編輯:關於Android編程
事件分發是Android中非常重要的機制,是用戶與界面交互的基礎。這篇文章將通過示例打印出的Log,繪制出事件分發的流程圖,讓大家更容易的去理解Android的事件分發機制。
一、必要的基礎知識
1、相關方法
Android中與事件分發相關的方法主要包括dispatchTouchEvent、onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent三個方法,而事件分發一般會經過三種容器,分別為Activity、ViewGroup、View。下表對這三種容器分別擁有的事件分發相關方法進行了整理。
事件相關方法
方法功能
Activity
ViewGroup
View
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent
事件分發
Yes
Yes
Yes
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent
事件攔截
No
Yes
No
public boolean onTouchEvent
事件消費
Yes
Yes
Yes
分發: dispatchTouchEvent如果返回true,則表示在當前View或者其子View(子子…View)中,找到了處理事件的View;反之,則表示沒有尋找到
攔截: onInterceptTouchEvent如果返回true,則表示這個事件由當前View進行處理,不管處理結果如何,都不會再向子View傳遞這個事件;反之,則表示當前View不主動處理這個事件,除非他的子View返回的事件分發結果為false
消費: onTouchEvent如果返回true,則表示當前View就是事件傳遞的終點;反之,則表示當前View不是事件傳遞的終點
2、相關事件
這篇文章中我們只考慮4種觸摸事件: ACTION_DOWN、ACTION_UP、ACTION_MOVE、ACTION_CANAL。 事件序列:一個事件序列是指從手指觸摸屏幕開始,到手指離開屏幕結束,這個過程中產生的一系列事件。一個事件序列以ACTION_DOWN事件開始,中間可能經過若干個MOVE,以ACTION_UP事件結束。 接下來我們將使用之前的文章自定義View——彈性滑動中例子來作為本文的示例,簡單增加一些代碼即可,修改之後的代碼請點擊查看。
二、示例的默認情況
我們可以從示例代碼的xml中看出,圖片都是可點擊的。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="com.idtk.customscroll.MainActivity"
>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/zhiqinchun"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/hanzhan"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/shengui"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/dayu"
android:clickable="true"/>
</com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView>
我們現在來點擊一下,查看下打印出的日志。
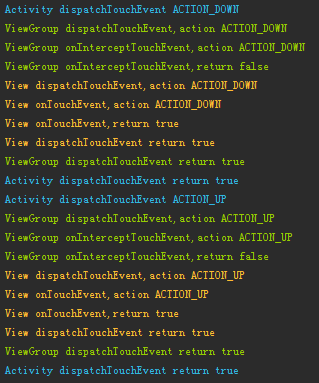
根據打印出的log來繪制一張事件傳遞的流程圖
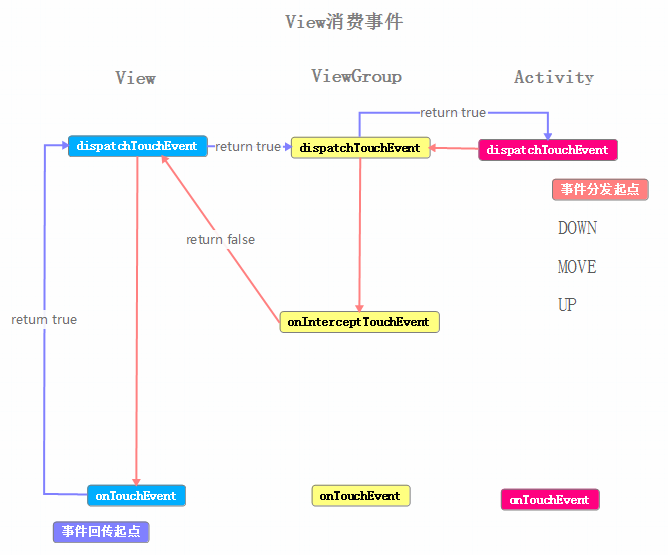
現在來理一下事件序列的流程:
這裡使用工作中的情況來模擬一下:老板(Activity)、項目經理(ViewGroup)、軟件工程師(View)
老板分配一個任務給項目經理(Activity#dispatchTouchEvent → ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent),項目經理選擇自己不做這個任務(ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent返回false),交由軟件工程師處理這個任務(<View#dispatchTouchEvent)(我們忽略總監與組長的情況),軟件工程師完成了這個任務(View#onTouchEvent返回true)
把結果告訴項目經理(返回結果true,View#dispatchTouchEvent→ ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent),項目經理把結果告訴老板(返回結果true,ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent→Activity#dispatchTouchEvent)
項目經理完成的不錯,老板決定把這個項目的二期、三期等都交給項目經理,同樣項目經理也覺得這個軟件工程師完成的不錯,所以也把二期、三期等都交給這個工程師來做
通過上面的傳遞過程,我們可以得出一些結論:
三、在View中不消費事件
我們現在修改示例代碼的xml部分,android:clickable="true"全部修改為android:clickable="false"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="com.idtk.customscroll.MainActivity"
>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/zhiqinchun"
android:clickable="false"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/hanzhan"
android:clickable="false"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/shengui"
android:clickable="false"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/dayu"
android:clickable="false"/>
</com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView>
這時再點擊一下,查看新打印出的日志
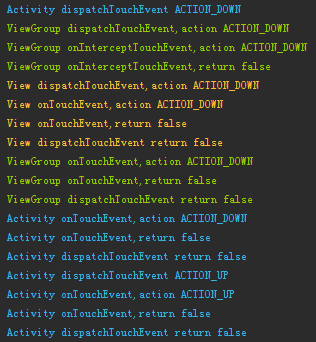
現在根據log中顯示的邏輯,分別繪制ACTION_DOWN事件與ACTION_UP事件傳遞的流程圖
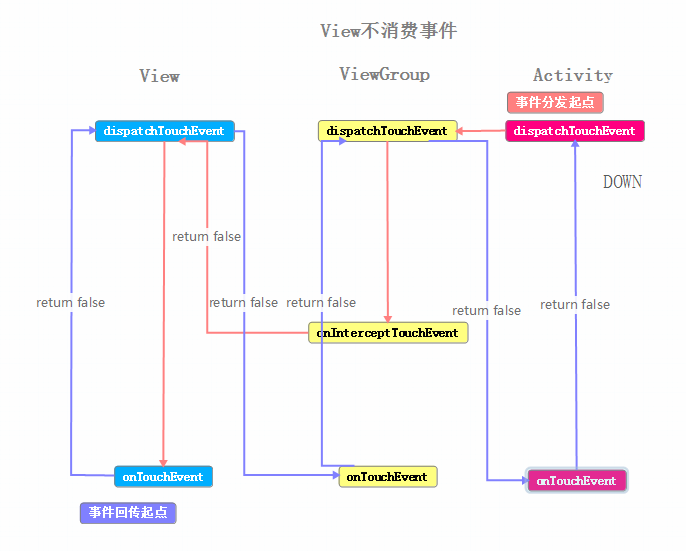
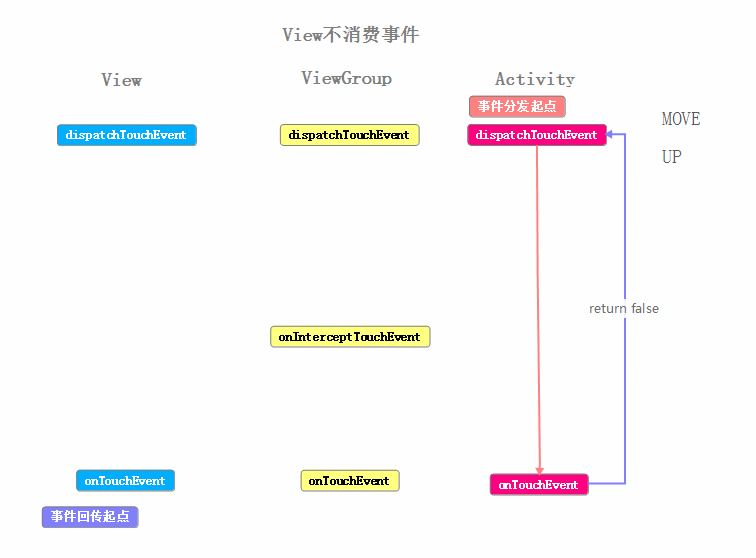
我們來整理下這個事件序列的流程:
這裡使用工作中的情況來模擬:依舊是老板(Activity)、項目經理(ViewGroup)、軟件工程師(View) 從老板交任務給項目經理,項目經理交任務給工程師,這一段流程和之前的例子相同。不同之處是軟件工程師沒有完成這個任務(View#onTouchEvent返回false),告訴項目經理我沒有完成,然後項目經理自己進行了嘗試,同樣沒有完成(ViewGroup#onTouchEvent返回false),項目經理告訴了老板,我沒有完成,然後老板自己試了下也沒有完成這個任務(Activity#onTouchEvent返回false),但之後的也有項目的二期、三期,不過老板知道你們完成不了,所以都是他自己進行嘗試,不過很慘都沒完成。(這段有點與正常情況不同,不過只是打個比方)
通過結合上面兩個例子,可以得出一些結論:
四、在ViewGroup中攔截事件
事件分發中攔截的情況,這裡我把它分為2種,一種是在ACTION_DOWN事件時,就進行攔截的;另一種是在ACTION_DOWN之後的事件序列中,對事件進行了攔截。
1、在事件開始時攔截
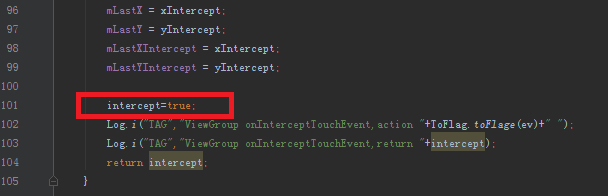
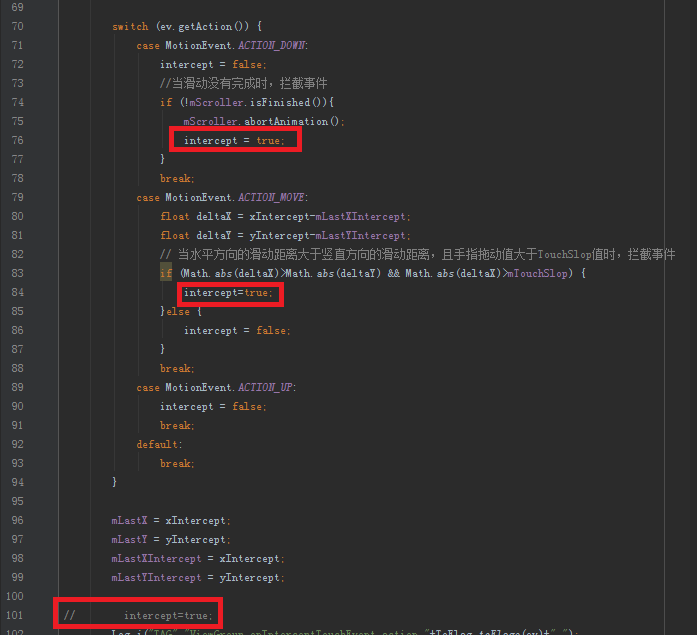
為了達到在ViewGroup中,一開始就攔截觸摸事件的效果,我們需要進行修改,在ParentView#onInterceptTouchEvent方法的最後部分,我注釋掉的intercept=true;進行恢復,然後為activity_main.xml中的ParentView增加android:clickable="true"屬性。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="com.idtk.customscroll.MainActivity"
>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/zhiqinchun"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/hanzhan"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/shengui"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/dayu"
android:clickable="true"/>
</com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView>
我們現在來看下攔截情況下的事件流程圖
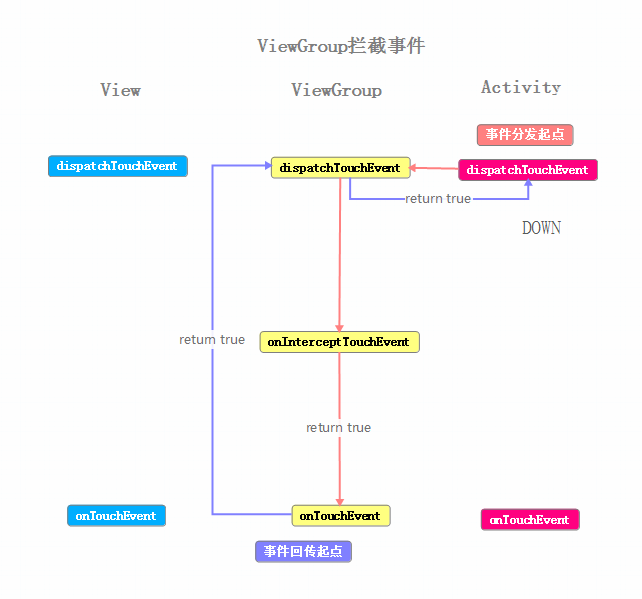
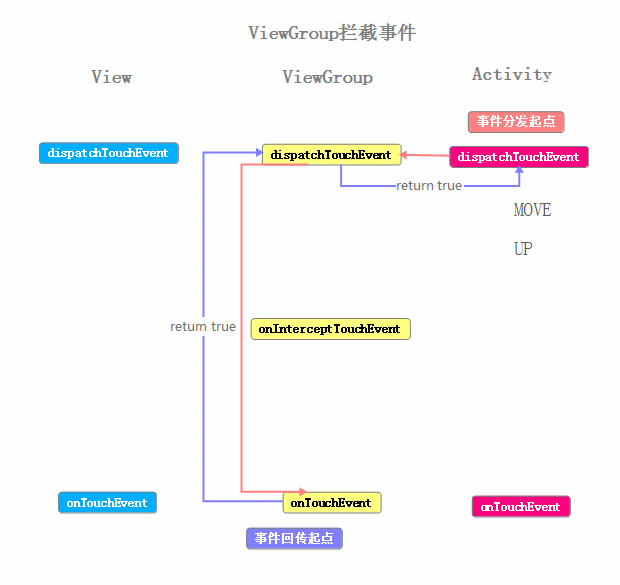
這裡大部分和之前的例子相同,主要的區別是在於ViewGroup#onInterceptTouchEvent方法中,對傳遞的事件進行了攔截,返回true,ACTION_DOWN事件就傳遞到了ViewGroup#onTouchEvent中進行處理,ACTION_DOWN事件之後的傳遞就與之前的例子相同了。另一點重要的區別是,在ViewGroup攔截下事件之後,此事件序列的其余事件,在進入ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent方法之後,不在需要進行是否攔截事件的判斷,而是直接進入了onTouchEvent方法之中。
使用工作中的情況來模擬:老板(Activity)、項目經理(ViewGroup)、軟件工程師(View) 老板吧任務交給項目經理,項目經理認為這個項目比較難,所以決定自己處理(ViewGroup#onInterceptTouchEvent,return true),項目經理比較厲害他把任務完成了(ViewGroup#onTouchEvent,return true),然後他告訴老板他完成了(return true,ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent→Activity#dispatchTouchEvent)。之後老板依舊會把任務交給項目經理,項目經理知道這個任務難度,所以不假思索(也就是這個事件序列中的其余事件沒有經過ViewGroup#onInterceptTouchEvent)的自己來做。
通過上面的例子,可以得出一些結論:
某個ViewGroup如果onInterceptTouchEvent返回為true,則ViewGroup攔截事件,將事件傳遞給其onTouchEvent方法進行處理
某個ViewGroup如果它的onInterceptTouchEvent返回為true,那麼這個事件序列中的後續事件,不會在進行onInterceptTouchEvent的判斷,而是由它的dispatchTouchEvent方法直接傳遞給onTouchEvent方法進行處理
2、在事件序列中攔截
這裡把使用的示例恢復到初始狀態,然後把我在ParentView#onInterceptTouchEvent方法,switch內的兩個注釋掉的intercept = true;代碼進行恢復,最後部分intercept = true;再次注釋掉。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="10dp"
tools:context="com.idtk.customscroll.MainActivity"
>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/zhiqinchun"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/hanzhan"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/shengui"
android:clickable="true"/>
<com.idtk.customscroll.ChildView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/dayu"
android:clickable="true"/>
</com.idtk.customscroll.ParentView>
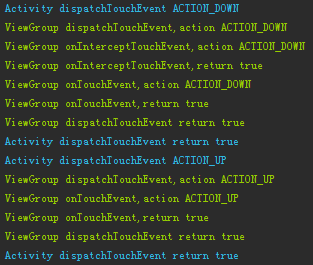
重新運行之後,滑動一個圖片,來看看Log
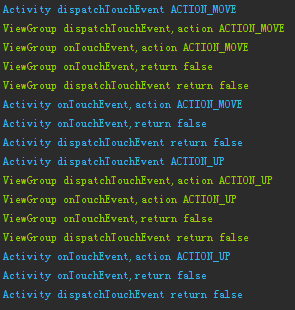
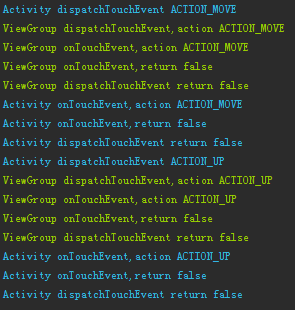
這裡分成兩張圖片,是因為中間有很多ACTION_MOVE,為了方便觀察,所以只截取了Log的首尾部分。 這裡的關鍵部分,就是紅框中的ACTION_CANCEL,可以看到ACTION_DOWN事件的傳遞時onInterceptTouchEvent並沒有攔截,返回false,在其後的事件ACTION_MOVE再次進入onInterceptTouchEvent時,ViewGroup對事件進行了攔截,這樣將會對View傳遞一個ACTION_CANCEL事件,之後的ACTION_MOVE事件就不再傳遞給View了。
使用工作中的情況來模擬:老板(Activity)、項目經理(ViewGroup)、軟件工程師(View) 這裡的情況就是,一期的任務和第一個例子一樣的情況一樣,由軟件工程師完成,不過忽然項目經理覺得二期的任務有點難,然後決定自己完成。這時就給工程師說,這個項目的後續任務,不要你來完成了(ACTION_CANCEL)。
從這裡也可以得出一個結論:
某個View接收了ACTION_DOWN之後,這個序列的後續事件中,如果在某一刻被父View攔截了,則這個字View會收到一個ACTION_CANCEL事件,並且也不會再收到這個事件序列中的後續事件。
五、小結
本文通過示例打印出的各種Log對Android的事件分發機制進行,得出如下結論。
事件相關方法
方法功能
Activity
ViewGroup
View
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent
事件分發
Yes
Yes
Yes
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent
事件攔截
No
Yes
No
public boolean onTouchEvent
事件消費
Yes
Yes
Yes
以上就是對Android 事件分發的資料整理,後續繼續補充相關資料,謝謝大家對本站的支持!
 Android之PreferenceActivity應用詳解(2)
Android之PreferenceActivity應用詳解(2)
看到很多書中都沒有對PreferenceActivity做介紹,而我正好又在項目中用到,所以就把自己的使用的在這總結一下,也方便日後查找。 PerferenceActiv
 浮窗開發之窗口層級
浮窗開發之窗口層級
最近在項目中遇到了這樣的需求:需要在特定的其他應用之上懸浮自己的UI交互(拖動、輸入等復雜的UI交互),和九游的浮窗類似,不過我們的比九游的體驗更好,我們越過了很多授權的
 Android中不得不談的setContentView
Android中不得不談的setContentView
寫在前面:幾個月之前在做項目的布局優化時,使用 Hierarchy Viewer 查看項目的層級結構,然後發現頂層的布局並不是在XML中我寫的根布局,而是嵌套了多層 La
 Android 使用XML做動畫UI的深入解析
Android 使用XML做動畫UI的深入解析
效果: http://www.56.com/u82/v_OTM4MDk5MTk.html第一步: 創建anim文件夾放置動畫xml文件在res文件夾下,創建一個