編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例為大家分享了AsyncTask異步類實現網頁內容放大縮小的詳細代碼,供大家參考,具體內容如下
WebActivity.java:
package com.supermario.filemanager;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.http.protocol.HTTP;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.DialogInterface.OnClickListener;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.webkit.WebSettings;
import android.webkit.WebView;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.ZoomControls;
public class WebActivity extends Activity {
//網頁浏覽器
private WebView webView;
//進度條布局和網頁內容主體布局
private RelativeLayout loadingLayout,webLayout;
//放大縮小控制器
private ZoomControls zoomControls;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.web);
//初始化頁面組件
webView = (WebView)findViewById(R.id.webkit);
loadingLayout = (RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.loadingLayout);
webLayout = (RelativeLayout)findViewById(R.id.weblayout);
zoomControls = (ZoomControls)findViewById(R.id.zoomControls);
WebSettings webSettings = webView.getSettings();
//設置可以使用js腳本
webSettings.setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
//執行異步進程
new MyAsyncTask().execute("");
}
private void reading(){
String filePath = getIntent().getStringExtra("filePath");
if (filePath != null) {
//讀取文件
webView.loadData(readWebDataToStringFromPath(filePath, new FileReadOverBack() {
@Override
public void fileReadOver() {
}
}), "text/html", HTTP.UTF_8);
} else {
new AlertDialog.Builder(WebActivity.this).setTitle("出錯了").setMessage("獲取文件路徑出錯!").setPositiveButton("返回", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
WebActivity.this.finish();
}
});
}
}
//將網頁數據讀取到一個字符串變量中
private String readWebDataToStringFromPath(String path,final FileReadOverBack fileReadOverBack){
File file = new File(path);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
try {
//讀取文件內容
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int readCount = 0;
while ((readCount = inputStream.read(bytes)) > 0) {
stringBuffer.append(new String(bytes, 0, readCount));
}
fileReadOverBack.fileReadOver();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
return "文件不存在!";
} catch (IOException e) {
return "文件讀取錯誤!";
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
interface FileReadOverBack{
void fileReadOver();
}
//異步處理類
class MyAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<String, String, String>{
//首先執行的函數
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
super.onPreExecute();
loadingLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
webLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
//後台執行
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... params) {
reading();
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
super.onPostExecute(result);
//設置載入進度條隱藏
loadingLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
//設置浏覽器內容可見
webLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// 放大按鈕
zoomControls.setOnZoomInClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
//將網頁內容放大
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
webView.zoomIn();
}
});
// 縮小按鈕
zoomControls.setOnZoomOutClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
//將網頁內容縮小
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
webView.zoomOut();
}
});
}
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android屏幕適配全攻略(最權威的官方適配指導)
Android屏幕適配全攻略(最權威的官方適配指導)
Android的屏幕適配一直以來都在折磨著我們這些開發者,本篇文章以Google的官方文檔為基礎,全面而深入的講解了Android屏幕適配的原因、重要概念、解決方案及最
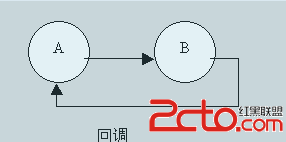 淺析android系統設計中的回調思想
淺析android系統設計中的回調思想
為何寫作本文??在慢慢深入接觸android開發的過程中,我越來越發現android中(至少應用曾的開發)用到了很多回調的思想。比如activity的生命周期,fragm
 Android--Activity生命周期
Android--Activity生命周期
熟悉javaEE的朋友們都了解servlet技術,我們想要實現一個自己的servlet,需要繼承相應的基類,重寫它的方法,這些方法會在合適的時間被servlet容器調用。
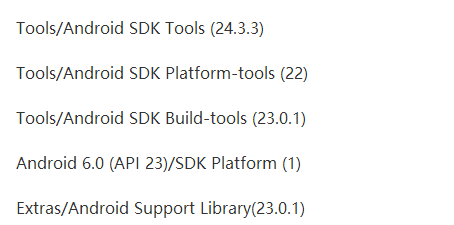 安卓轉戰React-Native之windows下android環境搭建爬坑血淚史
安卓轉戰React-Native之windows下android環境搭建爬坑血淚史
前言 最近又有新的項目立項,所以好久都沒有寫博客了,然後都是利用閒暇時間來學習React-native。由於安卓和ios的就業環境給移動端開發帶來前所未有的沖擊,於是乎很