編輯:關於Android編程
前言
在我們開始之前,希望您能最好已經滿足以下條件:
1、有一份編譯後的Android源碼(親自動手實踐才會有更深入的理解)
2、對Binder機制有一定的了解
本文啟動流程分析基於Android 5.1的源碼。為什麼是5.1的源碼呢?因為手邊編譯完的代碼只有這個版本…另外,用什麼版本的源碼並不重要,大體的流程並無本質上的區別,僅僅是實現細節的調整,找一個你熟悉的版本就好。
1、啟動時序圖
作為一個輕微強迫症的人,整理的時序圖,相信大家按圖索骥,一定能搞明白整個啟動流程:
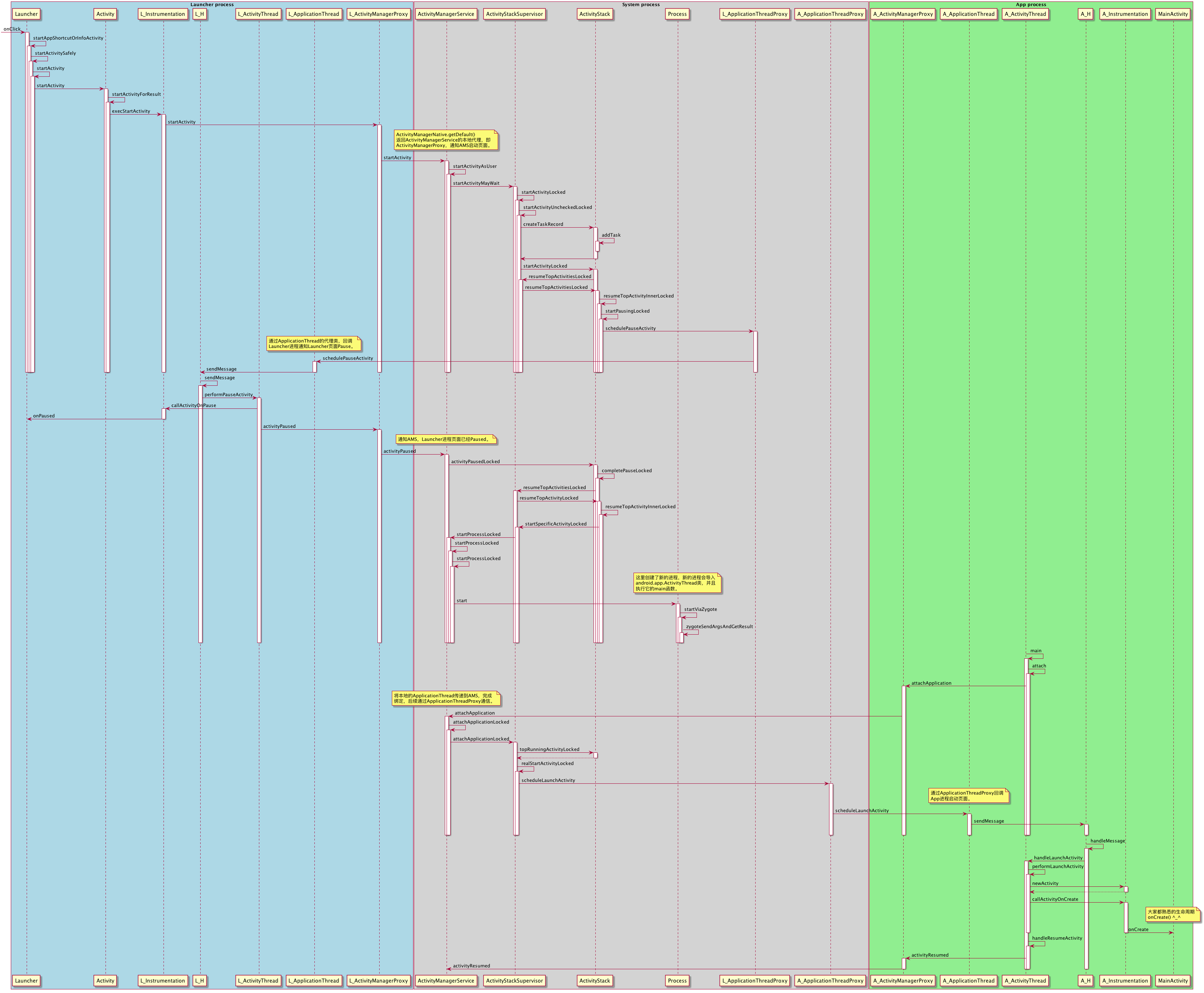
說明:為了讓大家更清楚的理解整個過程,將時序圖中劃分為三個部分:Launcher進程、System進程、App進程,其中有涉及共用的類以L / A進行區分表示跟哪個進程有關,便於理解。
2、關鍵類說明
整個啟動流程因為會涉及到多次Binder通信,這裡先簡要說明一下幾個類的用途,方便大家理解整個交互流程:
1、ActivityManagerService:AMS是Android中最核心的服務之一,主要負責系統中四大組件的啟動、切換、調度及應用進程的管理和調度等工作,其職責與操作系統中的進程管理和調度模塊相類似,因此它在Android中非常重要,它本身也是一個Binder的實現類。
2、Instrumentation:顧名思義,它用來監控應用程序和系統的交互。
3、ActivityThread:應用的入口類,系統通過調用main函數,開啟消息循環隊列。ActivityThread所在線程被稱為應用的主線程(UI線程)。
4、ApplicationThread:ApplicationThread提供Binder通訊接口,AMS則通過代理調用此App進程的本地方法。
5、ActivityManagerProxy:AMS服務在當前進程的代理類,負責與AMS通信。
6、ApplicationThreadProxy:ApplicationThread在AMS服務中的代理類,負責與ApplicationThread通信。
3、流程分析
首先交代下整個流程分析的場景:用戶點擊Launcher上的應用圖標到該應用主界面啟動展示在用戶眼前。
這整個過程涉及到跨進程通信,所以我們將其劃分為時序圖中所展示三個進程:Launcher進程、System進程、App進程。為了不貼過長的代碼又能說清楚進程間交互的流程,這裡簡述幾個重要的交互點。
從時序圖上大家也可以看到調用鏈相當長,對應的代碼量也比較大,而且時序圖只是分析了這個一個場景下的流程。道阻且長,行則將至!
3.1 Launcher響應用戶點擊,通知AMS
Launcher做為應用的入口,還是有必要交代一下的,我們來看看Launcher的代碼片段,Launcher使用的是packages/apps/Launcher3的的源碼。
public class Launcher extends Activity
implements View.OnClickListener, OnLongClickListener, LauncherModel.Callbacks,
View.OnTouchListener, PageSwitchListener, LauncherProviderChangeListener {
...
/**
* Launches the intent referred by the clicked shortcut.
*
* @param v The view representing the clicked shortcut.
*/
public void onClick(View v) {
// Make sure that rogue clicks don't get through while allapps is launching, or after the
// view has detached (it's possible for this to happen if the view is removed mid touch).
if (v.getWindowToken() == null) {
return;
}
...
Object tag = v.getTag();
if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
onClickAppShortcut(v);
} else if (tag instanceof FolderInfo) {
...
} else if (v == mAllAppsButton) {
onClickAllAppsButton(v);
} else if (tag instanceof AppInfo) {
startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(v);
} else if (tag instanceof LauncherAppWidgetInfo) {
...
}
}
private void startAppShortcutOrInfoActivity(View v) {
...
boolean success = startActivitySafely(v, intent, tag);
...
}
boolean startActivitySafely(View v, Intent intent, Object tag) {
...
try {
success = startActivity(v, intent, tag);
} catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) {
...
}
return success;
}
boolean startActivity(View v, Intent intent, Object tag) {
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
try {
...
if (user == null || user.equals(UserHandleCompat.myUserHandle())) {
// Could be launching some bookkeeping activity
startActivity(intent, optsBundle);
} else {
...
}
return true;
} catch (SecurityException e) {
...
}
return false;
}
}
通過starActicity輾轉調用到Activity:startActivityForResult而後則調用至Instrumentation:execStartActivity,代碼片段如下:
public class Instrumentation {
...
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
...
try {
...
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
...
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return null;
}
...
}
這裡的ActivityManagerNative.getDefault返回ActivityManagerService的遠程接口,即ActivityManagerProxy接口,有人可能會問了為什麼會是ActivityManagerProxy,這就涉及到Binder通信了,這裡不再展開。通過Binder驅動程序,ActivityManagerProxy與AMS服務通信,則實現了跨進程到System進程。
3.2 AMS響應Launcher進程請求
從上面的流程我們知道,此時AMS應該處理Launcher進程發來的請求,請參看時序圖及源碼,此時我們來看ActivityStackSupervisor:startActivityUncheckedLocked方法,目測這個方法已經超過600行代碼,來看一些關鍵代碼片段:
public final class ActivityStackSupervisor implements DisplayListener {
...
final int startActivityUncheckedLocked(ActivityRecord r, ActivityRecord sourceRecord,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
int startFlags, boolean doResume, Bundle options, TaskRecord inTask) {
final Intent intent = r.intent;
final int callingUid = r.launchedFromUid;
...
final boolean launchSingleTop = r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP;
final boolean launchSingleInstance = r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE;
final boolean launchSingleTask = r.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK;
int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
...
// We'll invoke onUserLeaving before onPause only if the launching
// activity did not explicitly state that this is an automated launch.
mUserLeaving = (launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION) == 0;
...
ActivityRecord notTop =
(launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_PREVIOUS_IS_TOP) != 0 ? r : null;
// If the onlyIfNeeded flag is set, then we can do this if the activity
// being launched is the same as the one making the call... or, as
// a special case, if we do not know the caller then we count the
// current top activity as the caller.
if ((startFlags&ActivityManager.START_FLAG_ONLY_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
...
}
...
// If the caller is not coming from another activity, but has given us an
// explicit task into which they would like us to launch the new activity,
// then let's see about doing that.
if (sourceRecord == null && inTask != null && inTask.stack != null) {
final Intent baseIntent = inTask.getBaseIntent();
final ActivityRecord root = inTask.getRootActivity();
...
// If this task is empty, then we are adding the first activity -- it
// determines the root, and must be launching as a NEW_TASK.
if (launchSingleInstance || launchSingleTask) {
...
}
...
}
...
if (inTask == null) {
if (sourceRecord == null) {
// This activity is not being started from another... in this
// case we -always- start a new task.
if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) == 0 && inTask == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "startActivity called from non-Activity context; forcing " +
"Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK for: " + intent);
launchFlags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK;
}
} else if (sourceRecord.launchMode == ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE) {
// The original activity who is starting us is running as a single
// instance... this new activity it is starting must go on its
// own task.
launchFlags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK;
} else if (launchSingleInstance || launchSingleTask) {
// The activity being started is a single instance... it always
// gets launched into its own task.
launchFlags |= Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK;
}
}
...
// We may want to try to place the new activity in to an existing task. We always
// do this if the target activity is singleTask or singleInstance; we will also do
// this if NEW_TASK has been requested, and there is not an additional qualifier telling
// us to still place it in a new task: multi task, always doc mode, or being asked to
// launch this as a new task behind the current one.
if (((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0 &&
(launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK) == 0)
|| launchSingleInstance || launchSingleTask) {
// If bring to front is requested, and no result is requested and we have not
// been given an explicit task to launch in to, and
// we can find a task that was started with this same
// component, then instead of launching bring that one to the front.
if (inTask == null && r.resultTo == null) {
// See if there is a task to bring to the front. If this is
// a SINGLE_INSTANCE activity, there can be one and only one
// instance of it in the history, and it is always in its own
// unique task, so we do a special search.
ActivityRecord intentActivity = !launchSingleInstance ?
findTaskLocked(r) : findActivityLocked(intent, r.info);
if (intentActivity != null) {
...
}
}
}
...
if (r.packageName != null) {
// If the activity being launched is the same as the one currently
// at the top, then we need to check if it should only be launched
// once.
ActivityStack topStack = getFocusedStack();
ActivityRecord top = topStack.topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(notTop);
if (top != null && r.resultTo == null) {
if (top.realActivity.equals(r.realActivity) && top.userId == r.userId) {
...
}
}
} else{
...
}
boolean newTask = false;
boolean keepCurTransition = false;
TaskRecord taskToAffiliate = launchTaskBehind && sourceRecord != null ?
sourceRecord.task : null;
// Should this be considered a new task?
if (r.resultTo == null && inTask == null && !addingToTask
&& (launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) != 0) {
...
if (reuseTask == null) {
r.setTask(targetStack.createTaskRecord(getNextTaskId(),
newTaskInfo != null ? newTaskInfo : r.info,
newTaskIntent != null ? newTaskIntent : intent,
voiceSession, voiceInteractor, !launchTaskBehind /* toTop */),
taskToAffiliate);
...
} else {
r.setTask(reuseTask, taskToAffiliate);
}
...
} else if (sourceRecord != null) {
} else if (!addingToTask &&
(launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_REORDER_TO_FRONT) != 0) {
} else if (inTask != null){
} else {
}
...
targetStack.startActivityLocked(r, newTask, doResume, keepCurTransition, options);
...
return ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
}
...
}
函數經過intent的標志值設置,通過findTaskLocked函數來查找存不存這樣的Task,這裡返回的結果是null,即intentActivity為null,因此,需要創建一個新的Task來啟動這個Activity。現在處理堆棧頂端的Activity是Launcher,與我們即將要啟動的MainActivity不是同一個Activity,創建了一個新的Task裡面來啟動這個Activity。
經過棧頂檢測,則需要將Launcher推入Paused狀態,才可以啟動新的Activity。後續則調用至ActivityStack:startPausingLocked,我們來看一下這個函數:
final class ActivityStack {
...
final boolean startPausingLocked(boolean userLeaving, boolean uiSleeping, boolean resuming,
boolean dontWait) {
if (mPausingActivity != null) {
...
}
ActivityRecord prev = mResumedActivity;
if (prev == null) {
...
}
...
mResumedActivity = null;
mPausingActivity = prev;
mLastPausedActivity = prev;
mLastNoHistoryActivity = (prev.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_HISTORY) != 0
|| (prev.info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_NO_HISTORY) != 0 ? prev : null;
prev.state = ActivityState.PAUSING;
...
if (prev.app != null && prev.app.thread != null) {
try {
...
prev.app.thread.schedulePauseActivity(prev.appToken, prev.finishing,
userLeaving, prev.configChangeFlags, dontWait);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
} else {
...
}
...
}
...
}
這裡的prev.app.thread是一個ApplicationThread對象的遠程接口,通過調用這個遠程接口的schedulePauseActivity來通知Launcher進入Paused狀態。至此,AMS對Launcher的請求已經響應,這是我們發現又通過Binder通信回調至Launcher進程。
3.3 Launcher進程掛起Launcher,再次通知AMS
這個流程相對會簡單一些,我們來看ActivityThread:
public final class ActivityThread {
...
private void handlePauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean userLeaving, int configChanges, boolean dontReport) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (r != null) {
...
performPauseActivity(token, finished, r.isPreHoneycomb());
// Make sure any pending writes are now committed.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
QueuedWork.waitToFinish();
}
// Tell the activity manager we have paused.
if (!dontReport) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityPaused(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
...
}
}
...
}
這部分Launcher的ActivityThread處理頁面Paused並且再次通過ActivityManagerProxy通知AMS。
3.4 AMS創建新的進程
創建新進程的時候,AMS會保存一個ProcessRecord信息,如果應用程序中的AndroidManifest.xml配置文件中,我們沒有指定Application標簽的process屬性,系統就會默認使用package的名稱。每一個應用程序都有自己的uid,因此,這裡uid + process的組合就可以為每一個應用程序創建一個ProcessRecord。
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNative
implements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {
...
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType, String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
...
try {
...
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
...
} catch () {
...
}
}
...
}
這裡主要是調用Process:start接口來創建一個新的進程,新的進程會導入android.app.ActivityThread類,並且執行它的main函數,這就是每一個應用程序都有一個ActivityThread實例來對應的原因。
3.5 應用進程初始化
我們來看Activity的main函數,這裡綁定了主線程的Looper,並進入消息循環,大家應該知道,整個Android系統是消息驅動的,這也是為什麼主線程默認綁定Looper的原因:
public final class ActivityThread {
...
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
...
Looper.loop();
...
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
...
if (!system) {
...
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
} else {
...
}
...
}
...
}
attach函數最終調用了ActivityManagerService的遠程接口ActivityManagerProxy的attachApplication函數,傳入的參數是mAppThread,這是一個ApplicationThread類型的Binder對象,它的作用是AMS與應用進程進行進程間通信的。
3.6 在AMS中注冊應用進程,啟動啟動棧頂頁面
前面我們提到了AMS負責系統中四大組件的啟動、切換、調度及應用進程的管理和調度等工作,通過上一個流程我們知道應用進程創建後通過Binder驅動與AMS產生交互,此時AMS則將應用進程創建後的信息進行了一次注冊,如果拿Windows系統程序注冊到的注冊表來理解這個過程,可能會更形象一些。
mMainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null)從堆棧頂端取出要啟動的Activity,並在realStartActivityLockedhan函數中通過ApplicationThreadProxy調回App進程啟動頁面。
public final class ActivityStackSupervisor implements DisplayListener {
...
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig)
throws RemoteException {
...
r.app = app;
...
try {
...
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage, r.task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState,
r.icicle, r.persistentState, results, newIntents, !andResume,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
...
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
...
}
...
}
此時在App進程,我們可以看到,經過一些列的調用鏈最終調用至MainActivity:onCreate函數,之後會調用至onResume,而後會通知AMS該MainActivity已經處於resume狀態。至此,整個啟動流程告一段落。
4、總結
通過上述流程,相信大家可以有了一個基本的認知,這裡我們忽略細節簡化流程,單純從進程角度來看下圖: launch_app_sim
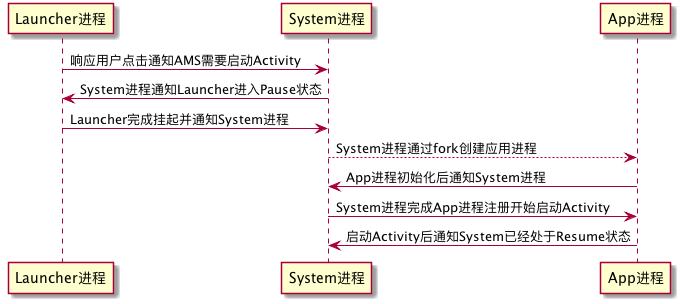
圖上所畫這裡就不在贅述,Activity啟動後至Resume狀態,此時可交互。以上就是分析Android中應用啟動流程的全部內容了,如何有疑問歡迎大家指正交流。
 Android 安卓 VPN設置 L2TP教程
Android 安卓 VPN設置 L2TP教程
第一步: 打開手機主菜單,選擇“設置”,然後選擇“無線和網絡”第二步:選擇“虛擬專用網設置&rd
 淺談android布局優化的三大標簽
淺談android布局優化的三大標簽
1、布局重用 標簽能夠重用布局文件,簡單的使用如下: ... 1)標簽可以使用單獨的layout屬性,這個也是必須使用的。 2)可
 簡單學習Android Socket的使用方法
簡單學習Android Socket的使用方法
這方面的知識不是孤立的,其中有關於,Socket編程,多線程的操作,以及I/O流的操作。當然,實現方法不止一種,這只是其中一種,給同是新手一點點思路。如果有什麼推薦的話,
 Android 快速索引(城市列表和聯系人)
Android 快速索引(城市列表和聯系人)
最近需要實現一個城市列表的快速索引功能。類似於聯系人應用,根據姓名首字母快速索引功能。 要實現這個功能只需要解決兩個問題: 1、對列表進行分組(具有同一特征