編輯:關於Android編程
黑白棋介紹
黑白棋,又叫蘋果棋,最早流行於西方國家。游戲通過相互翻轉對方的棋子,最後以棋盤上誰的棋子多來判斷勝負。黑白棋非常易於上手,但精通則需要考慮許多因素,比如角邊這樣的特殊位置、穩定度、行動力等。本游戲取名為黑白棋大師,提供了8種難度等級的選擇,從菜鳥、新手、入門、棋手到棋士、大師、宗師、棋聖,助你不斷提升棋力。
黑白棋游戲規則
游戲規則見黑白棋大師中的截圖。

黑白棋大師游戲截圖
游戲啟動界面。

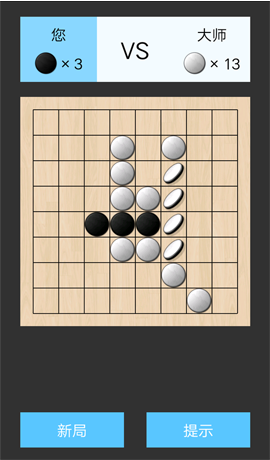
游戲過程中的一個截圖。
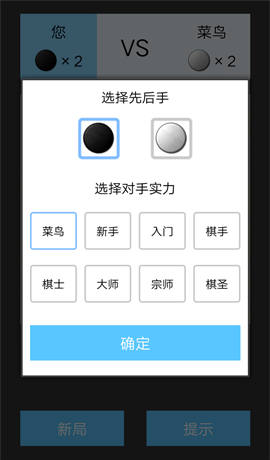
開新局時的選項,選擇先後手以及AI的水平。
幾個關鍵的類
Rule
Rule類實現游戲規則相關的方法,包括
1.判斷某一步是否合法
2.獲取所有的合法走步
3.走一步並翻轉敵方棋子
4.統計兩方棋子個數
Algorithm
Algorithm類實現極小極大算法,包括
1.局面評估函數,對當前局面打分,越高對max越有利,越低對min越有利
2.min()方法
3.max()方法
4.獲得一個好的走步
ReversiView
ReversiView繼承自SurfaceView,實現棋盤的界面,在該類定義棋盤界面的繪制、更新等操作。
RenderThread
RenderThread繼承自Thread,是控制ReversiView以一定fps更新、重繪界面的線程。
具體實現
棋盤表示
byte[][]二維數組存儲棋盤,-1表示有黑子,1表示有白子,0表示棋格為空
游戲規則類Rule的實現
提供幾個關於游戲規則的靜態方法。
判斷某一個位置是否位於棋盤內
public static boolean isLegal(int row, int col) {
return row >= 0 && row < 8 && col >= 0 && col < 8;
}
判斷某一方在某個位置落子是否合法
即判斷該子是否能與己方棋子在某個方向上夾住敵方棋子。
public static boolean isLegalMove(byte[][] chessBoard, Move move, byte chessColor) {
int i, j, dirx, diry, row = move.row, col = move.col;
if (!isLegal(row, col) || chessBoard[row][col] != Constant.NULL)
return false;
for (dirx = -1; dirx < 2; dirx++) {
for (diry = -1; diry < 2; diry++) {
if (dirx == 0 && diry == 0) continue;
int x = col + dirx, y = row + diry;
if (isLegal(y, x) && chessBoard[y][x] == (-chessColor)) {
for (i = row + diry * 2, j = col + dirx * 2; isLegal(i, j); i += diry, j += dirx) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == (-chessColor)) {
continue;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == chessColor) {
return true;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
某一方走一步子
將各個方向上被翻轉的棋子的顏色改變,並返回這些棋子在棋盤的位置,方便顯示翻轉動畫。
public static List<Move> move(byte[][] chessBoard, Move move, byte chessColor) {
int row = move.row;
int col = move.col;
int i, j, temp, m, n, dirx, diry;
List<Move> moves = new ArrayList<Move>();
for (dirx = -1; dirx < 2; dirx++) {
for (diry = -1; diry < 2; diry++) {
if (dirx == 0 && diry == 0)
continue;
temp = 0;
int x = col + dirx, y = row + diry;
if (isLegal(y, x) && chessBoard[y][x] == (-chessColor)) {
temp++;
for (i = row + diry * 2, j = col + dirx * 2; isLegal(i, j); i += diry, j += dirx) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == (-chessColor)) {
temp++;
continue;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == chessColor) {
for (m = row + diry, n = col + dirx; m <= row + temp && m >= row - temp && n <= col + temp
&& n >= col - temp; m += diry, n += dirx) {
chessBoard[m][n] = chessColor;
moves.add(new Move(m, n));
}
break;
} else
break;
}
}
}
}
chessBoard[row][col] = chessColor;
return moves;
}
獲取某一方當前全部合法的落子位置
public static List<Move> getLegalMoves(byte[][] chessBoard, byte chessColor) {
List<Move> moves = new ArrayList<Move>();
Move move = null;
for (int row = 0; row < 8; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < 8; col++) {
move = new Move(row, col);
if (Rule.isLegalMove(chessBoard, move, chessColor)) {
moves.add(move);
}
}
}
return moves;
}
統計玩家和AI的棋子個數
public static Statistic analyse(byte[][] chessBoard, byte playerColor) {
int PLAYER = 0;
int AI = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == playerColor)
PLAYER += 1;
else if (chessBoard[i][j] == (byte)-playerColor)
AI += 1;
}
}
return new Statistic(PLAYER, AI);
}
游戲算法類Algorithm的實現
極大過程和極小過程
這兩個過程的函數形式為:
復制代碼 代碼如下:
private static MinimaxResult max(byte[][] chessBoard, int depth, int alpha, int beta, byte chessColor, int difficulty);
private static MinimaxResult min(byte[][] chessBoard, int depth, int alpha, int beta, byte chessColor, int difficulty);
chessBoard為棋盤;depth為博弈樹搜索深度;alpha和beta用於alpha-beta剪枝,在max方法中alpha不斷更新為局面評分的較大值,在min方法中beta不斷更新為局面評分的較小值,當alpha >= beta時就進行剪枝;chessColor表示棋子顏色;difficulty表示游戲難度,對應於不同的AI水平。
由於黑子先行,黑子總是調用max()方法,白子調用min()方法。
下面以極大過程為例。
如果深度為0,只要返回當前局面評分即可。如果雙方均沒有步可走,表示已經達到最終局面,返回該局面評分。如果僅單方無處可走,調用min遞歸即可。
正常情況下有步可走,遍歷每個合法的走步,如果alpha大於等於beta,剪枝直接break,否則走步並遞歸。
best是當前max節點維護的一個最佳值,調用的min方法的alpha是取得alpha和best的較大值。
private static MinimaxResult max(byte[][] chessBoard, int depth, int alpha, int beta, byte chessColor, int difficulty) {
if (depth == 0) {
return new MinimaxResult(evaluate(chessBoard, difficulty), null);
}
List<Move> legalMovesMe = Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, chessColor);
if (legalMovesMe.size() == 0) {
if (Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, (byte)-chessColor).size() == 0) {
return new MinimaxResult(evaluate(chessBoard, difficulty), null);
}
return min(chessBoard, depth, alpha, beta, (byte)-chessColor, difficulty);
}
byte[][] tmp = new byte[8][8];
Util.copyBinaryArray(chessBoard, tmp);
int best = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Move move = null;
for (int i = 0; i < legalMovesMe.size(); i++) {
alpha = Math.max(best, alpha);
if(alpha >= beta){
break;
}
Rule.move(chessBoard, legalMovesMe.get(i), chessColor);
int value = min(chessBoard, depth - 1, Math.max(best, alpha), beta, (byte)-chessColor, difficulty).mark;
if (value > best) {
best = value;
move = legalMovesMe.get(i);
}
Util.copyBinaryArray(tmp, chessBoard);
}
return new MinimaxResult(best, move);
}
private static MinimaxResult min(byte[][] chessBoard, int depth, int alpha, int beta, byte chessColor, int difficulty) {
if (depth == 0) {
return new MinimaxResult(evaluate(chessBoard, difficulty), null);
}
List<Move> legalMovesMe = Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, chessColor);
if (legalMovesMe.size() == 0) {
if (Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, (byte)-chessColor).size() == 0) {
return new MinimaxResult(evaluate(chessBoard, difficulty), null);
}
return max(chessBoard, depth, alpha, beta, (byte)-chessColor, difficulty);
}
byte[][] tmp = new byte[8][8];
Util.copyBinaryArray(chessBoard, tmp);
int best = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Move move = null;
for (int i = 0; i < legalMovesMe.size(); i++) {
beta = Math.min(best, beta);
if(alpha >= beta){
break;
}
Rule.move(chessBoard, legalMovesMe.get(i), chessColor);
int value = max(chessBoard, depth - 1, alpha, Math.min(best, beta), (byte)-chessColor, difficulty).mark;
if (value < best) {
best = value;
move = legalMovesMe.get(i);
}
Util.copyBinaryArray(tmp, chessBoard);
}
return new MinimaxResult(best, move);
}
alpha-beta剪枝原理
先解釋下alpha和beta的物理含義,alpha表示max節點迄今為止的最佳局面評分,beta表示min節點迄今為止的最佳局面評分。
舉個例子見下圖(數值為虛構),假設深度是兩層,每個結點有兩行數字,上方的兩個數分別是alpha和beta,表示作為參數傳到該層的alpha和beta。下方的數表示了該節點best的更新過程。
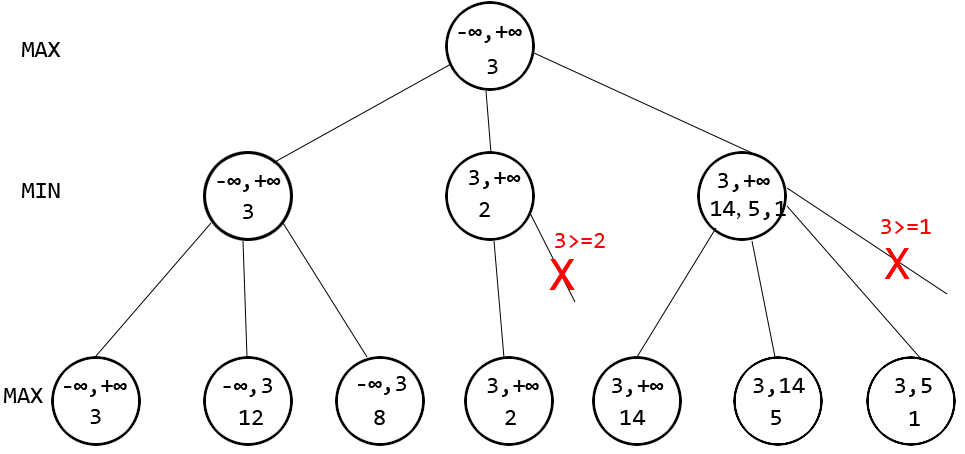
看圖中第一個紅色的叉號,該位置處會更新beta為正無窮和2的較小值,即2,導致alpha大於等於beta成立,發生剪枝,對應於min方法中相應位置處的break操作。
獲得AI計算出的最佳走步
該方法用於AI走步以及提示功能。
public static Move getGoodMove(byte[][] chessBoard, int depth, byte chessColor, int difficulty) {
if (chessColor == Constant.BLACK)
return max(chessBoard, depth, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chessColor, difficulty).move;
else
return min(chessBoard, depth, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chessColor, difficulty).move;
}
局面評估函數
局面評估函數決定了AI水平的高低。對應於不同的AI等級,設計了不同的評估函數。
菜鳥級別只關注棋子個數,新手、入門、棋手3個級別不僅關注棋子的個數,而且關注特殊位置的棋子(邊、角),棋士和大師級別在棋子個數、邊角之外還考慮了行動力,即對方下輪可選的下子位置的個數,宗師和棋聖考慮穩定度和行動力。穩定度將在下一小節介紹。
private static int evaluate(byte[][] chessBoard, int difficulty) {
int whiteEvaluate = 0;
int blackEvaluate = 0;
switch (difficulty) {
case 1:
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 1;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 1;
}
}
}
break;
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if ((i == 0 || i == 7) && (j == 0 || j == 7)) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 5;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 5;
}
} else if (i == 0 || i == 7 || j == 0 || j == 7) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 2;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 2;
}
} else {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 1;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 1;
}
}
}
}
break;
case 5:
case 6:
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if ((i == 0 || i == 7) && (j == 0 || j == 7)) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 5;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 5;
}
} else if (i == 0 || i == 7 || j == 0 || j == 7) {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 2;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 2;
}
} else {
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += 1;
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += 1;
}
}
}
}
blackEvaluate = blackEvaluate * 2 + Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, BLACK).size();
whiteEvaluate = whiteEvaluate * 2 + Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, WHITE).size();
break;
case 7:
case 8:
/**
* 穩定度
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
int weight[] = new int[] { 2, 4, 6, 10, 15 };
if (chessBoard[i][j] == WHITE) {
whiteEvaluate += weight[getStabilizationDegree(chessBoard, new Move(i, j))];
} else if (chessBoard[i][j] == BLACK) {
blackEvaluate += weight[getStabilizationDegree(chessBoard, new Move(i, j))];
}
}
}
/**
* 行動力
*/
blackEvaluate += Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, BLACK).size();
whiteEvaluate += Rule.getLegalMoves(chessBoard, WHITE).size();
break;
}
return blackEvaluate - whiteEvaluate;
}
穩定度計算
我們知道,在黑白棋中,棋盤四角的位置一旦占據是不可能再被翻轉的,因此這幾個位置上的子必然是穩定子,而邊上的子只有可能沿邊的方向被翻轉,穩定的程度高於中間的位置上的子。
因此,試圖給每個子定義一個穩定度,描述該子不被翻轉的穩定程度。
一共有四個方向,即左-右,上-下,左上-右下,右上-左下。舉個例子,下面代碼中的 (drow[0][0], dcol[0][0])表示向左移動一個單位的向量,(drow[0][1], dcol[0][1])表示向右移動一個單位的向量。
對於棋盤中某個子的位置,向左找到第一個不是該顏色的位置(可以是出界),再向右找到第一個不是該顏色的位置(可以是出界),如果這兩個位置至少有一個出界,或者兩個均為敵方棋子,穩定度加1。
對於另外三個方向作同樣操作。可以看到,角上的棋子的穩定度必然為4,其他位置則根據具體情況並不恆定不變。
private static int getStabilizationDegree(byte[][] chessBoard, Move move) {
int chessColor = chessBoard[move.row][move.col];
int drow[][], dcol[][];
int row[] = new int[2], col[] = new int[2];
int degree = 0;
drow = new int[][] { { 0, 0 }, { -1, 1 }, { -1, 1 }, { 1, -1 } };
dcol = new int[][] { { -1, 1 }, { 0, 0 }, { -1, 1 }, { -1, 1 } };
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
row[0] = row[1] = move.row;
col[0] = col[1] = move.col;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
while (Rule.isLegal(row[i] + drow[k][i], col[i] + dcol[k][i])
&& chessBoard[row[i] + drow[k][i]][col[i] + dcol[k][i]] == chessColor) {
row[i] += drow[k][i];
col[i] += dcol[k][i];
}
}
if (!Rule.isLegal(row[0] + drow[k][0], col[0] + dcol[k][0])
|| !Rule.isLegal(row[1] + drow[k][1], col[1] + dcol[k][1])) {
degree += 1;
} else if (chessBoard[row[0] + drow[k][0]][col[0] + dcol[k][0]] == (-chessColor)
&& chessBoard[row[1] + drow[k][1]][col[1] + dcol[k][1]] == (-chessColor)) {
degree += 1;
}
}
return degree;
}
以上就是Android黑白棋游戲實現過程及代碼解析的全部內容,相信本文對大家開發Android黑白棋游戲很有幫助,謝謝大家對本站的支持。
 Android游戲開發之黑白棋
Android游戲開發之黑白棋
黑白棋介紹黑白棋,又叫蘋果棋,最早流行於西方國家。游戲通過相互翻轉對方的棋子,最後以棋盤上誰的棋子多來判斷勝負。黑白棋非常易於上手,但精通則需要考慮許多因素,比如角邊這樣
 android NDK環境搭建
android NDK環境搭建
由於Linux系統的權限限制和Android封裝架構限制,很多涉及底層設備、接口、驅動控制的應用開發,不得不使用到本文的NDK開發環境(基於Android源碼或內核源碼修
 Android開發 Activity和Fragment詳解
Android開發 Activity和Fragment詳解
1.Activity的生命周期1)多個Activity組成Activity棧,當前活動位於棧頂。我們先來看看各種Activity基類的類圖:當Activity類定義出來之
 Android基礎入門教程——8.3.2 繪圖類實戰示例
Android基礎入門教程——8.3.2 繪圖類實戰示例
本節引言: 前兩節我們學了Bitmap和一些基本的繪圖API的屬性以及常用的方法,但心裡總覺得有點 不踏實,總得寫點什麼加深下映像是吧,嗯,本節我們就來寫兩個