編輯:關於Android編程
一直都在看自定義View,經過一個星期的堅持,基本上能夠寫出一些比較實用的控件效果了,今天天氣太熱,就待在家裡玩手機,然後手機沒電了,在充電的時候,看到了手機的充電動畫,覺得挺酷,然後自己我就仔細的分析了一下這裡的動畫內容,就覺得,這個我也能寫出來,所以就有了這篇博客。純屬原創。
先看看效果,因為圖片的原因,只能看到靜態的。

這個就是效果圖了。當然了,這麼看好像不怎麼樣,但是配上了動畫,還是挺好看的。
自定義控件的話,其實做的多了,運用的多了,就會覺得自定義View,跟在Photo shop 裡面畫圖一樣,我們通過建立圖層,然後再圖層裡面繪制自己想要的效果。
這裡其實也是一樣的,運用到了我前面講的一些知識,比如這篇:
Android自定義View弧線進度控件,原理上大體相當,結合這次的效果,我們看看,這裡面是有四個弧形,兩個圓,還有一個類似於時鐘刻度的效果。所以知道這些的話,這就比較容易實現了。
首先,新建一個類,取名為VIVOPhone,然後繼承自View,重載三個構造函數,然後進入主題。
同樣的,我們先看看運用到了哪些變量
// 定義五個畫筆 private Paint mSmileRing, mBigRing, mInCrilePaint, mInLine, mTextPaint; // 控件的高寬 private float mWidth, mHeight; // 矩形的空間 private RectF mRectF; // 四個弧線的開始角度 private float startAngle = 270, startAngle2 = 270, startAngle3 = 270, startAngle4 = 270, sweepAngle = 90; // 文字 private String text = "70%"; // 文字的大小 private float tvSize = 80; // 刻度的進度 private float progress;
然後我們開始初始化數據。
private void initView() {
mSmileRing = new Paint();
mSmileRing.setAntiAlias(true);
mSmileRing.setStrokeWidth(5);
mSmileRing.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mSmileRing.setColor(Color.parseColor("#12ADFF"));
mBigRing = new Paint();
mBigRing.setAntiAlias(true);
mBigRing.setStrokeWidth(20);
mBigRing.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mBigRing.setColor(Color.parseColor("#12ADFF"));
mInCrilePaint = new Paint();
mInCrilePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mInCrilePaint.setStrokeWidth((float) 0.5);
mInCrilePaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mInCrilePaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#eeeeee"));
mInLine = new Paint();
mInLine.setAntiAlias(true);
mInLine.setStrokeWidth(3);
mInLine.setColor(Color.parseColor("#00ff00"));
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(tvSize);
mTextPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#ffffff"));
}
這裡主要是對畫筆進行初始化,包括設置大小、寬度、樣式、顏色等等。這個方法,最後還是要在構造函數裡面調用。
畫筆初始化好了,接下來就看看怎麼給變量賦值;
一樣的,我們還是在onSizeChange()方法裡面寫賦值的操作。代碼如下:
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
}
這裡很簡單,就是給高跟寬賦值。
好了,最後看看onDraw方法是怎麼寫的。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvasOutArc1(canvas, mRectF);
canvasOutArc2(canvas, mRectF);
canvasOutArc3(canvas, mRectF);
canvasOutArc4(canvas, mRectF);
drawCircle(canvas);
drawCircleIn(canvas);
canvasDrawText(canvas);
}
沒錯,我這裡把每一個的繪制都抽成了方法,這樣是為了更好的管理和閱讀。看到一個:
/**
* 繪制最外面的弧線
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void canvasOutArc1(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.1), (float) (mWidth * 0.1),
(float) (mWidth * 0.9), (float) (mWidth * 0.9));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle, sweepAngle + 90, false, mSmileRing);
}
這個是最外層的圓,接下來就是第二個,第三個,第四個,我全部列出來。
/**
* 繪制外層的第二個
*
* @param canvas
* @param mRectF
*/
private void canvasOutArc2(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.14), (float) (mWidth * 0.14),
(float) (mWidth * 0.85), (float) (mWidth * 0.85));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle2, sweepAngle + 30, false, mBigRing);
}
第三個:
/**
* 繪制裡面第二個小的
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void canvasOutArc3(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.22), (float) (mWidth * 0.22),
(float) (mWidth * 0.795), (float) (mWidth * 0.795));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle3, sweepAngle, false, mSmileRing);
}
第四個:
/**
* 繪制裡面第二個小的
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void canvasOutArc4(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.255), (float) (mWidth * 0.255),
(float) (mWidth * 0.75), (float) (mWidth * 0.75));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle4, sweepAngle, false, mBigRing);
}
然後就是兩個圓了:
第一個圓,這裡面還包含了鋸齒:
// 繪制內切圓和鋸齒
private void drawCircle(Canvas canvas) {
float radius = (float) (mHeight - (mHeight * 0.3) * 2 - (mWidth * 0.17));
float yuanX = (float) (mHeight / 2);
float yuanY = (float) (mWidth / 2);
canvas.drawCircle(yuanX, yuanY, radius, mInCrilePaint);
canvas.save();
float nowWidth = (float) (getMeasuredWidth());
float nowHeight = getMeasuredHeight();
for (int i = 0; i < 72; i++) {
// canvas.drawLine(nowWidth / 2, nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2,
// nowWidth / 2, nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2 + 30, mInLine);
if (i >= progress) {
mInLine.setColor(Color.parseColor("#555555"));
} else {
mInLine.setColor(Color.parseColor("#00ff00"));
}
canvas.drawLine(nowWidth / 2,
(float) (nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2 + mWidth / 3.7),
nowWidth / 2, (float) (nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2
+ mWidth * 0.05 + mWidth / 3.7), mInLine);
canvas.rotate(5, getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2);
}
}
第二個圓:
// 繪制最裡面的圓
private void drawCircleIn(Canvas canvas) {
float radius = (float) (mHeight - (mHeight * 0.3) * 2 - (mWidth * 0.22));
float yuanX = (float) (mHeight / 2);
float yuanY = (float) (mWidth / 2);
canvas.drawCircle(yuanX, yuanY, radius, mInCrilePaint);
canvas.save();
}
最後暴露給外面一個方法,用於動畫效果:
public void setData(int startAngle, float d) {
this.startAngle = startAngle;
this.startAngle2 = 360 - startAngle;
this.startAngle3 = startAngle;
this.startAngle4 = 360 - startAngle;
progress = d / 4;
postInvalidateDelayed(500);
}
這裡為了效果更明顯,我讓它五毫秒的速度更新UI,這裡就是View的全部內容,下面,我把所有的代碼都列出來:
布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@drawable/bg" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <com.example.vivoopen.weight.VivoView android:id="@+id/vivo" android:layout_width="180dip" android:layout_height="180dip" android:layout_centerInParent="true" /> </RelativeLayout>
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private VivoView view;
private boolean isRun = true;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
view = (VivoView) findViewById(R.id.vivo);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
synchronized (view) {
while (isRun) {
Message msg;
for (int i = 0; i < n2; i = i + 10) {
msg = new Message();
msg.obj = i;
SystemClock.sleep(100);
msg.what = 1;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
msg = new Message();
msg.what = 2;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}
}).start();
}
int n2 = 2;
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case 1:
int a = (Integer) msg.obj;
view.setData(a, a);
break;
case 2:
n2 = 359;
break;
default:
break;
}
};
};
}
VivoView.java:
public class VivoView extends View {
// 定義五個畫筆
private Paint mSmileRing, mBigRing, mInCrilePaint, mInLine, mTextPaint;
// 控件的高寬
private float mWidth, mHeight;
// 矩形的空間
private RectF mRectF;
// 四個弧線的開始角度
private float startAngle = 270, startAngle2 = 270, startAngle3 = 270,
startAngle4 = 270, sweepAngle = 90;
// 文字
private String text = "70%";
// 文字的大小
private float tvSize = 80;
// 刻度的進度
private float progress;
public VivoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
initView();
}
public VivoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView();
}
public VivoView(Context context) {
super(context);
initView();
}
private void initView() {
mSmileRing = new Paint();
mSmileRing.setAntiAlias(true);
mSmileRing.setStrokeWidth(5);
mSmileRing.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mSmileRing.setColor(Color.parseColor("#12ADFF"));
mBigRing = new Paint();
mBigRing.setAntiAlias(true);
mBigRing.setStrokeWidth(20);
mBigRing.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mBigRing.setColor(Color.parseColor("#12ADFF"));
mInCrilePaint = new Paint();
mInCrilePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mInCrilePaint.setStrokeWidth((float) 0.5);
mInCrilePaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mInCrilePaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#eeeeee"));
mInLine = new Paint();
mInLine.setAntiAlias(true);
mInLine.setStrokeWidth(3);
mInLine.setColor(Color.parseColor("#00ff00"));
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setStrokeWidth(3);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(tvSize);
mTextPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor("#ffffff"));
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvasOutArc1(canvas, mRectF);
canvasOutArc2(canvas, mRectF);
canvasOutArc3(canvas, mRectF);
canvasOutArc4(canvas, mRectF);
drawCircle(canvas);
drawCircleIn(canvas);
canvasDrawText(canvas);
}
// 繪制文字
private void canvasDrawText(Canvas canvas) {
float textSize = mTextPaint.measureText(text);
float x = mWidth / 2 - textSize / 2;
float y = mHeight / 2 + textSize / 5;
canvas.drawText(text, x, y, mTextPaint);
}
// 繪制最裡面的圓
// 繪制內切圓和鋸齒
private void drawCircleIn(Canvas canvas) {
float radius = (float) (mHeight - (mHeight * 0.3) * 2 - (mWidth * 0.22));
float yuanX = (float) (mHeight / 2);
float yuanY = (float) (mWidth / 2);
canvas.drawCircle(yuanX, yuanY, radius, mInCrilePaint);
canvas.save();
}
// 繪制內切圓和鋸齒
private void drawCircle(Canvas canvas) {
float radius = (float) (mHeight - (mHeight * 0.3) * 2 - (mWidth * 0.17));
float yuanX = (float) (mHeight / 2);
float yuanY = (float) (mWidth / 2);
canvas.drawCircle(yuanX, yuanY, radius, mInCrilePaint);
canvas.save();
float nowWidth = (float) (getMeasuredWidth());
float nowHeight = getMeasuredHeight();
for (int i = 0; i < 72; i++) {
// canvas.drawLine(nowWidth / 2, nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2,
// nowWidth / 2, nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2 + 30, mInLine);
if (i >= progress) {
mInLine.setColor(Color.parseColor("#555555"));
} else {
mInLine.setColor(Color.parseColor("#00ff00"));
}
canvas.drawLine(nowWidth / 2,
(float) (nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2 + mWidth / 3.7),
nowWidth / 2, (float) (nowHeight / 2 - nowWidth / 2
+ mWidth * 0.05 + mWidth / 3.7), mInLine);
canvas.rotate(5, getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2);
}
}
/**
* 繪制最外面的弧線
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void canvasOutArc1(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.1), (float) (mWidth * 0.1),
(float) (mWidth * 0.9), (float) (mWidth * 0.9));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle, sweepAngle + 90, false, mSmileRing);
}
/**
* 繪制外層的第二個
*
* @param canvas
* @param mRectF
*/
private void canvasOutArc2(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.14), (float) (mWidth * 0.14),
(float) (mWidth * 0.85), (float) (mWidth * 0.85));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle2, sweepAngle + 30, false, mBigRing);
}
/**
* 繪制裡面第二個小的
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void canvasOutArc3(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.22), (float) (mWidth * 0.22),
(float) (mWidth * 0.795), (float) (mWidth * 0.795));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle3, sweepAngle, false, mSmileRing);
}
/**
* 繪制裡面第二個小的
*
* @param canvas
*/
private void canvasOutArc4(Canvas canvas, RectF mRectF) {
mRectF = new RectF((float) (mWidth * 0.255), (float) (mWidth * 0.255),
(float) (mWidth * 0.75), (float) (mWidth * 0.75));
canvas.drawArc(mRectF, startAngle4, sweepAngle, false, mBigRing);
}
public void setData(int startAngle, float d) {
this.startAngle = startAngle;
this.startAngle2 = 360 - startAngle;
this.startAngle3 = startAngle;
this.startAngle4 = 360 - startAngle;
progress = d / 4;
postInvalidateDelayed(500);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持本站。
 Android群英傳知識點回顧——第十章:Android性能優化
Android群英傳知識點回顧——第十章:Android性能優化
知識點目錄 10.1 布局優化 10.1.1 Android UI渲染機制 10.1.2 避免Overdraw 10.1.3 優化布局層級 10.1.4 避免嵌套過多無用
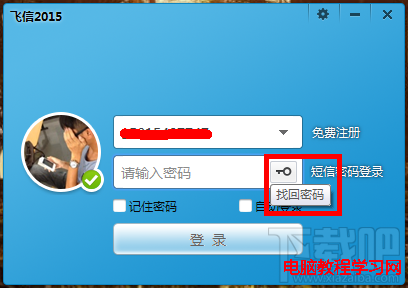 飛信忘記密碼怎麼辦?
飛信忘記密碼怎麼辦?
飛信現在在生活之中運用越來越廣泛,他是中國移動推出的一款可以免費點對點短信的軟件,那麼如果我們把密碼忘記了怎麼辦呢?怎樣修改呢?下面小編來給大家介紹怎樣去找
 手機SD卡損壞的修復方法
手機SD卡損壞的修復方法
經常會網友遇到手機使用時間較久後會遇到提示“SD卡已損壞,您可能必須將其重新格式化”故障,導致手機SD卡無法使用。最近身邊有朋友手機
 Android自定義控件LinearLayout實例講解
Android自定義控件LinearLayout實例講解
很多時候Android常用的控件不能滿足我們的需求,那麼我們就需要自定義一個控件了。今天做了一個自定義控件的實例,來分享下。首先定義一個layout實現按鈕內部布局:&n