr:border_width="2dp" /> <com.hx.circleimageview.CircleImageView android:id="@+id/image2" android:layout_width="150dp" android:layout_height="150dp" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/crazy_2" attr:type="round" attr:border_width="2dp" /> <com.hx.circleimageview.CircleImageView android:id="@+id/image3" android:layout_width="250dp" android:layout_height="150dp" android:layout_margin="10dp" android:src="@drawable/crazy_3" attr:type="round" attr:round_Radius="20dp" attr:border_color="#9400D3" attr:border_width="5dp" /> </LinearLayout>
我們在JAVA中對三個ImageView添加點擊事件
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.image1:
image1.setBorderColor(Color.BLACK);
break;
case R.id.image2:
image2.setImageResource(R.drawable.crazy_3);
break;
case R.id.image3:
int type = image3.getType() == CircleImageView.TYPE_CIRCLE ? CircleImageView.TYPE_ROUND : CircleImageView.TYPE_CIRCLE;
image3.setType(type);
break;
}
運行後效果圖如下:
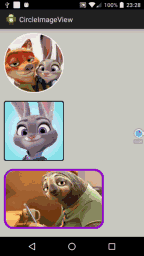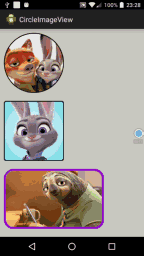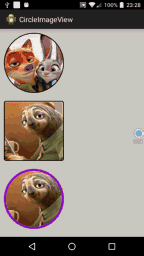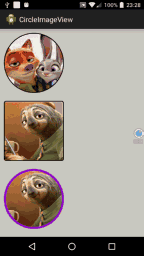
源碼下載:http://xiazai.jb51.net/201609/yuanma/Android-ImageView(jb51.net).rar
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android App卡頓慢優化之多線程優化
Android App卡頓慢優化之多線程優化
本博客涉及的內容有:多線程並發的性能問題,介紹了AsyncTask,HandlerThread,IntentService與ThreadPool分別適合的使用場景以及各自
 關於Google 教程中 Manage the Activity Lifecycle 示例的學習
關於Google 教程中 Manage the Activity Lifecycle 示例的學習
昨天晚上我看了Google training裡面Manage the Activity Lifecycle這一節,看了以後學到很多以前看書,看視頻都沒有了解過的東西,Go
 Android操作系統的架構設計分析
Android操作系統的架構設計分析
之前一直在Android應用層上做工作,最近開始研究Android平台上的東東了,主要是在Android Frameworks層和系統庫層進行研究。以下是我自己的理解,領
 Android viewpager在最後一頁滑動之後跳轉到主頁面的實例代碼
Android viewpager在最後一頁滑動之後跳轉到主頁面的實例代碼
先給大家說下實現思路主要有是兩個監聽:一是addOnPageChangeListener();二是setOnTouchListener();addOnPageChange