編輯:關於Android編程
本篇繼續來講自定義ViewGroup,給大家帶來一個實例:FlowLayout。何為FlowLayout,就是控件根據ViewGroup的寬,自動的往右添加,如果當前行剩余空間不足,則自動添加到下一行,所以也叫流式布局。Android並沒有提供流式布局,但是某些場合中,流式布局還是非常適合使用的,比如關鍵字標簽,搜索熱詞列表等,比如下圖:

定義FlowLayout
LayoutParams,onLayout的寫法都和上一篇講WaterfallLayout一模一樣,在此不再贅述了,沒看過的可以參照上一篇Android自定義ViewGroup(二)之WaterfallLayout。
在這裡主要說的是onMeasure方法,注釋見下方:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 獲得它的父容器為它設置的測量模式和大小
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int childCount = getChildCount();
// 如果是wrap_content情況下,記錄寬和高
int wrapWidth = 0;
int wrapHeight = 0;
//記錄每一行的寬度,width不斷取最大寬度
int lineWidth = 0;
//每一行的高度,累加至height
int lineHeight = 0;
// 遍歷每個子元素
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 測量每一個child的寬和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到child的lParams
LayoutParams lParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 當前子空間實際占據的寬度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
// 當前子空間實際占據的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 如果加上當前child,則超出最大寬度,然後開啟新行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth) {
//記錄新行頭一個標簽坐標,為onLayout做准備
lParams.left = 0;
lParams.top = wrapHeight + lineHeight + vSpace;
lParams.right = childWidth;
lParams.bottom = lParams.top + childHeight;
//取最大的,注意這裡lineWidth是包括右側hSpace的,需要減掉
wrapWidth = Math.max(lineWidth - hSpace, childWidth);
// 重新開啟新行,開始記錄,可以看到行寬包括最右側hSpace
lineWidth = childWidth + hSpace;
// 疊加當前高度,同理,加上下側vSpace
wrapHeight += lineHeight + vSpace;
// 開啟記錄下一行的高度
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
//記錄每一個標簽坐標,為onLayout做准備
lParams.left = lineWidth;
lParams.top = wrapHeight;
lParams.right = lParams.left + childWidth;
lParams.bottom = lParams.top + childHeight;
//在本行追加標簽,累加值到lineWidth,lineHeight取最大高度
lineWidth += childWidth + hSpace;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
// 如果是最後一個
if (i == childCount - 1) {
//將當前記錄的最大寬度和當前lineWidth做比較,取較大值
wrapWidth = Math.max(wrapWidth, lineWidth - hSpace);
//布局高加上最後一行高
wrapHeight += lineHeight;
}
}
setMeasuredDimension((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth : wrapWidth, (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight : wrapHeight);
}
使用FlowLayout
直接看xml吧,一看便知:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:attr="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.hx.flowlayout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#E1E6F6" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.hx.flowlayout.FlowLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" attr:hSpace="20" attr:vSpace="10"> <TextView android:text="標簽" /> <TextView android:text="Welcome" /> <TextView android:text="IT工程師" /> <TextView android:text="程序猿" /> <TextView android:text="Android" /> <TextView android:text="Java" /> <TextView android:text="ViewGroup" /> <TextView android:text="FlowLayout" /> </com.hx.flowlayout.FlowLayout> <com.hx.flowlayout.FlowLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_margin="10dp" attr:hSpace="20" attr:vSpace="10"> <TextView android:text="標簽" /> <TextView android:text="Welcome" /> <TextView android:text="IT工程師" /> <TextView android:text="程序猿" /> <TextView android:text="Android" /> <TextView android:text="Java" /> <TextView android:text="ViewGroup" /> <TextView android:text="FlowLayout" /> </com.hx.flowlayout.FlowLayout> </LinearLayout>
這裡寫的比較啰嗦,所有TextView都是寫在xml裡面的,當然我們也可以通過Java代碼來動態添加。
再來看看style吧,這裡我們定義了兩種不同的風格,具體見下面:
<style name="flow_text_style_1"> <item name="android:layout_width">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:background">@drawable/flow_text_bg_1</item> <item name="android:textColor">#ffffff</item> <item name="android:textSize">16sp</item> </style> <style name="flow_text_style_2"> <item name="android:layout_width">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:background">@drawable/flow_text_bg_2</item> <item name="android:textColor">#4B0082</item> <item name="android:textSize">20sp</item> </style>
找到background我們再進去看看,這裡使用的是shapeDrawable,之後我會寫一些關於shapeDrawable的文章:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <solid android:color="#FFFFFF"/> <corners android:radius="40dp"/> <stroke android:color="#C9C9C9" android:width="2dp"/> <padding android:bottom="2dp" android:left="10dp" android:right="10dp" android:top="2dp" /> </shape>
效果圖如下:
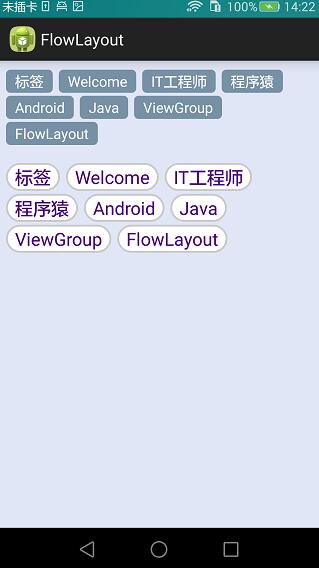
源碼下載:http://xiazai.jb51.net/201609/yuanma/Android-FlowLayout(jb51.net).rar
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android——百度APIstore+Json——獲取新聞頻道+新聞數據
Android——百度APIstore+Json——獲取新聞頻道+新聞數據
package com.example.jreduch08.util;import android.content.Context;import androi
 [Android]OkHttp的簡單封裝-輔助框架
[Android]OkHttp的簡單封裝-輔助框架
序言OkHttp 的強大算是毋庸置疑了;OkHttp 基本在網絡層能完成任何事情,適用任何情況;正因為如此 OkHttp 每次構建一個請求的時候不得不寫大量的代碼來完成相
 Android編程實現3D旋轉效果實例
Android編程實現3D旋轉效果實例
本文實例講述了Android編程實現3D旋轉效果的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:下面的示例是在Android中實現圖片3D旋轉的效果。實現3D效果一般使用Open
 Android開發之Location用法實例分析
Android開發之Location用法實例分析
本文實例講述了Android開發中Location用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:Location 在Android 開發中還是經常用到的,如通過經緯度獲取天氣,根