編輯:關於Android編程
本文實例講述了Android實現的仿淘寶購物車。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
夏的熱情漸漸退去,秋如期而至,豐收的季節,小編繼續著實習之路,走著走著,就走到了購物車,逛過淘寶或者是京東的小伙伴都知道購物車裡面的寶貝可不止一件,對於愛購物的姑娘來說,購物車裡面的商品恐怕是爆滿,添加不進去了,以前逛淘寶的時候,小編沒有想過要怎麼樣實現購物車,就知道在哪兒一個勁兒的逛,但是現在不一樣了,小編做為一個開發者,想的就是該如何實現,搗鼓了兩天的時間,用listview來實現,已經有模有樣了,現在小編就來簡單的總結一下實現購物車的心路歷程,幫助有需要的小伙伴,歡迎小伙伴們留言交流。
首先,小編簡單的介紹一下listview,ListView 控件可使用四種不同視圖顯示項目。通過此控件,可將項目組成帶有或不帶有列標頭的列,並顯示伴隨的圖標和文本。 可使用 ListView 控件將稱作 ListItem 對象的列表條目組織成下列四種不同的視圖之一:1.大(標准)圖標2.小圖標3.列表4.報表 View 屬性決定在列表中控件使用何種視圖顯示項目。還可用 LabelWrap 屬性控制列表中與項目關聯的標簽是否可換行顯示。另外,還可管理列表中項目的排序方法和選定項目的外觀。今天小編主要和小伙伴們分享一下,如何使用listview實現購物的功能。做過Android的小伙伴都知道一個xml對應一個Java類,但是購物車有點不一樣,因為她裡面的商品有可能不只一件,所以我們需要有兩個xml,兩個java類,相對應的還需要一個適配器adapter,一個model,下面小編來詳細的介紹一下實現購物車的過程。
第一步,寫model層,類似我們之前寫過的實體層,具體代碼如下所示:
/***
* 說明:購物車的相關信息
* 作者:丁國華
* 時間:2015年8月10日 09:41:18
*/
package jczb.shoping.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.R.string;
public class shoppingCart implements Serializable {
private String proImg;
private String ProName;
private String shopPrice;
private String markPrice;
private String proCount;
public String getProImg() {
return proImg;
}
public void setProImg(String proImg) {
this.proImg = proImg;
}
public String getProName() {
return ProName;
}
public void setProName(String proName) {
ProName = proName;
}
public String getShopPrice() {
return shopPrice;
}
public void setShopPrice(String shopPrice) {
this.shopPrice = shopPrice;
}
public String getMarkPrice() {
return markPrice;
}
public void setMarkPrice(String markPrice) {
this.markPrice = markPrice;
}
public String getProCount() {
return proCount;
}
public void setProCount(String proCount) {
this.proCount = proCount;
}
}
第二步,我們編寫xml裡面的文件,需要編寫兩個xml文件,首先我們來編寫activity_shoppingcart.xml的文件,代碼如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:background="#438FCB"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<!-- 尖括號的布局 -->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:padding="8dp"
android:src="@drawable/tb_icon_actionbar_back" />
<!-- 購物車的布局 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="5.49"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="購物車"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
<!-- 編輯的布局 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="3.18"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="編輯"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<!-- listview,購物車裡面的東西有可能比較多,需要用listview來進行顯示 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_marginTop="0dp">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/cart_shopping_listview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:divider="#808080"
android:dividerHeight="0.5dp">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<!-- 全選的布局 -->
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="全選"/>
<!-- 合計的布局 -->
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="right"
android:paddingRight="10dp"
android:textColor="#F63A19"
android:text="合計:¥88"/>
<!-- 去結算的布局 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/jiesuan_button"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:background="@drawable/android_login_color"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="結算"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout >
我們來看一下xml布局的效果,如下圖所示:
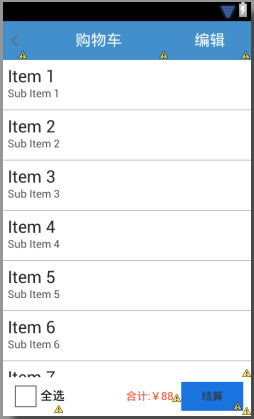
接著我們來布局第二個xml,activity_shoppingcart_item.xml,代碼如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<!-- 小對勾的布局 -->
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/pro_checkbox"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:focusable="false"
android:focusableInTouchMode="false" />
<!-- 圖片布局 -->
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/pro_image"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:src="@drawable/detail_show_1"/>
<!-- 商品名稱和價格的布局 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- 商品名稱的布局 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/pro_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="連衣裙女夏季"
/>
<!-- 價格的布局 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="33dp"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/pro_shopPrice"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="¥88"
android:textSize="16sp"/>
<!-- <TextView
android:id="@+id/pro_markPrice"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="¥66"
android:textSize="16sp"/> -->
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="33dp"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<!-- 加號 -->
<Button
android:id="@+id/pro_add"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="34dp"
android:text="+" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/pro_count"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="88"
android:textSize="13sp"/>
<!-- 減號-->
<Button
android:id="@+id/pro_reduce"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="34dp"
android:layout_marginRight="0dp"
android:text="-" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
布局效果如下所示:

第三步、我們來編寫適配器adapter中的代碼,即ShoppingCartAdapter,具體代碼如下所示:
package jczb.shoping.adapter;
import java.util.List;
import cn.jpush.android.data.r;
import jczb.shoping.adapter.productsListAdapter.ViewHolder;
import jczb.shoping.adapter.productsListAdapter.searchList;
import jczb.shoping.model.productSonSorting_cate;
import jczb.shoping.model.shoppingCart;
import jczb.shoping.model.sonSortigns;
import jczb.shoping.ui.R;
import jczb.shoping.ui.ShoppingCartActivity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.DialogInterface.OnClickListener;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.CheckBox;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ShoppingCartAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context mContext;
private List<shoppingCart> mList;
public ShoppingCartAdapter(Context mContext,List<shoppingCart> mList) {
super();
this.mContext = mContext;
this.mList = mList;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (mList==null) {
return 0;
}else {
return this.mList.size();
}
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (mList == null) {
return null;
} else {
return this.mList.get(position);
}
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ViewHolder holder = null;
if (convertView == null) {
holder = new ViewHolder();
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(this.mContext).inflate(R.layout.activity_shoppingcart_item, null,true);
holder.image=(ImageView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.pro_image);
holder.chose=(CheckBox) convertView.findViewById(R.id.pro_checkbox);
holder.proName=(TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.pro_name);
holder.proPrice=(TextView)convertView.findViewById(R.id.pro_shopPrice);
holder.proCount=(TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.pro_count);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
if (this.mList != null) {
shoppingCart shoppingList=this.mList.get(position);
holder.proName.setText(shoppingList.getProName().toString());
holder.proPrice.setText(shoppingList.getShopPrice().toString());
holder.proCount.setText(shoppingList.getProCount().toString());
}
return convertView;
}
/*定義item對象*/
public class ViewHolder {
ImageView image;
TextView proName;
CheckBox chose;
TextView proPrice;
TextView proCount;
}
}
第四步,編寫java類裡面的代碼,我們先來編寫ShoppingCartItemActivity.java中的內容,具體代碼如下所示:
package jczb.shoping.ui;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class ShoppingCartItemActivity extends Activity {
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_shoppingcart_item);
}
}
第五步,編寫ShoppingCartActivity.java裡面的內容,如下所示:
package jczb.shoping.ui;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import jczb.shoping.adapter.ShoppingCartAdapter;
import jczb.shoping.common.AgentApi;
import jczb.shoping.model.shoppingCart;
import jczb.shoping.ui.SearchActivity.ViewHolder;
import jczb.shoping.ui.ShoppingcartActivity2.myThread;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import android.R.string;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.CheckBox;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class ShoppingCartActivity extends Activity{
TextView jiesuan,proName,shopPrice,proCount;
ListView aListView;
private LayoutInflater layoutInflater;
private TextView name;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_shoppingcart);
findViewByID();
/*開始線程*/
new Thread(new myThread()).start();{
}
/*根據ID找到控件*/
public void findViewByID(){
aListView=(ListView) findViewById(R.id.cart_shopping_listview);
}
//開辟線程
public class myThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
Message msg = new Message();
try {
Map<String, String> parmas = new HashMap<String, String>();
parmas.put("username", "1");
parmas.put("password", "2");
String url = "http://192.168.1.110:8080/SchoolShopJson/ShoppingCart.txt";
// 要發送的數據和訪問的地址
String result = AgentApi.dopost(parmas, url);
// 如果返回的為空或者初始化時輸入的ip地址無效(會返回下面的字符串),說明服務器連接失敗!
if (result == null) {
// 使用-1代表服務器連接失敗
msg.what = -1;
} else {
msg.what=1;
msg.obj=result;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 使用-1代表程序異常
msg.what = -2;
msg.obj = e;
}
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
protected void initView() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/*子線程-解析數據*/
private Handler mHandler = new Handler(){
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case -1:
Toast.makeText(ShoppingCartActivity.this, "服務器連接失敗!",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case -2:
Toast.makeText(ShoppingCartActivity.this, "哎呀,出錯啦...",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case 1:
String temp = (String)msg.obj;
//將拿到的json轉換為數組
List<shoppingCart> ShoppingcartInfo = JSON.parseArray(temp,shoppingCart.class);
ListView.setAdapter(new ShoppingCartAdapter(ShoppingCartActivity.this, ShoppingcartInfo));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
}
我們來看一下運行的效果,如下所示:

更多關於Android相關內容感興趣的讀者可查看本站專題:《Android布局layout技巧總結》、《Android視圖View技巧總結》、《Android編程之activity操作技巧總結》、《Android操作SQLite數據庫技巧總結》、《Android操作json格式數據技巧總結》、《Android數據庫操作技巧總結》、《Android文件操作技巧匯總》、《Android編程開發之SD卡操作方法匯總》、《Android開發入門與進階教程》、《Android資源操作技巧匯總》及《Android控件用法總結》
希望本文所述對大家Android程序設計有所幫助。
 Android實現便於批量操作可多選的圖片ListView實例
Android實現便於批量操作可多選的圖片ListView實例
本文實例講述了Android實現便於批量操作可多選的圖片ListView。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:之前項目需要實現一個可多選的圖片列表,用戶選中一到多張圖片後,批
 Android/java源代碼實現DES算法原理+整理
Android/java源代碼實現DES算法原理+整理
1.初始置換/IP置換// 初始置換表 private static final int[] IP_Table = { 58, 50, 42, 34, 26, 18, 1
 android adb使用
android adb使用
#####################################################################################
 Android實現Banner界面廣告圖片循環輪播(包括實現手動滑動循環)
Android實現Banner界面廣告圖片循環輪播(包括實現手動滑動循環)
前言:經常會看到有一些app的banner界面可以實現循環播放多個廣告圖片和手動滑動循環。本以為單純的ViewPager就可以實現這些功能。但是蛋疼的事情來了
 Android adt v22.6.2-1085508 自動創建 appcompat_v7 解決方法,最低版本2.2也不會出現
Android adt v22.6.2-1085508 自動創建 appcompat_v7 解決方法,最低版本2.2也不會出現
Android 開發工具升級到22.6.2在創建工程時只要選擇的最低版本